Ansonia, Connecticut facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ansonia, Connecticut
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Upper Main Street Historic District
|
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
Copper City
|
|||
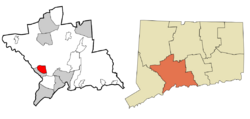 New Haven County and Connecticut New Haven County and Connecticut |
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| U.S. state | Connecticut | ||
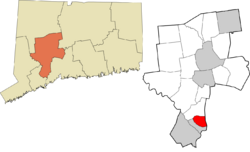
| County | New Haven | ||
| Region | Naugatuck Valley | ||
| Incorporated (town) | 1889 | ||
| Incorporated (city) | 1893 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Mayor-Board of Aldermen | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 6.19 sq mi (16.02 km2) | ||
| • Land | 6.02 sq mi (15.59 km2) | ||
| • Water | 0.17 sq mi (0.44 km2) | ||
| Elevation | 82 ft (25 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 18,918 | ||
| • Density | 3,142.5/sq mi (1,213.5/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (Eastern) | ||
| ZIP Code |
06401
|
||
| Area code(s) | 203/475 | ||
| FIPS code | 09-01150 | ||
| GNIS ID | 205107 | ||
| Major highways | |||
| Commuter Rail | |||
Ansonia is a city in New Haven County, Connecticut, United States. It sits right on the Naugatuck River. The city is just north of Derby and about 12 miles (19 km) northwest of New Haven.
Ansonia is part of the Naugatuck Valley Planning Region. In 2020, about 18,918 people lived here. The city's ZIP code is 06401.
You can get to Ansonia by train using the Metro-North Railroad. The Ansonia Station connects to New York City's Grand Central Terminal. Buses from Connecticut Transit also serve the city. Connecticut Route 8 is a major highway that runs through Ansonia.
Ansonia was started in 1844 by a kind businessman named Anson Green Phelps. It's often called "The Copper City" because it used to be a big center for making things from copper and brass. Many other factories also made rubber, plastics, iron, and textiles. The famous Ansonia Clock Company began here in 1851.
David Humphreys, a soldier and diplomat from the American Revolutionary War, was born in Ansonia.
Contents
History
The area where Ansonia is today was first settled in 1652. It was originally part of Derby. Early settlers farmed and used the Naugatuck River to power sawmills and gristmills.
In 1844, Anson Green Phelps wanted to expand the industrial area of Derby. He bought land along the east side of the river. This area is now downtown Ansonia. Phelps had a canal dug to use the river's power for new factories. He named this new industrial village "Ansonia" after his own first name.
Ansonia quickly grew with many factories. It became the busiest part of Derby. In 1864, Ansonia became its own borough within Derby. Then, in 1889, it officially separated from Derby and became a separate town. In 1893, Ansonia became a city.
By the late 1800s, Ansonia was known for making heavy machinery, electrical parts, and brass and copper products. Ansonia, along with nearby towns like Derby and Shelton, became a very important industrial area in Connecticut.
America's First Bicycle
In 1866, an inventor named Pierre Lallement lived in Ansonia. He created and patented the very first bicycle with pedals and a rotary crank.
Ansonia in the 20th Century
Ansonia faced a big challenge in 1955. The Naugatuck River flooded badly due to a hurricane. Many homes and businesses were destroyed. The Maple Street Bridge, which connected the two sides of Ansonia, was washed away.
After the flood, a flood wall was built along the river to protect factories and Main Street. New housing was also built where homes and businesses had been destroyed.
Over the years, shopping moved away from Ansonia's Main Street to larger malls. However, in recent times, Main Street has become lively again. New shops, like antique stores and coffee shops, have opened.
For many years, Ansonia had its own daily newspaper called the "Evening Sentinel." It was very popular. But in the 1980s, it was closed down. Now, there is an online news site called The Valley Independent Sentinel. It started in 2009.
Famous people have visited Ansonia. In 1960, John F. Kennedy stopped in front of City Hall during his presidential campaign. He drew a huge crowd. Later, in 1992, President George H. W. Bush also visited Ansonia.
In 2000, the Lower Naugatuck Valley, including Ansonia, was named an "All America City." This award recognizes cities that work together to solve problems.
Rubber Plant Fire
In May 2001, a large rubber factory called Latex Foam Company caught fire. The fire was huge and destroyed the entire building. Firefighters from many towns worked for five days to put it out. Smoke spread over the city, and the river's ecosystem was affected.
A new Target store was built on the empty lot where the factory once stood. It opened in 2007. The Latex Foam Company later moved to a new location in nearby Shelton.
Geography
Ansonia covers about 6.19 square miles (16.0 square kilometers). Most of this is land, with a small amount of water. The city is divided by the Naugatuck River. It spreads out from the river's banks up into the hills.
On the west side of the river, Ansonia borders Derby and Seymour. On the east side, the Hilltop neighborhood touches Woodbridge.
The land along the river used to have many factories. Some are still there, and some are no longer in use. Most of Ansonia is covered by homes. These are usually one or two-family houses. The Ansonia Nature Center on Hilltop has open fields and woodlands for everyone to enjoy.
An airport once existed on Hilltop. During the Cold War, missiles were kept there. Now, that land is used for residential housing and a horse farm.
Neighborhoods
- Downtown – This is the original industrial part of Ansonia. It stretches from the old factories to the newer shopping areas.
- Library District – This area is around the Ansonia Library. It has many historic Victorian homes.
- North End – This runs along North Main Street, from downtown to the Seymour town line.
- Reservoir – This area is near the Quillinan Reservoir.
- Derby Hill – This section includes Elm Street, which is a historic district. It was part of the first settlement of Derby.
- Hilltop – This area was mostly farmland. After World War II, it became the largest residential area in the city.
- West Ansonia – This is the residential area on the west side of the Naugatuck River.
- Windy Hill – A part of West Ansonia, from the Derby town line to Grove Street.
- Silver Hill – This section of West Ansonia is along Silver Hill Road. Some parts are shared with Derby.
Climate
Ansonia has warm, humid summers and cool to cold winters. It has a humid continental climate.
Demographics
Ansonia's population was 18,918 in 2020. The city is home to people from many different backgrounds.
Economy
Theodore H. White, a famous author, called the Naugatuck Valley "the seedbed of Yankee ingenuity." This means it was a place where people were very clever and invented many things.
The Farrel Corporation, which made machines for plastics and rubber, had its main office here. Ansonia Copper & Brass also made metal products in the city. The Ansonia Clock Company started making clocks here in 1851.
Over the past few decades, many of the big factories have closed. However, Ansonia's housing market has improved. This is because many companies have moved to nearby towns, creating more jobs.
Mayors
Ansonia has had many mayors since it became a city. The current mayor is David S. Cassetti.
Transportation
Ansonia has a train station for the Metro-North Railroad. You can take a train from Waterbury to Bridgeport. From Bridgeport, you can connect to the main line to Grand Central Terminal in New York City. The trip to New York City takes about two hours.
Bus
Buses from Connecticut Transit New Haven also serve Ansonia. They connect the city to New Haven.
Landmarks
Ansonia has many interesting landmarks. These include the old factory buildings along the Naugatuck River. The Ansonia Library is a public library. The Anna Sewell Memorial Fountain honors the author of "Black Beauty." There is also a YMCA and a National Guard Armory.
Many beautiful Victorian and Queen Anne style houses can be seen in Ansonia. The Ansonia Opera House was built in 1870 and is the oldest opera house in Connecticut.
Ansonia is known for its many churches. There are five Catholic churches, each with a history tied to different ethnic groups. There are also many other Christian churches and a Buddhist temple.
The current Ansonia High School was built in 1999. Before that, the old high school building, designed by a famous architect, became Ansonia Middle School.
Notable people
Many interesting people have come from Ansonia:
- Ralph Beardsley (1891–1920), a racing car driver.
- Tom Condon, a lawyer and former professional football player.
- John Cooke (1937–2005), who won a gold medal in rowing at the 1956 Summer Olympics.
- David Humphreys (1752–1818), a close helper to George Washington and a diplomat.
- Vincent R. Impellitteri (1900–1987), who was the Mayor of New York City.
- Pierre Lallement (1843–1891), the inventor of the first bicycle with pedals.
- Anson Greene Phelps (1781–1853), the founder of Ansonia.
- Nick Pietrosante (1937–1988), a professional football player.
- Bob Skoronski, a professional football player who won two Super Bowls with the Green Bay Packers.
On the National Register of Historic Places

Several places in Ansonia are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. This means they are important historical sites.
- Ansonia Library – 53 South Cliff St. (added 1985)
- Gen. David Humphreys House – 37 Elm St. (added 1972)
- Richard Mansfield House – 35 Jewett St. (added 1971)
- Upper Main Street Historic District (Ansonia, Connecticut) – 36–100, 85–117 Main St. (added 1982), which includes the Ansonia Opera House (built 1870)
- United States Post Office–Ansonia Main – 237 Main St. (added 1985)
Gallery
See also
 In Spanish: Ansonia (Connecticut) para niños
In Spanish: Ansonia (Connecticut) para niños