History of Punjab facts for kids

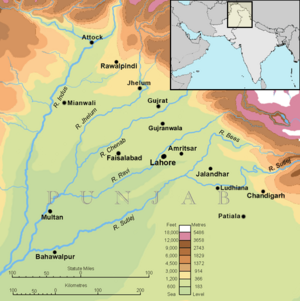
Punjab is a large and historic region in South Asia. It is divided between two countries: India and Pakistan. The name "Punjab" means "Land of Five Rivers" because of the five major rivers that flow through it: the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej. This region has been home to many different cultures and empires for thousands of years.
In 1947, when British India became independent, the Punjab Province was split into two parts. The western part became part of the new country of Pakistan, and the eastern part remained in India. This division caused many people to move from one side to the other, leading to difficult times for families and communities.
Contents
Ancient History of Punjab
The Punjab region has a very long and interesting history, going back thousands of years. It was one of the first places where large civilizations grew in South Asia.
Early Civilizations and Settlements
One of the oldest known civilizations, the Indus Valley Civilization, thrived in Punjab around 2500 to 1900 BCE. Cities like Harappa were very advanced for their time. They had well-planned streets, drainage systems, and large buildings. People living there were skilled at making pottery, jewelry, and tools. They also had a system of writing, though we still don't fully understand it.

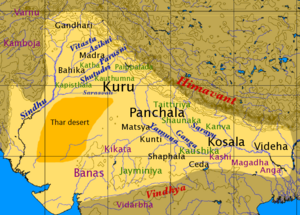
After the Indus Valley Civilization, the Vedic period began around 1500 BCE. During this time, the Vedas, which are ancient religious texts, were written. The Punjab region was an important center for early Hinduism and the development of Sanskrit language.
Great Empires and Invaders
Over the centuries, many powerful empires and invaders came to Punjab.
- Persian and Greek Influence: In the 6th century BCE, parts of Punjab were conquered by the Persian Empire. Later, in 326 BCE, Alexander the Great and his Greek army reached Punjab. His invasion had a big impact, even though his stay was short.
- Mauryan Empire: After Alexander, the Mauryan Empire rose to power. This was one of the largest empires in ancient India. Emperor Ashoka helped spread Buddhism throughout the region.
- Other Kingdoms: Over time, other kingdoms like the Guptas and various local rulers controlled Punjab. The region was often a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange.
Medieval Punjab: New Faiths and Rulers
The medieval period brought new religions and powerful empires to Punjab, shaping its future.
Arrival of Islam
Starting in the 8th century, Islam began to spread into Punjab. Muslim rulers, like those from the Ghaznavid dynasty, established their control. Cities like Multan became important centers for Islamic learning and culture.

The Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire ruled Punjab for several centuries, starting in the 16th century. The Mughals were powerful rulers who built many famous buildings and forts.

- Art and Architecture: The Mughals built grand mosques, gardens, and forts, especially in Lahore, which was a major city. The Badshahi Mosque is a great example of their amazing architecture.
- Cultural Blending: Mughal rule led to a mix of Indian and Islamic cultures, influencing art, music, and food in Punjab.
Rise of Sikhism
During the Mughal period, a new religion called Sikhism began in Punjab.

- Guru Nanak: Sikhism was founded by Guru Nanak in the 15th century. He taught about one God and equality for all people.
- Sikh Gurus: Over time, ten Sikh Gurus guided the Sikh community. They faced challenges from the Mughal rulers, leading to conflicts.
- Banda Singh Bahadur: After the Gurus, Banda Singh Bahadur led the Sikhs in battles against the Mughals in the early 18th century.

Sikh Empire and British Rule
The 18th and 19th centuries saw the rise of a powerful Sikh kingdom and then the arrival of the British.
The Sikh Empire
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Maharaja Ranjit Singh united the different Sikh groups and created the Sikh Empire. This empire was very strong and well-organized.

- Expansion: Ranjit Singh expanded his empire to include much of Punjab and surrounding areas.
- Modern Army: He built a modern army with the help of European officers.
- Religious Tolerance: His empire was known for its religious tolerance, allowing people of different faiths to live peacefully.
British Control
After Maharaja Ranjit Singh's death in 1839, the Sikh Empire faced challenges. The British East India Company, which was gaining power in India, fought two wars with the Sikhs.
- Anglo-Sikh Wars: The First Anglo-Sikh War (1845-1846) and the Second Anglo-Sikh War (1848-1849) led to the defeat of the Sikh Empire.
- Punjab Becomes British: By 1849, Punjab became part of British India. The British introduced new systems of administration, education, and infrastructure, like railways.

Partition of Punjab in 1947
The most significant event in modern Punjab's history was its division in 1947.
The Decision to Divide
When British India gained independence, it was decided to create two separate countries: India and Pakistan. This decision was based on religious lines, with India being mostly Hindu and Pakistan being mostly Muslim. Punjab, with its mixed population of Muslims, Sikhs, and Hindus, was split.
Impact of the Partition
The division of Punjab caused huge challenges. Millions of people had to leave their homes and move to the other side of the new border. This was a very difficult time, with many families separated and communities facing hardship. The partition created the modern-day Punjab in India and Punjab in Pakistan.
Images for kids
-
Coins of the Hindu Shahis from the 8th century, which later influenced Abbasid coins.