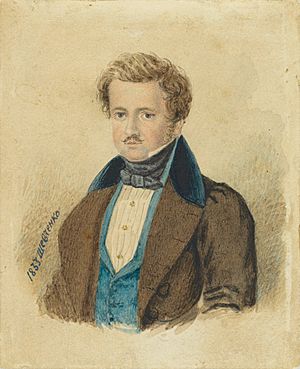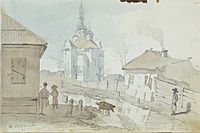Taras Shevchenko facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Taras Shevchenko
|
|
|---|---|

Shevchenko photographed by Andrey Denyer, c. 1859
|
|
| Native name |
Тарас Григорович Шевченко
|
| Born | 9 March [O.S. 25 February] 1814 Moryntsi, Kiev Governorate, Russian Empire |
| Died | 10 March [O.S. 26 February] 1861 (aged 47) Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire |
| Resting place | National Preserve "Taras Hill", Kaniv, Ukraine |
| Pen name | Kobzar Darmohrai, Perebendya |
| Occupation | Poet and artist |
| Language |
|
| Education | Member Academy of Arts (1860) |
| Alma mater | Imperial Academy of Arts (1845) |
| Period | 1840–1861 |
| Notable works | Kobzar |
| Signature | |
 |
|
| Military career | |
| Allegiance | Russian Empire |
| Service/ |
Imperial Russian Army |
| Years of service | 1847–1857 |
| Rank | Private |
| Unit | Orsk (1847–1850) Fort - Shevchenko (1850–1857) |
| Battles/wars | 1848 Aral Expedition 1851 Karatau Expedition |
Taras Hryhorovych Shevchenko (Ukrainian: Тарас Григорович Шевченко [tɐˈrɑz ɦrɪˈɦɔrowɪtʃ ʃeu̯ˈtʃɛnko], pronounced [tɐˈrɑs] without the middle name; born March 9, 1814 – died March 10, 1861), also known as Kobzar Taras, was a famous Ukrainian poet, writer, and artist. He was also a public figure and studied folklore and cultures. His writings are seen as the start of modern Ukrainian literature. They also greatly shaped the modern Ukrainian language.
Shevchenko was a member of the Imperial Academy of Arts. In 1847, he was arrested for writing poems in Ukrainian. He was also accused of criticizing the Russian Imperial family. Even though he was not part of the Brotherhood of Saints Cyril and Methodius, the secret police saw him as a strong supporter of Ukrainian independence.
Contents
Life Story of Taras Shevchenko
Childhood and Early Years
Taras Shevchenko was born on March 9, 1814. His birthplace was the village of Moryntsi in the Russian Empire. He was the third child in his family. His parents, Hryhoriy and Kateryna, were serf peasants. This meant they were owned by a landlord, Vasily Engelhardt.
Family stories say that Taras's ancestors were Cossacks. Cossacks were brave warriors who fought in uprisings. These uprisings were put down, and many people became poor and enslaved.
In 1816, Taras's family moved to Kyrylivka. He spent his childhood there. When he was young, Taras got lost looking for "iron pillars that hold up the sky." Some traveling merchants called Chumaks helped him find his way home.
In 1822, Taras started school with a local teacher named Sovhyr. He learned about the works of Hryhoriy Skovoroda. Around this time, Taras also began to draw horses and soldiers.
Taras faced many hardships. His older sister Kateryna got married in 1823. Soon after, his mother died, leaving six children. His father remarried a widow named Oksana. She treated Taras very badly. In 1824, Taras traveled with his father, who was a merchant.
When Taras was eleven, his father died. Taras became an orphan. His stepmother left him and returned to her village.
Taras then worked for a church clerk named Bohorsky. He did chores and studied. He also read some Ukrainian books. But Bohorsky treated him poorly, so Taras ran away. He looked for a painting teacher in other villages. He worked for a deacon and other people.
In 1827, Taras met Oksana Kovalenko, a friend from his childhood. He later wrote about her in his poems. Taras also worked for a priest, driving his son to school and selling fruit. In 1828, he became a servant for a lord in Vilshana. There, he got permission to study with a local artist.
Becoming a Free Artist
When Taras was 14, his first owner died. Taras and the other serfs became the property of the owner's son, Pavlo Engelhardt. Taras became a house servant for Pavlo. One night in 1829, Pavlo caught Taras secretly drawing. He punished Taras severely.
From 1828 to 1831, Shevchenko lived with his master in Vilno (Vilnius). He might have attended art lectures there. In 1831, Engelgardt moved to Saint Petersburg. He took Shevchenko with him. Engelgardt wanted Shevchenko to be his "chamber artist." So, he sent Taras to study with a painter named Vasiliy Shiriayev.
Shevchenko lived in Saint Petersburg and studied art. In his free time, he drew statues in the Summer Garden. He also started writing his poems during this period. In 1833, he painted a portrait of his master, Pavlo Engelgardt.
In Saint Petersburg, Shevchenko met other Ukrainian artists. They introduced him to famous Russian artists, like Karl Briullov. Briullov helped Shevchenko gain his freedom. He painted a portrait of a famous poet, Vasily Zhukovsky. This portrait was sold in a lottery. The money from the lottery was used to buy Shevchenko's freedom on May 5, 1838.
First Artistic Achievements
After gaining his freedom, Shevchenko joined the Academy of Arts. He studied in Karl Briullov's workshop. The next year, he became a student at the Association for the Encouragement of Artists.
Shevchenko quickly showed his talent. He won a silver medal for landscape painting. In 1840, he won another silver medal for his first oil painting, The Beggar Boy Giving Bread to a Dog.
Shevchenko started writing poetry while he was still a serf. In 1840, his first poetry book, Kobzar, was published. This book was very important for Ukrainian poetry. It brought a new style and feeling to Ukrainian writing.
In 1841, his long poem Haidamaky was released. He also wrote plays. In 1842, he released part of a tragedy called Mykyta Haidai. In 1843, he finished the play Nazar Stodolia.
Shevchenko visited Ukraine three times between 1843 and 1846. He was deeply affected by the difficult lives of Ukrainians. He visited his family, who were still serfs. He also met important Ukrainian writers and thinkers.
In 1844, Shevchenko wanted to show the beauty of Ukraine. He decided to create an album of etchings called Picturesque Ukraine. These etchings showed historical ruins and cultural sites. Only six etchings were printed because he did not have enough money to continue.
-
Gypsy Fortune Teller, 1841. Winner of the 1841 Silver Medal at the Imperial Academy of Arts
-
The Ascension Cathedral built in Pereiaslav in 1700 by Hetman Ivan Mazepa, 1845
-
Bohdan's church in Subotiv,
1845
Years in Exile
In 1845, Shevchenko became a non-classed artist. He went back to Ukraine. There, he met members of the Brotherhood of Saints Cyril and Methodius. This was a secret group that wanted to make the Russian Empire more free. They also wanted Slavic nations to be united.
Shevchenko was arrested on April 5, 1847, along with members of the group. The Tsar, Nicholas I, read Shevchenko's poem "Dream." The poem criticized the Tsar and his wife. The Tsar was very angry.
Shevchenko was accused of writing poems in Ukrainian that were "outrageous." He was also accused of promoting Ukrainian independence. The Tsar personally ordered his punishment. Shevchenko was exiled as a private soldier to a military base in Orsk, near the Ural Mountains. He was forbidden to write or paint.
In 1848, he joined a Russian naval trip to the Aral Sea. Even though he was a private, he was treated well. His job was to sketch the landscapes around the sea. He returned with many drawings and paintings. These artworks showed the nature of the Aral Sea and the people of Kazakhstan.
After this, he was sent to a harsh prison fortress called Novopetrovsk. He spent seven difficult years there. In 1851, he joined a geological trip. Finally, in 1857, Shevchenko was freed from exile. A new emperor gave him amnesty. But he was not allowed to return to Saint Petersburg. He had to stay in Nizhny Novgorod.
In May 1859, Shevchenko got permission to go back to Ukraine. He wanted to buy land near a village. But in July, he was arrested again. He was then released and told to return to Saint Petersburg.
Final Years and Legacy
Taras Shevchenko spent his last years creating new poems, paintings, and engravings. He also worked on his older pieces. But his hard life in exile had made him very sick. Shevchenko died in Saint Petersburg on March 10, 1861.
He was first buried in Saint Petersburg. But Shevchenko had wished to be buried in Ukraine. His friends arranged for his body to be moved. He was re-buried on May 8 on Chernecha hora (Monk's Hill). This hill is near the Dnipro River and Kaniv. A large mound was built over his grave. Today, it is a special memorial site.
Shevchenko died just seven days before serfs were freed in 1861. His life and works are deeply respected by Ukrainians everywhere. He had a huge impact on Ukrainian culture and literature.
Poetic Works
Taras Shevchenko wrote 237 poems. Only 28 of them were published in the Russian Empire during his lifetime. Another 6 were published in the Austrian Empire.
Example of Poetry: "Testament" (Zapovit)
Shevchenko's poem "Testament" (Zapovit), written in 1845, is very famous. It has been translated into over 150 languages. It was also set to music in the 1870s.
|
Taras Shevchenko, |
Translated by Vera Rich, |
Translated by John Weir, |
Artwork and Artistic Style
About 835 of Shevchenko's artworks still exist today. Some are original paintings, and some are prints. There are also copies made by other artists. We know of over 270 more works that are now lost.
His art was created between 1830 and 1861. It shows places in Ukraine, Russia, and Kazakhstan. He painted portraits, scenes from myths and history, and everyday life. He also drew buildings and landscapes.
Shevchenko used many different art methods. These included oil painting on canvas, watercolor, sepia, inking, and pencil. He also used etching on paper. Many of his works are finished paintings. But his sketches and studies are also important. They help us understand how he worked.
Shevchenko's Family Life
Taras Shevchenko never got married. He had six brothers and sisters. He also had at least three step-siblings.
Shevchenko's Lasting Legacy


Impact on Ukrainian Culture
Taras Shevchenko's writings are the base of modern Ukrainian literature. He is also seen as the founder of the modern written Ukrainian language. His poetry helped Ukrainians feel a stronger sense of national identity. His influence on Ukrainian thought and literature is still very strong today.
Shevchenko was inspired by Romanticism. He found his own way to write poetry. His poems explored themes important to Ukraine. They also showed his personal ideas about Ukraine's past and future.
His artistic work is also very important. Many of his paintings, drawings, and etchings show his unique talent. He also experimented with photography. Shevchenko helped develop the art of etching in the Russian Empire. In 1860, he was given the title of Academician for his etching work.
Shevchenko's influence on Ukrainian culture is huge. Even during Soviet times, his anti-Tsarist ideas were highlighted. But his strong Ukrainian nationalism was often downplayed. In modern Ukraine, he is seen as a national hero. His importance to the Ukrainian nation is unmatched.
His poems have inspired people during important times. For example, his poem "Testament" resonated with protestors during the Euromaidan. It also connected with Ukraine's struggle during the invasion from Russia in 2022.
Monuments and Memorials
There are many monuments to Shevchenko in Ukraine. The most famous ones are at his memorial in Kaniv and in the center of Kyiv. The Kyiv Metro station, Tarasa Shevchenka, is named after him. Other notable monuments are in Kharkiv, Lviv, and Luhansk.
The first statues of Shevchenko were built in the Soviet Union. The first one was in Romny in 1918. Others were in Moscow and Petrograd. The early statues did not last because they were made of weak materials. The Romny statue was later remade in bronze. The original Romny statue is now in Kyiv.
Ukrainian composers have set Shevchenko's poems to music. Tamara Maliukova Sidorenko and Antin Rudnytsky are two examples. Artist Hanna Veres made textiles dedicated to him.
After Ukraine became independent in 1991, many cities replaced statues of Lenin with statues of Taras Shevchenko. Streets and squares were also renamed after him. There is a high school named after him in Romania.
Even after the 2022 invasion, a monument to Taras Shevchenko still stands in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It was rebuilt in 2000.
Outside of Ukraine, monuments to Shevchenko are in many countries. These were often put up by local Ukrainian communities. There are memorials in Canada and the United States. A famous one is in Washington, D.C., near Dupont Circle. It was designed by Ukrainian Canadian artists. There are also monuments in Brazil, Croatia, Paris, Yerevan, and Copenhagen.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tarás Shevchenko para niños
In Spanish: Tarás Shevchenko para niños
- Legacy of Taras Shevchenko
- List of things named after Taras Shevchenko
- Taras Shevchenko Place, a street in New York City
- Izbornyk, contains collection of his works (free access)
- Shevchenko National Prize, Ukrainian State literary and artistic award
- Shevchenko Park (disambiguation)