Phoenicean juniper facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Phoenicean juniper |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Specimen from Roussillon, France | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Juniperus |
| Section: | Juniperus sect. Sabina |
| Species: |
J. phoenicea
|
| Binomial name | |
| Juniperus phoenicea |
|
 |
|
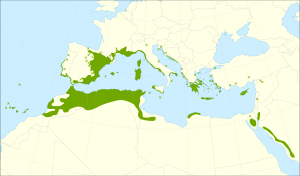
| Natural range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Phoenicean juniper (scientific name: Juniperus phoenicea) is a type of juniper tree. It is also known as Arâr. You can find it all around the Mediterranean region.
Description
The Phoenicean juniper can grow as a large shrub or a small tree. It usually reaches about 5 to 8 meters (16 to 26 feet) tall. Its trunk can be up to 1 to 2 meters (3 to 6.5 feet) wide. The tree often has a rounded or uneven top.
Its bark is dark grayish-brown and can peel off in strips. The leaves come in two forms. Young plants have needle-like leaves that are 5 to 14 millimeters long. Older plants have small, flat, scale-like leaves that are 1 to 2 millimeters long. These adult leaves are green to blue-green. They grow in pairs or in groups of three.
Most Phoenicean junipers have both male and female parts on the same plant (this is called monoecious). However, some individual plants have only male or only female parts (this is called dioecious).
The female cones look like berries. They are 6 to 14 millimeters wide and are orange-brown. Sometimes, they have a pinkish, waxy coating. Each cone holds 3 to 8 seeds. These cones take about 18 months to fully grow. Birds often eat the berries and help spread the seeds. The male cones are smaller, about 2 to 4 millimeters long. They release their pollen in early spring, which the wind then carries away.
Taxonomy
There are two main types, or varieties, of Phoenicean juniper. Some scientists consider them as slightly different kinds (subspecies), while others think they are completely separate species.
- Juniperus phoenicea var. phoenicea: This type is found across the entire area where the species grows. Its cones are round, about as wide as they are long. Its leaves are small and blunt. This variety releases its pollen in the spring.
- Juniperus phoenicea var. turbinata (also known as Juniperus turbinata): This type only grows in sandy areas near the coast. Its cones are oval, meaning they are longer than they are wide. Its leaves are long and thin. This variety releases its pollen in the autumn.
Distribution and Habitat
You can find the Phoenicean juniper all over the Mediterranean region. This includes countries from Morocco and Portugal in the west, all the way to Croatia, Italy, Turkey, and Egypt in the east. It also grows south in the mountains of Lebanon, the Palestine region, and in western Saudi Arabia near the Red Sea. You can also find it on the islands of Madeira and the Canary Islands.
This tree usually grows in low areas near the coast. However, in the southern parts of its range, like the Atlas Mountains, it can grow as high as 2,400 meters (7,900 feet) above sea level.
Ecology
The Phoenicean juniper prefers a hot, dry climate with lots of sunlight. It grows well on rocky or sandy ground. It likes soil that contains a lot of lime, with a pH between 7.7 and 7.9, which means it's a bit basic. However, it can also grow in soil with other types of minerals. Even though its roots don't go very deep, it can survive with as little as 200 millimeters (8 inches) of rain each year.
This juniper often grows together with other plant species, forming thick bushes and scrubs. In places like France and Spain, the Phoenicean juniper has a life cycle of about 25 years. In 2016, the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species listed it as a stable species, meaning it is not currently at risk of disappearing.
However, human activity can threaten its habitat, especially in coastal areas. This includes people living there and tourists visiting. People sometimes plant non-native plants, like certain pines or agave, to help stabilize sand dunes. But these outside plants can interfere with the natural plants that belong there. The Phoenicean juniper is also easily threatened by fires because it burns quickly and doesn't grow back well after a fire. This means new plants often need to be planted if a fire damages the area.
Uses
Juniper berries are used as a seasoning in cooking. They are also used to flavor alcoholic beverages, especially gin. In the past, juniper berries were used in traditional medicine for various health issues. However, there is no strong scientific proof that they actually help.
Some extracts from juniper berries or wood have been used for their smell, especially in cosmetics. But it's not fully proven that using ointments made from this juniper on your skin is safe. Juniper extracts used on the skin might cause allergic reactions in some people. Also, they should be avoided during pregnancy.
The wood of the Phoenicean juniper is used to make small objects and for inlay work in carpentry. In Africa, it is often used in building homes. It is also an important source of fuel and for making charcoal.
Culture
The Phoenicean juniper is the plant symbol of the island of El Hierro, which is one of the Canary Islands.
See also
 In Spanish: Juniperus phoenicea para niños
In Spanish: Juniperus phoenicea para niños
- List of animal and plant symbols of the Canary Islands






