Biology facts for kids
Biology is the exciting science that studies life and all living things. It explores how living things grow, behave, and interact with each other. It also looks at how life has changed over millions of years through evolution.
Living things include a huge variety of organisms. These range from tiny microorganisms like bacteria and archaea to larger forms like plants, animals, and fungi (like mushrooms).
People who study biology are called biologists. They try to understand how different parts of living things work. They also investigate how organisms live together and how they affect their environment. Biology has been a formal science for about 200 years. Before that, people studied natural history, which was a less organized way of learning about nature.
Like all sciences, biology uses the scientific method. This means biologists must show proof for their ideas. Other scientists must also be able to test these ideas themselves. This helps make sure the information is accurate and reliable.
Contents
What Do Biologists Study?
Biologists ask many important questions about life. They want to know:
- "What makes this living thing special?" This is studied through comparative anatomy.
- "How do its different parts work?" This is called physiology.
- "How can we group living things together?" This involves classification and taxonomy.
- "What does this living thing do?" This covers behaviour and growth.
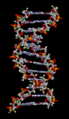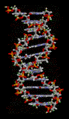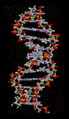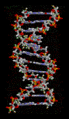
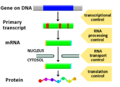
- "How are traits passed down from parents?" This is the field of genetics.
- "What is the history of life on Earth?" This is studied in palaeontology.
- "How do organisms interact with their surroundings?" This is the focus of ecology.
All modern biology is deeply connected to evolution. Evolution helps us understand how the living world became the way it is today. It explains the amazing diversity of life we see around us.
Different Areas of Biology
Biology is a very big subject with many different branches. Each branch focuses on a specific part of life or a certain type of organism. Here are some of the main areas:
Studying Life's Structures
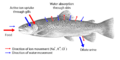
- Anatomy: The study of the body's structure, like bones and organs.
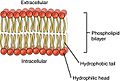
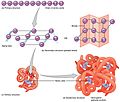
- Cell biology: Looking at cells, the basic building blocks of life.
- Histology: The study of tissues, which are groups of similar cells.
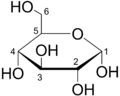
- Molecular biology: Exploring life at a very tiny level, like molecules.
Exploring Different Organisms
- Botany: The study of plants.
- Zoology: The study of animals.
- Microbiology: The study of tiny living things like bacteria and viruses.
- Bacteriology: A specific study of bacteria.
- Virology: The study of viruses.
- Mycology: The study of fungi, like mushrooms and molds.
- Entomology: The study of insects.
- Ichthyology: The study of fish.
- Herpetology: The study of reptiles and amphibians.
- Ornithology: The study of birds.
- Mammalogy: The study of mammals.
How Life Works and Changes
- Biochemistry: The study of the chemical processes in living things.
- Physiology: How the parts of living things work.
- Genetics: How traits are passed from parents to offspring.
- Evolutionary biology: How life changes over long periods of time.
- Developmental biology: How organisms grow and develop from a single cell.
- Embryology: The study of embryos and their development.
Life and Its Environment
- Ecology: How living things interact with each other and their environment.
- Biogeography: Where different species live around the world.
- Marine biology: The study of life in the ocean.
- Limnology: The study of fresh water environments like lakes and rivers.
Other Important Fields
- Ethology: The study of animal behaviour.
- Palaeontology: The study of ancient life through fossils.
- Taxonomy: The science of naming and classifying organisms.
- Parasitology: The study of parasites.
- Human biology: The study of humans.
- Anthropology: The study of human societies and cultures.
- Primatology: The study of primates.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Biología para niños
In Spanish: Biología para niños
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |