Antarctic Plate facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Antarctic Plate |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Type | Major |
| Approximate area | 60,900,000 km2 (23,500,000 sq mi) |
| Movement1 | South-west |
| Speed1 | 12–14 mm (0.47–0.55 in)/year |
| Features | Antarctica, Kerguelen Plateau, Southern Ocean |
| 1Relative to the African Plate | |
The Antarctic Plate is one of the Earth's largest tectonic plates. Think of it as a giant puzzle piece that makes up our planet's surface. This plate holds the entire continent of Antarctica. It also includes the Kerguelen Plateau and many islands in the Southern Ocean and other nearby oceans.
Millions of years ago, the Antarctic Plate was part of a huge supercontinent called Gondwana. This was the southern part of an even bigger landmass called Pangea. After Gondwana broke apart, the Antarctic Plate slowly moved Antarctica south. This long journey caused the continent to become very cold, just like it is today.
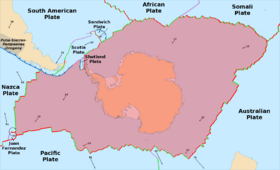
The edges of the Antarctic Plate mostly meet other plates at mid-ocean ridges. These are places where new Earth crust is created. The plates next to the Antarctic Plate are the Nazca Plate, the South American Plate, the African Plate, the Somali Plate, the Indo-Australian Plate, and the Pacific Plate. It also meets the Scotia Plate at a special type of boundary called a transform boundary.
The Antarctic Plate covers an area of about 60,900,000 km2 (23,500,000 sq mi). This makes it the fifth-largest tectonic plate on Earth. It moves slowly, about 1 cm (0.4 in) every year, heading towards the Atlantic Ocean.
Contents
Antarctic Plate Movement
How the Antarctic Plate Moves Under South America
About 14 million years ago, the Antarctic Plate began to slide underneath the continent of South America. This process is called subduction. It's like one giant puzzle piece slowly diving beneath another.
At first, this subduction happened only at the very southern tip of Patagonia. Patagonia is a region in South America. Over time, parts of the Nazca Plate and the Chile Rise were pulled under. This allowed more northern parts of the Antarctic Plate to start subducting under Patagonia.
Today, the place where these three plates meet, called the Chile Triple Junction, is near the Taitao Peninsula in Chile.
How Subduction Changed Patagonia
The subduction of the Antarctic Plate had a big effect on Patagonia. It caused the land there to lift up. This happened because the movement reduced the strong downward pull in the Earth's mantle that was caused by the Nazca Plate subducting.
This lifting created what scientists call dynamic topography. It raised old Quaternary-aged marine terraces and beaches. You can still see these lifted beaches along the Atlantic coast of Patagonia today.
Land on the Antarctic Plate
The Antarctic Plate includes many important land areas and islands.
- Amsterdam Island (France)
- Antarctica (Antarctic Treaty System)
- East Antarctica
- Transantarctic Mountains
- West Antarctica
- Crozet Islands (France)
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands (Australia)
- Kerguelen Islands (France)
- Peter I Island (Antarctic Treaty System)
- Prince Edward Islands (South Africa)
- Saint Paul Island (France)
- South Orkney Islands (Antarctic Treaty System)
- South Shetland Islands (Antarctic Treaty System)
- Shetland Plate
See also
 In Spanish: Placa antártica para niños
In Spanish: Placa antártica para niños

