Poison facts for kids
Poisons are substances that can cause death or injury if a living thing takes them in. This can happen by drinking or eating them, or by absorbing them through the skin. Poisons usually cause harm through a chemical reaction in the body. How much harm a poison does depends on how much of it is taken in. Substances that are poisonous are called toxic. If a poison causes death, it is called a lethal poison.
In medicine and zoology, there are special words for different types of harmful substances. Toxins are poisons made by living things, like bacteria. Venoms are special poisons that some animals use to hurt other species. Animals like snakes or spiders use venom for hunting or to defend themselves. If an animal or plant is poisonous, it means it's harmful to eat, like many types of mushrooms. If an animal is venomous, it means it can harm you with a bite or a sting, like a bee or a snake. For very dangerous bites, scientists have made special medicines called antivenoms.
Sometimes, a substance can be helpful in small amounts but harmful in large amounts. For example, drinking too much alcoholic drinks can make a person very sick and affect how they think and act. But alcohol can also be used as a disinfectant to clean things and kill germs.
Some poisons have an antidote. An antidote is a substance that can slow down or stop the effects of a poison. Sometimes, the antidote itself can be a poison if too much is used. For example, Atropine is a medicine that can be used as an antidote for certain nerve gases or insecticides. However, if you take too much Atropine, it can also be harmful. Even so, Atropine is on the World Health Organization's list of very important medicines.
There are other kinds of dangerous materials:
- Carcinogens: These are substances that can cause cancer, like asbestos.
- Mutagens: These can cause changes in your body's cells, like some types of radiation.
- Teratogens: These can cause birth defects, like certain medicines or too much alcohol during pregnancy.
Pollution can also be poisonous. For example, if a lot of food waste or milk gets into a river, tiny living things called microbes will eat it. These microbes use up all the oxygen in the water, which can kill fish and other living things in the waterway.
Poison Gas
In wars, some countries have used poison gases against their enemies. This is known as chemical warfare.
Poison gases like chlorine gas and mustard gas were used in World War I. Later, during World War II, the Nazis used a type of hydrogen cyanide gas to kill many people in special camps.
Poison gas has also been used to kill people as a form of punishment.
Sometimes, people are accidentally poisoned by gas. For example, a broken furnace or heating system can release carbon monoxide, which is a dangerous gas that you cannot see or smell.
There are different kinds of poison gases:
- Corrosive gases can cause serious burns to the skin, eyes, and lungs.
- Nerve agents are poisons that can kill by harming the central nervous system (your brain and nerves).
- Blister agents cause painful blisters on the skin and inside the body.
- Choking agents make fluid build up in a person's lungs, making it hard to breathe, almost like they are drowning.
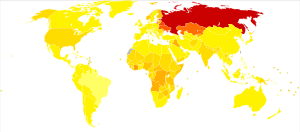
Poisoning Deaths
In 2010, about 180,000 people died from poisoning around the world. This number was a bit lower than in 1990, when about 200,000 people died. In the United States, about 727,500 visits to the emergency room were because of poisoning.
Related Pages
- Exposure to toxins (how toxins affect the body)
- Toxicity (how harmful a substance is)
- Chemical weapons
- NFPA 704 "fire diamond" (a system that shows how dangerous a chemical is)
Images for kids
-
Poisoning of Queen Bona by Jan Matejko.
See also
 In Spanish: Veneno para niños
In Spanish: Veneno para niños
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |