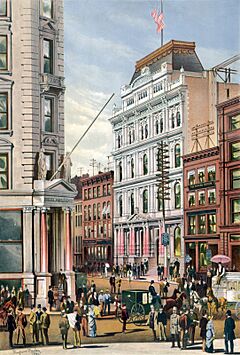New York Stock Exchange facts for kids
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), often called "The Big Board", is a famous stock exchange located in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It's the largest stock exchange in the world based on the total value of all the companies listed on it, which was over $25 trillion in July 2024. The NYSE is owned by a company called Intercontinental Exchange. Many American adults invest money in the stock market through places like the NYSE.
| New York Stock Exchange | |
|---|---|
Quick facts for kids NYSE Logo 2022.svg |
|
| New York Stock Exchange Facade 2015.jpg | |
| Type | Stock exchange |
| Location | [[New York City]], U.S. |
| Founded | May 17, 1792 |
| Owner | Intercontinental Exchange |
| Key people |
|
| Currency | United States dollar |
| No. of listings | 2,223 (July 2024) |
| MarketCap | US$28.33 trillion (July 2024) |
| Indexes |
|
Contents
History of the NYSE
The New York Stock Exchange began a long time ago, even before it had a formal building. In 1792, twenty-four stockbrokers signed an agreement called the Buttonwood Agreement. They met under a buttonwood tree on Wall Street to trade stocks. Before this, people bought and sold stocks through auctioneers, who also sold things like wheat and tobacco.
The first stocks traded were mostly government bonds from the Revolutionary War. Stocks from early banks like the First Bank of the United States and the Bank of New York were also traded.
Becoming a Formal Exchange
In 1817, the brokers decided to get more organized. They visited Philadelphia to see how their stock exchange worked. They then created new rules and formed the New York Stock and Exchange Board. This group started renting special places just for trading stocks. Before this, trading often happened in coffee houses. The NYSE moved to several locations before settling at its current spot in 1865.
The invention of the electrical telegraph helped New York's market become very important. In 1864, another exchange called the Open Board of Stock Brokers started. It had a more modern way of trading. In 1869, this Open Board merged with the NYSE. This merger helped the NYSE grow even bigger and become the main place for trading stocks. The American Civil War also made more people interested in buying and selling stocks.
Changes and Rules
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, the stock market had many ups and downs, including big crashes. After a huge crash in 1929, which led to the Great Depression, the government decided that more rules were needed to protect investors. The NYSE also added its own rules to keep things fair.
From its start until 2000, stock prices on the NYSE were quoted in fractions, like 1/8 or 1/16 of a dollar. This was based on an old Spanish trading system. But on August 28, 2000, the NYSE started quoting prices in decimals, like $0.01, which is much easier to understand. All stocks were traded this way by the end of 2001.
Important Moments in NYSE History
20th Century Events
- World War I (1914): The exchange closed briefly when World War I began. It reopened later that year to help the war effort by trading bonds.
- Wall Street Bombing (1920): A bomb exploded outside the NYSE building, killing forty people.
- Black Thursday (1929): On October 24, 1929, the stock market crashed, followed by another big crash on October 29, known as Black Tuesday. These events are often seen as the start of the Great Depression.
- Government Oversight (1934): The exchange officially registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), a government agency that oversees stock markets.
- Traders on the Floor (1963):
- Yippie Protest (1967): A famous prank happened when Abbie Hoffman and others threw fake dollar bills onto the trading floor from the gallery. This led the NYSE to put up bulletproof glass around the gallery.
- Black Monday (1987): On October 19, 1987, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) dropped by 22.6% in one day. This was one of the biggest one-day drops ever.
- Mini-Crash of 1989: On October 13, 1989, the Dow dropped significantly after a big business deal fell apart.
- 1997 Mini-Crash: On October 27, 1997, the Dow dropped again due to problems in Asian markets. This was the first time the "circuit breaker" rule was used, which temporarily stops trading to prevent panic.
21st Century Events
- Rage Against the Machine (2000): The band Rage Against the Machine tried to enter the exchange during a music video shoot, causing the doors to be closed.
- September 11 Attacks (2001): The NYSE closed for four trading days after the September 11 attacks because it was very close to the World Trade Center. When it reopened, the market dropped significantly.

- Flash Crash (2010): On May 6, 2010, the Dow Jones Industrial Average suddenly dropped almost 1,000 points in minutes before recovering. This event was called the "Flash Crash."
- Hurricane Sandy (2012): The stock exchange closed for two days because of Hurricane Sandy. The last time it closed for two full days due to weather was in 1888.
- Technical Issues (2015): On July 8, 2015, technical problems stopped trading for several hours. The NYSE confirmed it was not a cyberattack.
- First Female President (2018): Stacey Cunningham became the first female president of the NYSE in its 226-year history.
- COVID-19 Pandemic (2020): In March 2020, the NYSE temporarily switched to all-electronic trading due to the COVID-19 pandemic. It reopened for in-person trading in May 2020.
- Trading Glitch (2023): On January 24, 2023, a technical glitch caused problems with trade orders for many stocks.
The NYSE Building
The main New York Stock Exchange Building was built in 1903. It's located at 18 Broad Street and was designed in a grand style called Beaux Arts. Another building next to it at 11 Wall Street was finished in 1922 in a similar style. Both buildings are considered important historical landmarks.
How Trading Works
The New York Stock Exchange is a place where buyers and sellers can trade shares of companies that are publicly listed. The NYSE is open for trading from Monday to Friday, 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM Eastern Time, except on holidays.
The Auction System
The NYSE uses a "continuous auction" system. This means that traders can buy and sell stocks throughout the day. Traders gather around specific "posts" on the trading floor. At each post, there's a special broker who acts like an auctioneer. They help bring buyers and sellers together to make trades. Sometimes, these brokers even use their own money to help trades happen smoothly.
In 1995, the trading process started to become more electronic with wireless handheld computers. This allowed traders to send and receive orders electronically. By 2007, most NYSE stocks could be traded electronically through a "hybrid market" system. This means people can send orders for immediate electronic trading or send them to the floor for the auction.
After the big market crash in 1987, the NYSE put in place "circuit breaker" rules. These rules are designed to slow down trading if the market drops too quickly. If the market falls by a certain percentage, trading can be halted for 15 minutes to prevent panic selling. If it drops even more, trading can be stopped for the rest of the day.
Trading "Seats"
For a long time, to trade directly on the NYSE, you had to own a "seat." This term came from the fact that members used to sit in chairs to trade. The number of seats was limited, and they were very valuable. In 1929, a seat sold for $625,000, which would be over six million dollars today!
In 2005, the NYSE changed. It merged with another company and became a for-profit, publicly traded company. Instead of buying "seats," people now buy one-year licenses to trade directly on the exchange.
NYSE Composite Index
In the mid-1960s, the NYSE Composite Index was created. This index measures the value of *all* the stocks traded on the NYSE. This is different from the Dow Jones Industrial Average, which only tracks 30 large companies. The NYSE Composite Index helps people see how the entire market on the NYSE is doing.
Opening and Closing Bells

The NYSE's opening and closing bells are famous signals that mark the start and end of each trading day. The opening bell rings at 9:30 AM ET, and the closing bell rings at 4:00 PM ET. There are bells in four main sections of the NYSE, and they all ring at the same time when a button is pressed.
Bell History
The signal to start and stop trading wasn't always a bell. At first, a gavel (a small hammer) was used. Later, in the late 1800s, a gong was used. When the NYSE moved to its current building in 1903, the bell system we see today was put in place. The bells were made by Bevin Brothers in Connecticut, a town known for making bells.
Today, it's a common and highly publicized event for a VIP or a celebrity to stand at the NYSE podium and push the button to ring the bells. Companies often plan new product launches or other big announcements for the same day their representatives ring the bell. This tradition of having special guests ring the bells started regularly in 1995. Before that, the exchange's floor managers usually rang them.
Famous Bell-Ringers
Many people who ring the bell are business leaders whose companies are listed on the exchange. They often ring the bell to announce new products or important company news. However, many famous people from outside the business world have also rung the bell. These include:
- Political Figures: Former New York City Mayor Rudy Giuliani, former South African President Nelson Mandela, and former UN Secretaries-General Kofi Annan and Ban Ki-moon.
- Athletes: Joe DiMaggio and Michael Phelps.
- Entertainers: Rapper Snoop Dogg, singer Liza Minnelli, the rock band Kiss, and the cast of Rain: A Tribute to The Beatles.
- Public Heroes: Members of the New York City Police Department and New York City Fire Department after the September 11 attacks, and members of the United States Armed Forces.
- Fictional Characters: Even mascots and characters like Mickey Mouse, the Pink Panther, Mr. Potato Head, the Aflac Duck, and Darth Vader have rung the bell!
Official Holidays
The New York Stock Exchange is closed on several holidays throughout the year. These include New Year's Day, Martin Luther King Jr. Day, Washington's Birthday, Good Friday, Memorial Day, Juneteenth National Independence Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving, and Christmas. If a holiday falls on a weekend, it's observed on the closest weekday. The exchange also closes early on the day before Independence Day, the day after Thanksgiving, and Christmas Eve. On average, the NYSE has about 253 trading days each year.
Images for kids
-
President Ronald Reagan speaking at the NYSE in 1985.
-
Security at the NYSE after the September 11 attacks.
-
U.S. Secretary of Commerce Donald L. Evans rings the opening bell at the NYSE on April 23, 2003.
-
NASA astronauts Scott Altman and Mike Massimino ring the closing bell.
See also
 In Spanish: Bolsa de Nueva York para niños
In Spanish: Bolsa de Nueva York para niños
 | Jackie Robinson |
 | Jack Johnson |
 | Althea Gibson |
 | Arthur Ashe |
 | Muhammad Ali |