Anglo-Saxons facts for kids
| Englisċ | |
|---|---|

A page from the Lindisfarne Gospels (around 700 AD), showing a special monogram for Christ's name.
|
|
| Languages | |
| Old English | |
| Religion | |
| Anglo-Saxon paganism, later Christianity | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Angles, Saxons, Jutes, English people |
The Anglo-Saxons were a group of people who lived in Britain from about 450 AD to 1066 AD. They spoke a language called Old English, which is the ancestor of the modern English language we speak today. Their time in Britain is known as the Anglo-Saxon period.
They came to Britain from different parts of northern Europe. The main groups were the Angles, the Saxons, and the Jutes. Over time, these groups mixed with the local Romano-British people and formed a new culture. By the end of their era, most people in England thought of themselves as "English."
The Anglo-Saxon period ended in 1066 with the Norman Conquest, when William the Conqueror invaded England. Even though their rule ended, the Anglo-Saxon language, laws, and culture became the foundation for the modern country of England. Many of the most common words we use every day come from their Old English language.
Contents
The Story of the Anglo-Saxons
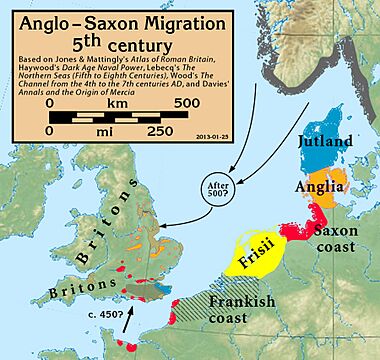
How the Anglo-Saxons Came to Britain
After the Roman Empire left Britain around 410 AD, the island was left without a strong army. The native people, known as the Romano-Britons, were attacked by tribes from the north, like the Picts. According to the writer Bede, a British leader named Vortigern invited some Anglo-Saxons to come to Britain as mercenaries, or paid soldiers, to help fight off these attacks.
These newcomers came from areas that are now part of Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark. The Angles, Saxons, and Jutes arrived in large numbers. Instead of just helping, they decided to stay and take land for themselves. This led to fighting between the settlers and the Britons. Over many years, the Anglo-Saxons took control of most of the land that we now call England.
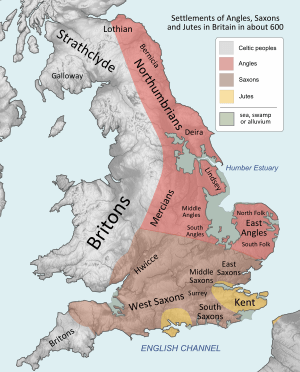
The Seven Kingdoms
For a long time, Anglo-Saxon England was not one single country. It was divided into several smaller kingdoms that often fought with each other. The most powerful of these are sometimes called the Heptarchy, which means "seven kingdoms."
The main kingdoms were:
- Wessex (the West Saxons)
- Sussex (the South Saxons)
- Essex (the East Saxons)
- Kent (settled by the Jutes)
- East Anglia (the East Angles)
- Mercia
- Northumbria (made of two smaller kingdoms, Bernicia and Deira)
Over time, some kingdoms became more powerful than others. For a while, Mercia was the strongest kingdom. Later, Wessex became the most powerful, and its kings would eventually unite all of England.
The Coming of Christianity
The early Anglo-Saxons were pagans. They worshipped many gods and goddesses, like Woden (the king of the gods) and Thunor (the god of thunder).
In 597 AD, the Pope sent a monk named Augustine to Britain to convert the Anglo-Saxons to Christianity. He went to the Kingdom of Kent and converted its king, Æthelberht. From there, Christianity slowly spread throughout the other kingdoms. Monasteries were built, which became important centers for learning and writing. Monks like Bede wrote books that tell us much of what we know about this time.
The Viking Age
Starting in the late 8th century, England faced a new threat: the Vikings. These raiders came from Scandinavia (modern-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden). They sailed across the sea in their famous longships to attack towns and monasteries.
In 865 AD, a huge Viking force called the "Great Heathen Army" arrived. They were not just raiding anymore; they wanted to conquer and settle. They took over Northumbria, East Anglia, and Mercia. This area of England, ruled by the Vikings, became known as the Danelaw.
Alfred the Great and the Unification of England

The only kingdom left to stand against the Vikings was Wessex, led by Alfred the Great. Alfred was a clever and brave king. After many battles, he defeated the Vikings at the Battle of Edington in 878 AD. He made a treaty with them that divided England between Wessex and the Danelaw.
Alfred was more than just a warrior. He built forts, created a navy, and reorganized his army. He also believed education was very important. He encouraged learning and had important books translated from Latin into Old English so more people could read them.
After Alfred, his son Edward the Elder and grandson Æthelstan continued to fight the Vikings. They gradually reconquered the Danelaw. In 937 AD, Æthelstan won a great victory at the Battle of Brunanburh. He became the first king to rule over all of England.
The End of the Anglo-Saxon Era
The unified Kingdom of England faced more trouble in the late 10th and early 11th centuries. New Viking attacks led to the Danish king Cnut the Great becoming king of England in 1016.
The Anglo-Saxon line of kings was restored with Edward the Confessor in 1042. But when Edward died in 1066 without a child, it caused a crisis. Three different men claimed the throne. One of them, William, Duke of Normandy, invaded England.
On October 14, 1066, William's Norman army fought the English army, led by the Anglo-Saxon king Harold Godwinson, at the Battle of Hastings. Harold was killed, and the English were defeated. William the Conqueror became the new king, which marked the end of the Anglo-Saxon period.
Life and Society
Kings, Thanes, and Ceorls

Anglo-Saxon society was organized in a hierarchy.
- At the top was the king. He was the main war leader and lawmaker. He was advised by a council of wise men called the Witan.
- Below the king were the thanes (or thegns). They were the noble warrior class who owned land and fought for the king.
- Most people were ceorls (churls). They were free farmers who owned or rented small amounts of land.
- At the very bottom were slaves, who had no freedom and were owned by others.
Loyalty was extremely important. A warrior was expected to be loyal to his lord, even to death. In return, a good lord gave his followers gifts, weapons, and protection.
Homes and Villages

Most Anglo-Saxons lived in small villages. They built simple houses made of wood with thatched roofs. The main building in a village was often a large hall where the local lord and his warriors lived, ate, and held feasts. These halls had a fire in the center for warmth and cooking, with a hole in the roof to let the smoke out.
People worked as farmers, growing crops like wheat and barley, and raising animals like cattle, sheep, and pigs. They also had skilled craftspeople, such as blacksmiths who made tools and weapons, and jewelers who made beautiful objects.
Women in Anglo-Saxon Society
Compared to later times, Anglo-Saxon women had a surprising amount of freedom. They could own property and land in their own right. A woman could not be forced to marry someone against her will. If a woman's husband died, she could inherit his property and had authority over her children. Some powerful women even ruled as abbesses over large monasteries.
Anglo-Saxon Culture
Art and Treasure

The Anglo-Saxons were master artists and craftspeople. They are famous for their amazing metalwork, decorated with complex patterns and animal designs.
Some of the most famous examples of their art include:
- The Sutton Hoo treasure: Discovered in a ship that was buried under a mound, this treasure included a spectacular helmet, a sword, a shield, and beautiful gold jewelry. It likely belonged to a great king.
- The Staffordshire Hoard: The largest collection of Anglo-Saxon gold and silver ever found. It contains hundreds of beautifully crafted pieces from weapons.
- Illuminated Manuscripts: Monks created stunningly beautiful books by hand. The most famous is the Lindisfarne Gospels, which is filled with colorful, detailed patterns and drawings.
-
The Ruthwell Cross, a tall stone cross with carvings, c. 750
-
A silver ring with Trewhiddle style animal patterns, c. 775 – c. 850
Architecture

Most Anglo-Saxon buildings were made of wood and have not survived. However, some of their stone churches can still be seen today.
Early churches were simple, but later ones became more complex. A special feature of Anglo-Saxon church architecture is the use of tall, narrow stone strips on the outside walls for decoration. They also built towers with unique features, like the "Rhenish helm" roof at Sompting Church.
-
St Peter-on-the-Wall, Essex: A very early and simple church from about c. 650
-
Brixworth, one of the largest surviving Anglo-Saxon churches
-
The tower of Barnack, built around c. 970
-
Sompting Church, which has the only surviving Anglo-Saxon tower of its kind
Language and Literature

The Anglo-Saxons spoke Old English. It sounds very different from modern English, but it is the foundation of our language. Many basic words like "water," "earth," "house," and "food" come from Old English.
They had a rich tradition of storytelling and poetry. Their poems did not use rhyme. Instead, they used alliteration, which is the repetition of sounds at the beginning of words.
The most famous work of Anglo-Saxon literature is the epic poem Beowulf. It tells the story of a great hero named Beowulf who fights monsters, including the fearsome Grendel and a fire-breathing dragon. Other important works include poems like The Wanderer and The Seafarer, which are about loneliness and hardship.
Images for kids
-
A scene from the Bayeux Tapestry showing the Battle of Hastings (1066).
-
Part of the 7th-century Franks Casket, showing a scene from an old Germanic legend.
-
A replica of the famous Sutton Hoo helmet.
-
Distinctive Anglo-Saxon stone strips on the tower of All Saints' Church, Earls Barton.
-
From the Book of Cerne, a portrait of Saint Mark.
See also
 In Spanish: Anglosajones para niños
In Spanish: Anglosajones para niños
- Anglo-Frisian languages
- Burial in Anglo-Saxon England
- Frisia
- Fyrd - Anglo-Saxon military organization
- States in Medieval Britain
- Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain