History of colonialism facts for kids
Colonialism is when one country takes control of another. This often means the powerful country sends its people to live there. They also control the weaker country's government and resources. This has happened for thousands of years. Even ancient groups like the Hittites and Incas practiced it.
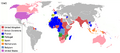
However, when people talk about colonialism, they usually mean the time when European countries built huge empires across the seas. These empires were far away and could only be reached by ships. Examples include British rule in India and French rule in Algeria.
Contents
Different Kinds of Empires
Sometimes, empires that grew by taking over land next to them are called imperialism. These are different from overseas empires.
Land-Based Empires
Some famous land-based empires include:
- The Mongol Empire, which stretched from the Pacific Ocean to Eastern Europe.
- The Empire of Alexander the Great.
- The Umayyad Caliphate.
- The Persian Empire.
- The Roman Empire.
- The Byzantine Empire.
The Ottoman Empire also grew across the Mediterranean Sea, North Africa, and into Southern Europe. It existed at the same time as European countries were colonizing other parts of the world.
European Overseas Empires Begin
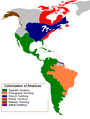
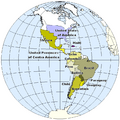
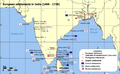
European colonialism started in the 1400s. The Spanish and Portuguese were the first to explore. They sailed to the Americas, and along the coasts of Africa, the Middle East, India, and East Asia.
During the 1500s and 1600s, England, France, and Holland also began building their own overseas empires. They claimed lands and set up colonies far from home.
Colonies Gain Independence
By the late 1700s and early 1800s, many European colonies in the Americas fought for and won their independence. This meant they became their own countries.
After losing their colonies in the New World, Spain and Portugal became weaker. They never regained their former power. But Britain, France, and Holland looked to new areas. They focused on South Africa, India, and Southeast Asia.
The Age of New Imperialism
In the 1800s, Europe changed a lot. This was due to the Industrial Revolution.
- More people lived in Europe.
- Armies became much better organized.
- Factories made powerful new weapons.
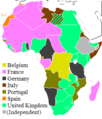
This time is known as the era of New Imperialism. European powers quickly took over vast amounts of land. A famous example is the Scramble for Africa. During this time, European countries divided almost all of Africa among themselves.
The End of Colonialism
After World War I, countries that lost the war had to give up their colonies. For example, Britain, which won the war, took over Tanzania from Germany.
However, after World War II, Europe's colonies began to gain independence. Many new countries were formed. In 1999, Portugal returned Macau to China. This was the last European colony in Asia. It marked the end of an era that had lasted for 500 years.
Images for kids
-
European claims in Africa, 1914, following the Scramble for Africa.
-
Elmina Castle, Ghana, one in a chain of about fifty fortified trading posts to enforce Portuguese trade rule along the coast. View from the sea in 1668.
-
Lord Clive meeting with Mir Jafar at the Battle of Plassey in 1757, painted by Francis Hayman
-
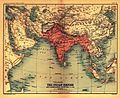
The British Indian Empire and surrounding countries in 1909