Kern River facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Kern River |
|
|---|---|

Panorama of the upper Kern River
|
|
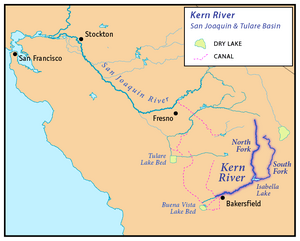
Map of the San Joaquin and Tulare Basin region with the Kern River highlighted. Some rivers shown are intermittent or normally dry. A few selected canals are shown. Below: Map of the San Joaquin and Tulare Basin region showing the old lakes and river courses.
|
|
| Other name(s) | Rio de San Felipe, La Porciuncula, Po-sun-co-la, Porsiuncula River |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Region | Sierra Nevada, San Joaquin Valley |
| District | Tulare County, Kern County |
| City | Bakersfield |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Kings-Kern Divide Sequoia National Park 13,608 ft (4,148 m) 36°41′48″N 118°23′53″W / 36.69667°N 118.39806°W |
| River mouth | Buena Vista Lake Bed San Joaquin Valley 299 ft (91 m) 35°16′4″N 119°18′25″W / 35.26778°N 119.30694°W |
| Length | 164 mi (264 km) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 3,612 sq mi (9,360 km2) |
| Type: | Wild, Scenic, Recreational |
| Designated: | November 24, 1987 |
The Kern River is a river in California, United States. It is about 165 miles (270 km) long. The river starts in the Sierra Nevada mountains. It flows southwest, passing through beautiful canyons. The Kern River is a popular spot for whitewater rafting and kayaking.
The river gets its water from snow melting near Mount Whitney. It is the most southern major river in the Sierra Nevada. It is also the only major Sierra river that flows south.
Long ago, the Kern River flowed into Buena Vista Lake and Kern Lake. These lakes are now mostly dry. The river's water was part of a basin that sometimes flowed into the San Joaquin River.
Today, most of the Kern River's water is used for farming. It helps water crops and refills underground water supplies. Some water also goes into Lake Webb and Lake Evans. These small lakes were made in 1973 for fun activities.
Even though it starts in a remote area, most of the Kern River is open to the public. Many people enjoy hiking and whitewater rafting here. The river flows quickly below Lake Isabella, making it great for rafting.
Contents
The Kern River's Journey
The Kern River starts in Sequoia National Park in Tulare County. The main part of the river, sometimes called the North Fork, begins from small lakes. These lakes are surrounded by tall mountains over 13,000 feet (4,000 m) high.
The Kern River flows south through deep valleys. It passes through Inyo National Forest and Sequoia National Forest. Many smaller streams join the Kern River along the way. Some of these streams create large waterfalls as they flow into the canyon.
Lake Isabella and Its Branches
Near Kernville, the river flows into a wide valley. Here, it forms Lake Isabella, which is held back by Isabella Dam. Lake Isabella is where the Kern River is joined by its largest branch, the South Fork Kern River. The South Fork also starts in Tulare County and flows west.
Below Isabella Dam, the Kern River flows southwest through a rugged canyon. This part of the river is popular for whitewater rafting. It also powers several hydroelectric plants. The river flows quickly here because water is released from the dam for farming and power.
Reaching Bakersfield
The river then winds through hills before reaching Bakersfield. This is the biggest city along the river. In Bakersfield, most of the river's water is sent into canals. These canals are used to water farms in the southern San Joaquin Valley. They also provide water for Bakersfield and nearby areas.
The land around Bakersfield is a rich plain. It was formed by the Kern River, which once spread out into large wetlands and seasonal lakes.
The Friant-Kern Canal adds some water back to the Kern River west of Bakersfield. The river channel continues southwest for about 20 miles (32 km). A special gate allows extra floodwaters from the Kern to flow into the California Aqueduct. Any remaining water goes into the seasonal Buena Vista Lake.
Historically, another branch of the Kern River flowed south to what is now Arvin. This branch formed the seasonal Kern Lake. Water from Kern Lake would then flow into Buena Vista Lake. In very wet years, Buena Vista Lake would overflow into other wetlands. These wetlands would then drain north into the former Tulare Lake.
The Kern River is one of the few rivers in the Central Valley that does not directly contribute water to the Central Valley Project. However, water from the Central Valley Project, mainly from the Friant-Kern Canal, is stored in the ground using the Kern River's system.
River's Past
The Kern River was named by John C. Frémont in 1845. He named it after Edward Kern, who was a mapmaker on Fremont's trip. Edward Kern almost drowned in the river's strong currents.
Before this, the river had other names. Spanish explorers called it "Rio de San Felipe" in 1776. Later, in 1806, it was renamed "La Porciuncula." Locals called it Po-sun-co-la for a while.
Gold was found along the upper river in 1853. The melting snow caused big floods in Bakersfield until the Isabella Dam was built in the 1950s. These floods often changed where the river flowed. Many of the canals that flow south from the river follow these old river paths.
The irrigated land near the river is very fertile. Farmers grow crops like alfalfa, carrots, fruit, and cotton. They also raise cattle. In 1987, the United States Congress made 151 miles (243 km) of the Kern's North and South Forks a National Wild and Scenic River. This protects its natural beauty.
The huge 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake was so strong it temporarily made the Kern River flow backward! Fish in the now-dry Tulare Lake were left stranded.
Managing the Kern River's water can be tricky. The area around Buena Vista Lake is dry, and the Kern River is its only major water source. There are often disagreements about how to use the water. Also, the Isabella Dam has had safety issues, which means less water can be stored there while repairs are made.
Animals and Plants
The Kern River is home to California's State Freshwater Fish, the California golden trout. These beautiful fish live in the Kern River's branches, like the South Fork Kern River and Golden Trout Creek. There are also two other types of trout found here: the Little Kern golden trout and the Kern River rainbow trout. Together, these three are known as the "Golden Trout Complex."
In 2008, the City of Bakersfield and the California Department of Fish and Game decided to move a family of California Golden beaver instead of harming them. Beavers are native to this area. People have shared stories about seeing beaver signs on the Kern River long ago. There's even a place called Beaver Canyon Creek, which suggests beavers lived there historically. Today, many beavers live in Ramshaw Meadows on the South Fork Kern River. Their dams help trap dirt, create pools, and improve the meadow and willow habitats.
River's Geology

The upper Kern River Canyon was formed by strong forces in the Earth. A fault line, called the Kern Canyon Fault, runs along the canyon. This fault has changed the river's path many times over millions of years. Long ago, the Kern River flowed into the San Joaquin Valley further south. But the land lifted, forcing the river to cut a new path, creating the steep canyon we see today.
During the Ice Ages, glaciers helped widen and deepen the upper part of the Kern River canyon. The Kern Canyon fault is very close to Isabella Dam, which is why its safety is carefully watched.
The Kern River Oil Field is next to the river near Bakersfield. In the past, a lot of dirty water from the oil field drained into the river. But now, rules make sure this water is cleaned at treatment plants. Then, it's used to water farms in the valley.
River Flow
The amount of water flowing in the Kern River changes a lot. This is because of water being taken out and the Isabella Dam. The most water usually flows just below Isabella Dam. However, the highest daily flows happen above the dam on the North Fork.
For example, a measuring station on the North Fork Kern River has recorded an average flow of 806 cubic feet per second (23 m3/s). The South Fork Kern River has an average flow of 123 cubic feet per second (3.5 m3/s). Below Isabella Dam, the average flow is 946 cubic feet per second (27 m3/s). But because water is taken out, the flow decreases a lot further down. Near Bakersfield, the river's average flow is only 312 cubic feet per second (8.8 m3/s).
Fun on the Kern River
Kern Canyon, northeast of Bakersfield, is a popular place for outdoor activities. People enjoy fishing, especially fly fishing. It's also great for whitewater rafting, whitewater kayaking, and riverboarding. Fishermen are especially interested in the Kern River rainbow trout, Little Kern golden trout, and California golden trout.
The Kern Canyon is also a favorite spot for camping, hiking, and picnicking. The US Forest Service maintains several campgrounds along the North Fork of the Kern River. Some of these campgrounds are open all year, while others are open during the summer.
The Kern River is well-known for its strong currents and can be dangerous. A sign at the entrance of Kern Canyon warns visitors: "Danger. Stay Out. Stay Alive." It also lists the number of deaths since 1968. As of May 22, 2020, 307 deaths have been recorded. The country singer Merle Haggard even wrote a song called "Kern River" about a fictional tragedy there.
Below the canyon, the Kern River flows through flatter land and into Bakersfield. Here, tubing is a popular activity. The Class II whitewater in Kernville is used for a special event called the slalom during the annual Kern River Festival.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Río Kern para niños
In Spanish: Río Kern para niños





