Box elder facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Box elder |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Acer |
| Section: | Acer sect. Negundo |
| Species: |
A. negundo
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acer negundo |
|
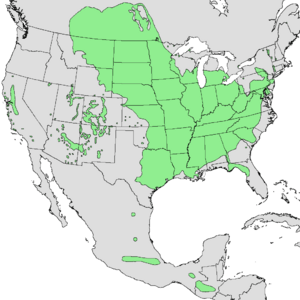 |
|
| Native range of Acer negundo | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Acer californicum var. texanum Pax Acer fauriei H.Lév. & Vaniot Acer fraxinifolium Nutt. Acer fraxinifolium Raf. Acer lobatum Raf. Acer negundo subsp. typicum (L.) Wesm. Acer negundo var. vulgare (L.) Pax Acer nuttallii (Nieuwl.) Lyon Acer trifoliatum Raf. Acer violaceum (Booth ex G.Kirchn.) Simonk. Negundo aceroides var. violaceum G. Kirchn. Negundo aceroides subsp. violaceus (Booth ex G. Kirchn.) W.A. Weber Negundo fraxinifolium var. crispum Loudon Negundo fraxinifolium var. violaceum Booth ex Loudon Negundo negundo (L.) H. Karst. Negundo texanum (Pax) Rydb. Rulac negundo (L.) Hitchc. |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Box Elder (scientific name: Acer negundo) is a type of maple tree. It is originally from North America. This tree grows quickly but does not live as long as some other trees. It has special leaves that are different from most maples.
Sometimes, the Box Elder is seen as a "weedy" plant. This means it can spread easily and grow in many places. It has been planted in many parts of the world. You can now find it in South America, Australia, Europe, and parts of Asia.
Contents
What Are the Box Elder's Common Names?
The Box Elder has many different names. This shows how well-known it is across a wide area. People call it "box elder" or "boxelder maple" because its light-colored wood looks like boxwood. Also, its leaves look like those of an elder plant.
Other names come from how it looks like an ash tree. Some names describe where it likes to grow, like "river maple." Other names refer to its sweet sap, like "sugar maple."
- In Canada, it is often called "Manitoba maple."
- In the British Isles, it is known as "box elder" or "ashleaf maple."
- In Russia, people call it "American maple."
How to Identify a Box Elder Tree
The Box Elder is a tree that grows fast. It usually lives for about 60 years. It can grow up to 10 to 25 meters (33 to 82 feet) tall. The trunk can be 30 to 50 centimeters (12 to 20 inches) wide. This tree often has many trunks and can form thick groups of trees.
Its young branches are green. They might have a white, pink, or purple waxy coating. The branches are smooth and can break easily. The bark on older trunks is light gray or brown. It has deep cracks and looks scaly.
Box Elder Leaves and Flowers
Most maple trees have simple leaves with several lobes. But the Box Elder is different. Its leaves are made up of several smaller leaflets. Usually, there are three to seven leaflets on one leaf. Each leaflet is about 5 to 10 cm (2 to 4 inches) long. They are light green and turn yellow in the fall.
The flowers are small and yellow-green. They appear in early spring. Male flowers grow in clusters. Female flowers hang down in long groups.
Box Elder Fruit and Seeds
The fruits of the Box Elder are called samaras. They are paired seeds with wings that hang down. Each seed is about 1 to 2 cm (0.4 to 0.8 inches) long. The wing is about 2 to 3 cm (0.8 to 1.2 inches) long and curves inward. These seeds fall in the autumn or stay on the tree through winter. Box Elder trees produce many seeds, and most of them can grow into new trees.
Unlike most maples, a Box Elder needs both a male and a female tree to make seeds.
Where Do Box Elder Trees Grow?
The Box Elder tree is native to most of the United States and Canada. It can be found as far south as Guatemala.
Even though it is native to North America, it is sometimes seen as a "weedy" plant. This means it can spread quickly and grow where it is not wanted. For example, in some parts of the northeastern United States, it has become much more common. People planted it a lot after World War II because it grows fast. This made the tree much more common than it used to be.
The Box Elder can quickly grow in both wild and developed areas. It is spreading in North America and other parts of the world. In Europe, it was brought over in 1688 to be a park tree. Now, it spreads fast and is considered an invasive species in places like Germany and Poland. It can also be found in eastern China and parts of Australia.
This tree likes bright sunlight. It often grows in areas that flood, like along rivers. It also grows well in disturbed places, like around houses or in empty lots.
Box Elder and Nature
Many animals eat the seeds of the Box Elder. Several birds and some squirrels enjoy them. The evening grosbeak especially likes these seeds.
The boxelder bug (Boisea trivittata) lays its eggs on all maples. However, it prefers the Box Elder tree. These bugs often gather in large groups on the tree's bark. The rosy maple moth also lays its eggs on maple leaves, including the Box Elder. If there are too many moth larvae, they can eat many of the leaves.
Small bumps, called galls, can form on the leaves. These are caused by tiny mites and midges. Other insects and fungi can also affect the leaves of the Box Elder.
How People Use Box Elder Trees
Box Elder Wood Uses
The wood of the Box Elder is light and soft. It is not usually used for big commercial projects. However, it can be used to make things like fiberboard. People also use it for decorative items, such as bowls or pens. Injured wood can develop a pretty red stain, which makes it special.
Native Americans have used the wood for many purposes:
- The Navajo used it to make tubes for bellows.
- The Cheyenne made bowls from it.
- People in Montana used large knots or burls from the trunk to make bowls, dishes, drums, and pipe stems.
- The Tewa used twigs for pipe stems.
- The Keres made twigs into prayer sticks.
The Dakota people and Omaha people made the wood into charcoal. They used this charcoal for ceremonial painting and tattooing. The Kiowa burned the wood in their altar fires during ceremonies.
Ancient wood flutes found in Arizona were made from Box Elder wood. These flutes are very old, dating back to 620–670 CE.
Box Elder in Medicine
Native Americans used the Box Elder for different medicines.
- The Cheyenne burned the wood as incense for spiritual medicines. They also used it during Sun Dance ceremonies.
- The Meskwaki and Ojibwa used a special liquid made from the inner bark to cause vomiting.
Box Elder as Food
The sap of the Box Elder can be used to make syrup. Native American groups like the Dakota, Omaha, Pawnee, and Cree used it this way.
- The Chiricahua and Mescalero Apache dried parts of the inner bark for winter food. They also boiled the inner bark until sugar crystals formed.
- The Cheyenne mixed boiled sap with animal hide shavings to make a candy.
- The Ojibwa mixed Box Elder sap with sugar maple sap to make a drink.
Box Elder in Gardens
Even though its wood is weak and it spreads many seeds, the Box Elder is a popular tree for planting. Many different types, called cultivars, have been created. Some popular ones include:
- 'Auratum' – has yellowish leaves.
- 'Flamingo' – has pink and white leaves, very popular.
- 'Pendulum' – has branches that hang down.
- 'Variegatum' – has creamy white edges on its leaves.
- 'Violaceum' – has young branches with a bluish color.
Box Elder and Health
Can Box Elder Be Harmful?
The seeds of the Box Elder tree contain a substance that can be harmful to horses. It can cause a serious illness in horses called seasonal pasture myopathy (SPM). This illness is similar to a sickness in humans caused by the same substance.
Box Elder Allergies
The pollen from the Box Elder tree can cause severe allergies. The tree releases its pollen in winter or spring. The exact time depends on where the tree is located.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Acer negundo para niños
In Spanish: Acer negundo para niños
 | Misty Copeland |
 | Raven Wilkinson |
 | Debra Austin |
 | Aesha Ash |
















