Inclinometer facts for kids
An inclinometer (also called a clinometer) is a cool tool that measures angles. It helps us figure out how much something is tilted, like a slope, how high something is (elevation), or how low it is (depression). It always measures these angles compared to the direction of gravity.
You might hear inclinometers called by other names too, like a tilt sensor, tilt meter, slope alert, or gradient meter. They can measure both upward and downward slopes. They use different units like degrees or percentage points. Did you know that an astrolabe, used long ago for celestial navigation (finding your way by stars), was a type of inclinometer?
A tilt sensor can measure tilting in two directions, like how a table might wobble. For bigger movements, you'd need more sensors. One way to measure tilt is by using an accelerometer, which senses movement. You can find these sensors in factories and even in game controllers! In airplanes, a part called the "ball" in the turn coordinator is also a kind of inclinometer.
Contents
History of Inclinometers
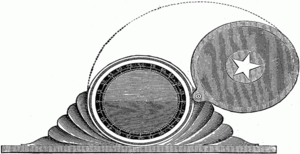
Inclinometers have been around for a long time. One example is the Well's in-clinometer. It had a flat base and a round, hollow disc filled with a heavy liquid. The disc had a scale around it, showing the angle of the liquid's surface. When the liquid was on the zero line, the base was flat. When it was on the 90-degree line, the base was straight up and down. This helped people measure slopes and drops.
A smart person named Al-Biruni, who lived a long time ago, needed to measure the sun's height. He didn't have the right tools, so he made his own. He drew a curved scale on a board and used a string with a weight (a plumb line). This simple tool was a type of inclinometer, and he used it to figure out his location's latitude!
Later, in the 1870s, the Abney level was invented. This was a handheld tool for surveying. It had a special tube to look through and an inclinometer. Surveyors could line up what they saw with a bubble in the inclinometer to measure angles.
A very famous inclinometer was in Charles Lindbergh's plane, "The Spirit of St. Louis," in 1927. He used a lightweight Rieker Inc P-1057 Degree Inclinometer to help him know how much his plane was climbing or diving.
How Inclinometers Are Used Today
Small, handheld inclinometers are used for many different tasks.
- In land surveying, they quickly measure the slope of hills or land features. They are also used for mapping caves.
- People looking for minerals use them to measure the tilt of rock layers.
- In forestry, inclinometers help measure the height of trees using simple math like triangulation.
- Big artillery guns use inclinometers to help aim shells over long distances.
- Special inclinometers called tiltmeters are built into large structures like dams. They help engineers check if the structure is staying stable over time.
What Affects Inclinometer Accuracy?
The accuracy of an inclinometer can change based on a few things:
- The strength of gravity in that spot.
- Changes in temperature can make the readings drift.
- Things like vibration, sudden shocks, or quick movements can also affect how well it measures.
- You need a clear view of what you are measuring.
- The object you are measuring should be clearly defined for the best results.
How Inclinometer Sensors Work
Inclinometer sensors create an "artificial horizon" to measure how much something is tilted compared to this horizon. They are used in many devices like cameras, airplane controls, and even car security systems. They also help make sure platforms are level or show the angle of a crane's arm.
When choosing an inclinometer, important things to think about are how wide a range of angles it can measure and how many directions (axes) it can sense. Usually, these directions are at right angles to each other.
Some common ways inclinometers work include using accelerometers, special liquids (like in liquid capacitive or electrolytic sensors), or even a gas bubble in a liquid.
You might have even used inclinometer technology in video games! Games like Yoshi's Universal Gravitation and Kirby Tilt 'n' Tumble have tilt sensors built right into their game cartridges. The controllers for the PlayStation 3 and Wii also use tilt to let you play games by moving the controller.
Inclinometers are also important in civil engineering. For example, they measure the tilt of land before buildings are constructed on it. Some modern inclinometers can even connect to computer networks using CAN technology, making them smart and easy to use.
Two-Axis Digital Inclinometers
Older leveling tools, like traditional spirit levels, usually only measure tilt in one direction. But many tasks, like leveling a machine or measuring a surface, involve angles in two directions. Two-axis inclinometers, which use tiny MEMS sensors, can measure angles in two directions at the same time.
Here are some cool things about two-axis MEMS inclinometers:
- They measure both "pitch" (front-to-back tilt) and "roll" (side-to-side tilt) at once. This saves time because you don't have to keep switching tools.
- They are very accurate, even when the temperature changes. This is because they use digital technology to correct for errors.
- These sensors can even create data about vibrations. This helps people installing machines check how well they are aligned and make sure they stay stable.
Inclinometers with Gyroscopes
Inclinometers measure tilt based on gravity. But what happens if there are sudden movements, vibrations, or shocks? These can mess up the tilt readings. To fix this, some inclinometers also use a gyroscope. A gyroscope is less affected by these sudden movements. A smart computer program can then combine the information from both the inclinometer and the gyroscope to get the most accurate tilt angle, separating real tilt from movement errors.
How to Use a Handheld Inclinometer
Using a handheld inclinometer is pretty simple!
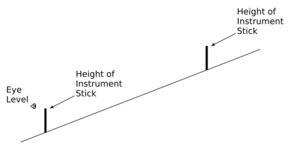
- Choose a Target: Pick something you want to measure, like the top of a tree or a building.
- Position Yourself: Stand a certain distance away from the object. Knowing this distance can help you figure out the object's height later.
- Sighting the Target: Look through the special tube or straw on the inclinometer towards the top of your target. Make sure you hold the inclinometer steady and that any string or pendulum hangs freely.
- Reading the Angle: Once you have the target in sight, look at where the string crosses the scale on the inclinometer. This number is the angle of elevation (if you're looking up) or depression (if you're looking down).
Cool Things Inclinometers Are Used For
Inclinometers have many uses in our world:
- Finding your latitude using stars like Polaris (in the Northern Hemisphere).
- Measuring the angle of the Earth's magnetic field.
- Showing if something is perfectly straight up or perfectly flat.
- In surveying, to measure how much something slopes.
- Warning equipment operators if their machine might tip over.
- Measuring slight changes in slopes, which is important in geophysics for monitoring volcanoes or landslides.
- Checking movements in walls or the ground in big building projects.
- Helping to aim cannons or guns by setting their firing angle.
- In some car safety systems.
- Showing how much a vehicle, boat, or airplane is tilting.
- Measuring the angle of a satellite dish towards a satellite.
- Adjusting solar panels to get the most energy from the sun.
- Measuring the height of buildings or trees using math.
- Measuring the angle of drilling in well logging (when drilling for oil or gas).
- Measuring how much a ship is leaning.
- Measuring the steepness of a ski slope.
- In structural geology, to understand how rocks are tilted.
- Measuring how much a body joint can move (like your knee or elbow).
- Setting the correct angle for line array speakers at concerts.
- Helping to prevent unsafe working conditions.
- The USDA Forest Service uses them to measure tree height.
- In logistics and transport, special single-use tilt indicators are attached to products during shipping to see if they were tilted too much.
Inclinometers in Games
Nintendo has used tilt sensor technology in several of its Game Boy games. These sensors let players control the game by twisting the game system!
- Yoshi's Universal Gravitation (Game Boy Advance)
- WarioWare: Twisted! (Game Boy Advance)
- Koro Koro Puzzle Happy Panechu! (Game Boy Advance) (Japan only)
- Kirby Tilt 'n' Tumble (Game Boy Color)
- Command Master (Game Boy Color) (Japan only)
Tilt sensors are also found in other game controllers, like the Microsoft Sidewinder Freestyle Pro and Sony's PlayStation 3 controller.
However, the Wii Remote and its Nunchuk attachment made tilt sensors a main way to play games. Along with accelerometers, these sensors are key to how most Wii games are controlled.
Today, tilt sensors are used in many different types of games, not just flight simulators. They are in sports games, first-person shooters, and even unique games like WarioWare: Smooth Moves. Imagine a virtual maze where you tilt your controller to guide a ball through obstacles – that's an inclinometer at work!
Images for kids
-
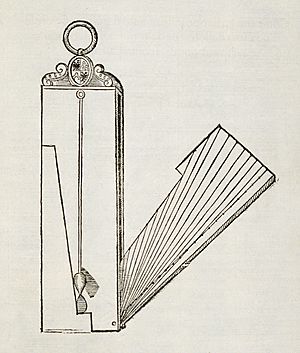
Clinometer designed to enable indirect fire capability with a Vickers machine gun circa 1918
See also
 In Spanish: Clinómetro para niños
In Spanish: Clinómetro para niños
- Grade (slope)
- Goniometer
- Hypsometer
- Liquid capacitive inclinometers
- Theodolite
- Tiltmeter