Colony of Virginia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Colony of Virginia
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1606–1776 | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
Motto:
|
|||||||||
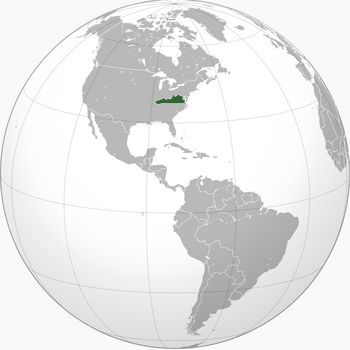
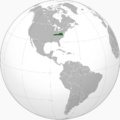
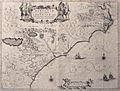
The Colony of Virginia with current country borders
|
|||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Status | Proprietary colony (1606–1624) Crown colony (1624–1776) |
||||||||
| Capital |
|
||||||||
| Common languages | English Siouan Iroquoian Algonquian |
||||||||
| Religion | Church of England (Anglicanism) | ||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
|
• Monarch
|
(First) James VI & I (Last) George III |
||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||
|
• 1584
|
Edward Wingfield (First) | ||||||||
|
• 1776
|
Lord Dunmore (Last) | ||||||||
| Legislature | General Assembly | ||||||||
|
• Upper House
|
Governor's Council (1607–1776) |
||||||||
|
• Lower House
|
House of Burgesses (1619–1776) |
||||||||
| Historical era | European colonization of the Americas | ||||||||
|
• Roanoke, Virginia: Origins Founding
|
April 10, 1606 | ||||||||
|
• Became royal colony
|
May 24, 1624 | ||||||||
| July 4, 1776 | |||||||||
| Currency | Virginia pound (1624–1793) | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
The Colony of Virginia was a British settlement in North America. It existed from 1606 until 1776. It was one of the first successful English colonies.
Before Virginia, England tried to settle Newfoundland in 1583. Another attempt was the Roanoke Colony in the late 1580s. Both failed. The Roanoke Colony mysteriously disappeared.
In 1606, King James I gave a charter to the Virginia Company. This company founded Jamestown in 1607. Jamestown was the first lasting English colony in North America. It faced many challenges like famine, disease, and conflicts with local Native American tribes.
Tobacco became Virginia's main export. Growing tobacco greatly changed the colony's society and how settlements were built. In 1624, King James I took control from the Virginia Company. Virginia then became a royal colony, directly ruled by the King.
After the English Civil War (1640s-1650s), King Charles II called Virginia "The Old Dominion." This was because of its loyalty to the English monarchy. From 1619 to 1776, the colony had a government called the General Assembly. It worked with a colonial governor. Jamestown was the capital until 1699. Then, Williamsburg became the capital.
Virginia declared independence from Great Britain in 1775. It became the Commonwealth of Virginia. This was one of the original thirteen states of the United States.
Contents
- What's in a Name?
- Early History
- Relations with Native Americans
- Geography and Settlements
- Economy
- Culture
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name?
The Name Virginia
"Virginia" is the oldest name for English claims in North America. In 1584, Sir Walter Raleigh explored the North Carolina coast. He heard about a leader named Wingina and a land called Wingandacoa.
Raleigh likely suggested the name "Virginia" around 1584. He named it after Queen Elizabeth I, who was known as the "Virgin Queen." The word Wingandacoa might have also influenced the name. Raleigh later learned that wingandacoa actually meant "What good clothes you wear!" in the local Native American language. It was not the name of the country.
The colony was also known as the Virginia Colony or the Province of Virginia.
"Old Dominion"
King Charles II gave Virginia the nickname "Old Dominion." This was to thank Virginians for staying loyal to the king during the English Civil War. The colony's seal had a Latin phrase, en dat virginia quintum. This means "Behold, Virginia gives the fifth." Virginia was seen as the fifth English land, after England, France, Scotland, and Ireland.
Today, the Commonwealth of Virginia still uses "Old Dominion" as its state nickname. The sports teams at the University of Virginia are called the "Cavaliers." This name refers to supporters of King Charles II. There is also a public university called "Old Dominion University" in Virginia.
Early History
Many European countries claimed parts of North America. Spain, France, Sweden, and the Netherlands all had claims. But England was the first to successfully settle the Mid-Atlantic coast. Spain and France had tried to build settlements in what is now Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia.
First Attempts to Settle (1583–1590)
In 1583, Sir Humphrey Gilbert tried to start a colony in Newfoundland. But he and his crew left and he died on the way back to England.
In 1585, Sir Walter Raleigh sent over 100 men to Roanoke Island (in modern North Carolina). They ran out of supplies and went back to England. Fifteen soldiers stayed behind, but they were never seen again.
In 1587, Raleigh sent another group to Roanoke. Their leader, John White, went back to England for supplies. But he could not return for three years because of a war. When he finally came back in 1590, the colony was gone. The houses were still there, but the settlers had disappeared. This is why it's called the ""Lost Colony"." The word Croatoan was carved into a tree. This was the name of a tribe on a nearby island. The first English child born in North America, Virginia Dare, was part of this lost group.
The Virginia Company (1606–1624)
After the Roanoke failures, England tried again. This time, they used "joint-stock companies." These companies were groups of investors who put money together to fund colonies.
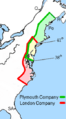
The 1606 Charter
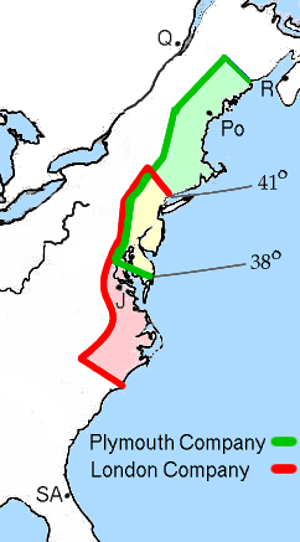
King James I gave a special paper, called a charter, to two parts of the Virginia Company: the Plymouth Company and the London Company. Each company could start colonies in different areas. The London Company could settle between what is now Cape Fear and Long Island Sound. The Plymouth Company could settle further north.
In 1607, the London Company founded Jamestown. The Plymouth Company started the Popham Colony in what is now Maine. The Popham Colony quickly failed due to hunger, sickness, and fights with Native Americans.
Jamestown's Beginnings
On December 20, 1606, Captain Christopher Newport led the London Company's ships from England. There were 105 men and boys on three ships: the Susan Constant, the Godspeed, and the Discovery. After a long trip, they landed at the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay. They named the spot Cape Henry.
They were told to find a place inland along a river. This would protect them from Spanish ships. They sailed up the largest river, which they named the James, after their king. They chose Jamestown Island because it was easy to defend and had deep water for ships. Within two weeks, they built their first fort and named the settlement Jamestown.
The colonists hoped to find gold and other valuable things. They also needed supplies from England and trade with the Native Americans. But their chosen spot had little game, no fresh water, and poor farming land. Many colonists died from disease and conflicts with Native Americans. It was hard to make money, and the colony almost failed.
The Powhatan Confederacy was a group of Native American tribes in eastern Virginia. Their leader was Wahunsenacawh, known to the English as Chief Powhatan. Jamestown was built on their land.
The "Starving Time"
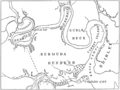
In 1609, a hurricane hit a supply fleet heading to Jamestown. The flagship, the Sea Venture, wrecked on the reefs of Bermuda. The survivors were stranded there. They eventually built two smaller ships and continued to Jamestown.
When they arrived, they found terrible conditions. Other supply ships had arrived, but with few supplies. A drought and fights with Native Americans made things worse. This period, from late 1609 to May 1610, was called the "Starving Time." Over 80% of the colonists died. Conditions were so bad that some colonists resorted to eating anything they could find to survive. The survivors decided to leave Jamestown and return to England.
Jamestown Saved
Just as the colonists were leaving Jamestown, new supply ships arrived. They were led by Thomas West, 3rd Baron De La Warr, also known as "Lord Delaware." He brought food, supplies, a doctor, and more colonists. Lord Delaware stopped the departing ships and insisted the colony would survive. The colonists were very thankful.
Lord Delaware was much tougher on the Native Americans. He attacked their villages and destroyed their crops. This started the first Anglo-Powhatan War.
Tobacco Brings Success
John Rolfe, a survivor from the Sea Venture, had brought new, sweeter tobacco seeds from Bermuda. By 1612, Rolfe successfully grew and exported this tobacco. It became Virginia's first profitable crop. Plantations and new settlements grew along the rivers. Jamestown finally became a permanent settlement. A period of peace followed in 1614 when John Rolfe married Pocahontas, Chief Powhatan's daughter.
Conflicts with Native Americans
Relations with Native Americans worsened after Pocahontas died in England in 1617. Diseases, bad harvests, and the growing demand for land for tobacco led to more fighting. After Chief Powhatan died in 1618, his brother, Opechancanough, became the new leader.
On March 22, 1622, Opechancanough led a surprise attack on English settlements along the James River. This attack killed 347 colonists. Many communities were destroyed. Jamestown was saved because a Native American boy named Chanco warned colonist Richard Pace. Pace then warned Jamestown.
For over ten years, the English settlers attacked the Powhatan. They burned villages, captured children, and destroyed crops. By 1634, a six-mile-long palisade (a wall of tall wooden stakes) was built across the Virginia Peninsula. This wall protected the colonists from attacks.
On April 18, 1644, Opechancanough led another attack, killing almost 500 colonists. But this was a smaller percentage of the growing population than in 1622.
Virginia Becomes a Royal Colony (1624–1652)
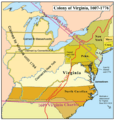
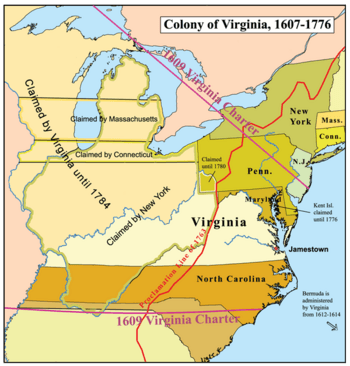
In 1624, King James I took away the Virginia Company's charter. The Virginia Colony became a crown colony, directly controlled by the King. Later, new colonies like Maryland (1632) and Carolina (1663) were created from Virginia's original claims. This made Virginia's borders much smaller.
Third Anglo-Powhatan War (1644–1646)
Another war with the Powhatan Confederacy began in 1644. It was their last attempt to drive out the English settlers. About 500 colonists died. Governor William Berkeley's forces attacked Opechancanough's stronghold in 1645. Opechancanough, who was very old, was captured and later killed while a prisoner. His death caused the Powhatan Confederacy to break apart.
The 1646 Treaty
In October 1646, a peace treaty was signed. The Native American tribes became subjects of the King of England. A clear border was drawn between Native American and English settlements. People from one side could not cross to the other without a special pass. This treaty gave the English large areas of land that were not yet settled.
English Civil War and Commonwealth (1642–1660)
During the English Civil War, some colonies, like Massachusetts, supported Parliament. But older colonies like Virginia and Bermuda stayed loyal to the King. In 1650, the English Parliament passed a law against these loyal colonies. It said that anyone trading with them was a "rebel" and a "traitor."
Virginia's population grew a lot during and after the war. Many "Cavaliers" (supporters of the King) came to Virginia. Governor William Berkeley saw the population grow from 8,000 in 1642 to 40,000 in 1677. Even though Virginia was loyal, a Puritan named Richard Bennett became governor in 1652, answering to Oliver Cromwell. When King Charles II returned to power in 1660, he rewarded Virginia for its loyalty by calling it the Old Dominion.
In 1676, Bacon's Rebellion challenged the colony's government. It was a military failure, but it led to Governor Berkeley being called back to England. In 1679, the Treaty of Middle Plantation was signed between King Charles II and several Native American groups.
Williamsburg Era
Virginia was the largest, richest, and most important of the American colonies. Wealthy landowners controlled the government and local affairs. They believed in a strict social order, with God at the top, then kings, and then wealthy landowners. This system was supported by laws that made sure the oldest son inherited all the land. This helped large plantations grow in size and power.
During the American Revolution, these laws were removed. Many loyalists (people loyal to Britain) left Virginia.
Relations with Native Americans
As English settlements grew, they took more and more Native American land. This led to many conflicts. For most of the 1600s, the English mainly fought with the Algonquian peoples of the coastal areas, especially the Powhatan Confederacy. After several wars, the Powhatan became less powerful.
In the late 1600s and 1700s, colonists moved westward. They met new groups like the Shawnee, Iroquoian-speaking peoples (like the Nottoway and Cherokee), and Siouan-speaking peoples (like the Tutelo and Saponi).
Iroquois Confederacy
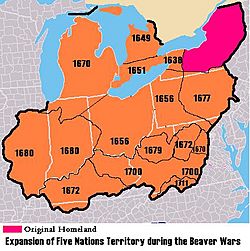
The Iroquois Confederacy expanded into western Virginia in the late 1600s. They arrived before the English settlers and pushed out the local Siouan tribes.
In 1714, Lieutenant Governor Alexander Spotswood built Fort Christanna. This fort helped educate and trade with friendly Native American tribes. It also protected them from hostile tribes. In 1722, the Treaty of Albany was signed. It involved the Iroquois, New York, Virginia, and Pennsylvania.
Geography and Settlements
The Virginia Colony grew over time. Its settlements changed from forts to plantations, farms, and small towns.
Early Settlements
The fort at Jamestown was the main settlement for many years. Other small forts were built for protection. Early attempts to settle areas like what is now Richmond failed because of Native American resistance.
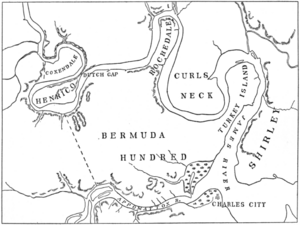
In 1611, Thomas Dale started building Henricus upriver from Jamestown. It was meant to be a new capital and have the first college in Virginia. But Henricus was destroyed in the 1622 Native American attack. Dale also founded the port town of Bermuda Hundred.
"Hundreds"
Once tobacco became a profitable crop, investors created large, self-sufficient areas called "hundreds." A "hundred" was a traditional English name for a land division. In Virginia, these "hundreds" were large farms needed to grow tobacco. They were often small towns or villages, sometimes protected by walls.
An example was Martin's Hundred, sponsored by investors in London. It was settled in 1618. Other "hundreds" included Bermuda Hundred and Flowerdew Hundred. By 1617, the colony was exporting 50,000 pounds of tobacco each year. This profit helped ensure the colony's economic survival.
Cities and Counties
In 1619, the settlements were divided into four "cities": Charles Cittie, Elizabeth Cittie, Henrico Cittie, and James Cittie (which included Jamestown). Each "city" stretched across the James River.
In 1634, the King ordered a local government system. Eight "shires" were created, which soon became "counties." This system is still used today.
In 1699, a new capital was built at Middle Plantation. It was soon renamed Williamsburg.
Northern Neck Proprietary
After the English Civil War, King Charles II gave a large area of land in Virginia to some of his supporters. This area was called the Northern Neck Proprietary. It was between the Rappahannock and Potomac Rivers. This land was part of Virginia, but the owners controlled how land was given out and collected money from it. This lasted until after the American Revolution.
Economy
The Virginia Company tried different ways to make the colony profitable. They looked for gold, but found none. They sent back things like wood and pitch. In 1608, they tried to make glass. In 1619, they built the first ironworks in North America.
In 1612, John Rolfe started growing tobacco from Bermuda. This crop quickly became very valuable in Europe. Growing tobacco became the main economic activity, especially in the Tidewater region. From 1616 to 1619, tobacco and sassafras were the only exports.
Colonists built large farms called plantations along the rivers to grow tobacco. This led to the use of enslaved Africans for labor. Workers would fill large barrels, called hogsheads, with tobacco. These barrels were then taken to special warehouses for inspection. In 1730, the Tobacco Inspection Act was passed. It made sure that tobacco sent out of Virginia was of good quality.
Culture
Population Growth
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1620 | 2,200 | — |
| 1630 | 2,500 | +13.6% |
| 1640 | 10,442 | +317.7% |
| 1650 | 18,731 | +79.4% |
| 1660 | 27,020 | +44.3% |
| 1670 | 35,309 | +30.7% |
| 1680 | 43,596 | +23.5% |
| 1690 | 53,046 | +21.7% |
| 1700 | 58,560 | +10.4% |
| 1710 | 78,281 | +33.7% |
| 1720 | 87,757 | +12.1% |
| 1730 | 114,000 | +29.9% |
| 1740 | 180,440 | +58.3% |
| 1750 | 231,033 | +28.0% |
| 1760 | 339,726 | +47.0% |
| 1770 | 447,016 | +31.6% |
| 1780 | 538,004 | +20.4% |
| Source: 1620–1760; 1770–1780 | ||
People from Different Places
Most colonists came from England. Later, many Scots-Irish people settled in the western parts of Virginia. There were also smaller groups from other places, like Germans. In 1608, the first Poles and Slovaks arrived as skilled workers. In 1619, the first Africans arrived. Many more Africans were brought to the colony as enslaved people. French Huguenots (Protestants) also came to Virginia to escape religious wars.
In the early 1700s, German-speaking colonists from Nassau-Siegen came to start the Germanna settlement. Some Welsh people also arrived.
Servitude and Slavery
Growing tobacco required a lot of workers. One way to get workers was through indentured servants. These were people who agreed to work for a set number of years in exchange for passage to America.
By the 1640s, laws began to change the status of servants. In 1640, John Punch was sentenced to serve for life as punishment for trying to escape. This was one of the first times slavery was legally recognized in Virginia. After this, lifelong servitude became more appealing to plantation owners.
Many indentured workers, especially Africans, could not read or write. This made it easy for owners to abuse them. Some owners tried to keep servants for life, even after their contracts ended. One example is Anthony Johnson, who successfully argued in court to keep John Casor as a lifelong servant. These cases showed how Black Africans were becoming enslaved people.
In the late 1600s, the Royal African Company had a monopoly on bringing enslaved Africans to the colonies. Many enslaved people were first sent to Barbados, then to Virginia and Carolina.
Religion
In 1619, the Anglican Church became the official religion of the colony. It stayed that way until after the American Revolution. Being the official religion meant that local taxes paid for church costs. The church also handled local duties like helping the poor. Wealthy planters controlled the church and chose the minister.
The Bishop of London oversaw the church in Virginia. He sent priests, but there were never enough. By the 1760s, other Protestant groups, like Baptists and Methodists, grew in number. They began to challenge the Anglicans.
In 1650, all 26 churches in Virginia were Anglican. After the First Great Awakening (1730–1755), the number of churches in Virginia grew a lot. By 1776, there were 377 places of worship, including many Baptist and Presbyterian churches.
Education
The first printing press in Virginia started in Jamestown in 1680. But it was soon shut down by the Governor. The first newspaper, the Virginia Gazette, began in Williamsburg in 1736.
The Syms-Eaton Academy, started in 1634, was America's first free public school. Wealthy families often hired private teachers. For most of the 1600s, young men had to go to England or Scotland for a university education.
In 1693, the College of William & Mary was founded in Middle Plantation (later Williamsburg). It had a school for Virginia Indians, which also taught local students. The college was very important for learning in the colony.
After 1747, some Virginians went to colleges like Princeton and the University of Pennsylvania. As people moved west, new schools were founded. These included what would become Hampden–Sydney College (1775) and Washington and Lee University.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Colonia de Virginia para niños
In Spanish: Colonia de Virginia para niños
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |