Norman language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Norman |
|
|---|---|
| Normaund | |
| Native to |
Previously used:
|
| Region | Normandy and the Channel Islands |
| Native speakers | Unknown due to conflicting definitions (2017)
|
| Language family | |
| Early forms: |
Old Norman
|
| Dialects |
Augeron
Cauchois
Cotentinais
|
| Writing system | Latin (French orthography) |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-hc & 51-AAA-hd |
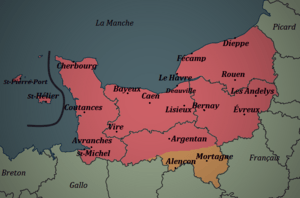
Areas where the Norman language is strongest include Jersey, Guernsey, the Cotentin and the Pays de Caux.
|
|
Norman is a fascinating language mainly spoken in a region of France called Normandy. It's a type of Romance language, which means it grew out of Latin, the language of ancient Rome. Norman is very similar to French, and people often call it "Norman French."
After the Norman Conquest in 1066, Norman had a big impact on the English language. Many English words we use today came from Norman. Forms of Norman are still used in the Channel Islands, which are close to Normandy.
Contents
Where Norman is Spoken Today
Norman is mostly spoken in Normandy, a region in northwestern France. It is also spoken on the Channel Islands, which are British islands located off the coast of Normandy.
Norman in the Channel Islands
The Channel Islands have their own special forms of Norman. These include:
- Jèrriais on the island of Jersey
- Guernésiais on the island of Guernsey
- Auregnais on Alderney, which is part of Guernsey
- Sercquiais on Sark, another dependency of Guernsey
Sadly, Auregnais is no longer spoken by anyone as their first language. Sercquiais is also very endangered, with only a few speakers left. However, Jèrriais and Guernésiais still have speakers and receive support from their local governments to help keep them alive.
Norman in France
In mainland Normandy, there are several dialects of Norman. Some of the main ones include:
- Augeron
- Cauchois
- Cotentinais
These dialects are also highly endangered, with fewer and fewer speakers. However, some local groups are working to preserve them.
Norman's History and Impact
Norman is part of the Oïl languages family. This group includes French and other languages that developed in northern France. Norman came from Old Norman, which was spoken by the Normans. The Normans were descendants of Vikings who settled in Normandy.
The Norman Conquest
The most famous event involving the Norman language was the Norman Conquest in 1066. William the Conqueror, Duke of Normandy, invaded England and became king. For hundreds of years after this, Norman French was the language of the English royal court, law, and government.
This had a huge effect on the English language. Before the conquest, Old English was the main language. After the Normans arrived, thousands of Norman French words were added to English. These words often related to:
- Government and law (e.g., justice, parliament)
- Food (e.g., beef, pork)
- Art and fashion (e.g., fashion, jewel)
This mix of Old English and Norman French helped create the English language we speak today.
Norman Beyond England
Norman was also used in other places where the Normans traveled and settled. This included:
- Parts of Ireland
- The Kingdom of Sicily (modern-day southern Italy)
- The Principality of Antioch in the Middle East
In these places, Norman was often used by the ruling class. However, it did not usually replace the local languages.
Saving the Language
Like many regional languages, Norman faces challenges today. Most people in Normandy now speak French. In the Channel Islands, English is the main language.
However, there are efforts to keep Norman alive. Local groups and governments in Jersey and Guernsey support teaching and using Jèrriais and Guernésiais. They hope to pass the language on to new generations.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma normando para niños
In Spanish: Idioma normando para niños


