Carrizo Plain facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Carrizo Plain National Monument |
|
|---|---|

Aerial view of the Carrizo Plain.
The San Andreas Fault is on the right. |
|
| Location | San Luis Obispo & Kern counties, California |
| Nearest city | California Valley, California |
| Area | 246,812 acres (998.81 km2) |
| Established | January 17, 2001 |
| Governing body | Bureau of Land Management |
| Website | Carrizo Plain National Monument |
|
Carrizo Plain Rock Art Discontiguous District
|
|
| Area | 1215 |
| NRHP reference No. | 01000509 |
| Significant dates | |
| Added to NRHP | May 23, 2001 |
| Designated NHLD | March 2, 2012 |

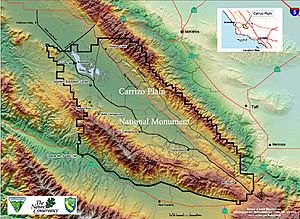
The Carrizo Plain is a huge, flat grassland area in southeastern San Luis Obispo County, California. It's about 50 miles (80 km) long and up to 15 miles (24 km) wide. This special place is home to the Carrizo Plain National Monument, which covers about 246,812 acres (1,000 km²). It's the biggest natural grassland left in California!
The Carrizo Plain is famous for a few things. It has a historic site called Painted Rock. This rock is covered in ancient art. The plain is also known for the San Andreas Fault, a huge crack in the Earth's crust. This fault runs along the eastern edge of the plain.
Contents
Exploring the Carrizo Plain's Landscape
The Carrizo Plain stretches northwest from the town of Maricopa. The San Andreas Fault runs right alongside it. To the northeast, you'll see the Temblor Range mountains. Beyond them is California's huge Central Valley. To the southwest, there's another mountain range called the Caliente Range.
The plain is about 2,200 feet (670 meters) above sea level. In the middle, there's a large, salty lake called Soda Lake. It's about 3,000 acres (12 km²) big. All the rainwater from the surrounding hills flows into this lake. Near Soda Lake is the famous Painted Rock. It has amazing rock art made by the Chumash and Yokut people thousands of years ago.
The highest point in San Luis Obispo County is Caliente Mountain. It's 5,106 feet (1,556 meters) tall and is southwest of the plain. The Carrizo Plain has a dry, grassland climate. It doesn't have any trees and gets only about 9 inches (230 mm) of rain each year.
Seeing the San Andreas Fault Up Close
The Carrizo Plain is one of the best places to see the San Andreas Fault on the surface. You can clearly see the fault lines along the eastern side of the plain. They are at the bottom of the Temblor Range. The best time to see them is in the early morning or evening. The shadows make the fault lines stand out more.
Besides its beautiful spring wildflowers, the Carrizo Plain is known for Painted Rock. This sandstone cave has ancient drawings called pictographs. They were made by the Chumash people around 2000 BC.
Wallace Creek: A Moving Stream
Wallace Creek is a small stream that flows into Soda Lake. It's usually dry for most of the year. This creek is special because it crosses the San Andreas Fault. Over time, the movement of the fault has shifted the creek bed. It's now offset by about 425 feet (130 meters)!
About 23 feet (7 meters) of this shift happened during a big earthquake in 1857. The current part of the creek started forming about 3,700 years ago. Geologists have studied Wallace Creek carefully. They use it to learn about past earthquakes along the San Andreas Fault. It's one of the most amazing examples of how the fault moves the land.
How to Visit the Carrizo Plain
You can reach the Carrizo Plain using State Route 166 (at the south entrance) or State Route 58 (which crosses the northern part). These two roads are connected by Soda Lake Road. This is the main road through the plain. However, parts of it are gravel and can become hard to use after it rains.
Understanding the Plain's Geology
The most important geological feature of the Carrizo Plain is the San Andreas Fault. It runs along the northeast side of the plain. This part of the fault is the oldest section in the entire fault zone. The movement of the San Andreas Fault has created unique landforms. These include hills that block old stream channels and small ponds called sag ponds.
What is the Soil Like?

The soil in the Carrizo Plain is mostly made of alluvium. This is soil that has been carried and dropped by rivers or flowing water. The soil layers are thickest near Soda Lake. They get thinner as you go towards the mountains.
The soil here varies a lot. It can be clay, silt, sand, or gravel. The sandier soils are usually near the slopes. They drain water well. The soils with more clay are on the valley floor near Soda Lake. These soils don't drain water very well. The soils in the Carrizo Plain are not very fertile. This is because they have a lot of alkaline content and don't get much rain.
Amazing Animals of the Carrizo Plain
The Carrizo Plain is a very important home for wildlife. It has the largest number of endangered species in California. There are 13 species here that are listed as endangered by the state or federal government!
Some of these special animals include:
- San Joaquin kit fox – This is a small, nocturnal (active at night) fox. It used to be common but is now endangered.
- Blunt-nosed leopard lizard – This small lizard is gray to brown with dark spots. It's only found in California.
- Giant kangaroo rat – This is the biggest type of kangaroo rat. It's also only found in California and is critically endangered.
- San Joaquin antelope squirrel – This light tan squirrel has a white stripe down its back. Most of its natural home is now used for farms. So, the Carrizo Plain is very important for its survival.
Other animals that live here include tule elk, pronghorn, black-tailed jackrabbits, coyotes, and the Le Conte's thrasher bird.
Carrizo Plain National Monument: A Protected Place
How the Monument Was Created
In 1988, three groups worked together to protect the Carrizo Plain. These were the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM), the California Department of Fish and Game, and The Nature Conservancy. They bought a large piece of land, about 82,000 acres (330 km²), to protect it.
Later, in 2001, President Bill Clinton officially made the Carrizo Plain a National Monument. This means it's a special place protected by the government. Since then, the protected area has grown to about 250,000 acres (1,000 km²).
Camping in the Carrizo Plain
You can camp in the Carrizo Plain National Monument at two simple campgrounds: KCL Campground and Selby Campground. They are quite different.
KCL Campground is in the southern part of the monument. It's easy to get to from Soda Lake Road. This campground has picnic tables and firepits. There are also some trees that offer shade, which is rare in the valley. You can even stable horses here if you bring them!
Selby Campground is further north and a bit more rugged. A good gravel road leads to it from Soda Lake Road. This site is cut into the natural hills and canyons. It has picnic tables with shade covers and a permanent toilet (but no water). You can camp anywhere in the large flat areas. You can also hike into the nearby wilderness area for great views.
You can also do "car camping" in certain areas, mostly in the foothills. However, you are not allowed to camp on the main valley floor.
Solar Power in the Plain
The Carrizo Plain is one of the sunniest places in California. Because of this, it has been used for solar power projects. From 1983 to 1994, there was a huge solar power plant here. It was the largest in the world at the time! It had 100,000 solar panels and produced a lot of electricity.
This plant was built by an oil company called ARCO. They were pioneers in solar energy. Later, another company bought the plant. However, the price of oil didn't go up as expected. This made solar power less competitive, so the plant eventually closed down in the late 1990s. The solar panels from this plant were then sold and used around the world.
More recently, new solar projects have been built in the Carrizo Plain. For example, the Topaz Solar Farm started operating in 2014. It's one of the largest solar power plants in the world. The California Valley Solar Ranch also opened in 2013. These projects use the abundant sunshine to create clean energy.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Llanura de Carrizo para niños
In Spanish: Llanura de Carrizo para niños