Eggplant facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Eggplant |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Solanum
|
| Species: |
S. melongena
|
| Binomial name | |
| Solanum melongena |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Solanum ovigerum Dunal |
|
The eggplant (Solanum melongena) is also known as aubergine or brinjal. It is a type of nightshade plant grown for its tasty fruit. People in North America, Australia, and New Zealand usually call it "eggplant." In British English, it's called "aubergine," and in places like South Asia and South Africa, it's known as "brinjal."
This fruit is used a lot in cooking around the world. Eggplants belong to the Solanum plant family, which also includes familiar plants like the tomato and the potato. Eggplants were first grown by people from a wild plant called the thorn or bitter apple. This likely happened in two different places: one in South Asia and another in East Asia.
Contents
What Does an Eggplant Look Like?
The eggplant is a delicate plant that grows in warm places. It can live for many years, but people often grow it as an annual (meaning it lives for one year) in cooler areas. Its stem can sometimes be spiny.
Eggplant flowers can be white or purple. They have five petals and yellow parts called stamens. The fruit itself is usually egg-shaped, shiny, and purple. Inside, the flesh is white and has a meaty feel. When you cut an eggplant, the white part quickly turns brown.
Eggplant plants usually grow about 40 to 150 centimeters (1.3 to 5 feet) tall. They have large, lobed leaves that are about 10 to 20 cm (4 to 8 inches) long. Wild eggplants have small fruits, less than 3 cm (1 inch) across. But the eggplants we eat are much bigger, often 30 cm (12 inches) or more in length.
Botanically, the eggplant fruit is actually a berry. It has many small, soft seeds inside. These seeds are safe to eat, but they can taste a bit bitter. This is because they contain natural substances called alkaloids, similar to those found in tobacco.
Where Did Eggplants Come From?
Eggplants were first grown by people in southern and eastern Asia a very long time ago. The oldest known written record of the plant is from a Chinese farming book called Qimin Yaoshu, which was finished in the year 544.
The many Arabic and North African names for eggplant, and the fact that ancient Greeks and Romans didn't have names for it, suggest that Arabs brought it to the Mediterranean area in the early Middle Ages. A book about farming from 12th-century Arabic Spain even described how to grow aubergines.
Eggplants didn't arrive in England until the 16th century. An English botany book from 1597 mentioned that the plant grew almost everywhere in Egypt. It said that in London gardens, eggplants would grow flowers and small fruits, but they usually didn't ripen fully before winter.
Because eggplants are related to other nightshades, some people once thought the fruit was very poisonous. While the fruit is safe to eat, the flowers and leaves can be harmful if eaten in large amounts.
In old stories, eggplants sometimes had a special meaning. In 13th-century Italian folklore, people believed that eating eggplant could cause someone to go crazy! In 19th-century Egypt, it was said that people were "more common and more violent" when eggplants were in season during the summer.
Different Kinds of Eggplants
There are many different types, or cultivars, of eggplant. They come in various sizes, shapes, and colors, though purple is the most common. The eggplants you usually see in Europe and North America are long and oval-shaped, about 12–25 cm (5–10 inches) long, with dark purple skin.
In India and other parts of Asia, you can find a much wider range of eggplants. Some large types in India can weigh up to a kilogram (2.2 pounds). Their colors can be white, yellow, green, reddish-purple, or dark purple. Some even have a mix of colors, like white near the stem and pink or deep purple at the other end. You might also see green or purple eggplants with white stripes. Chinese eggplants are often long and thin, like a cucumber. Japanese types are also popular.
Here are some common types:
- Oval or long black eggplants include 'Harris Special Hibush', 'Burpee Hybrid', 'Black Magic', and 'Black Beauty'.
- Slim eggplants with purple-black skin include 'Little Fingers', 'Ichiban', and 'Pingtung Long'.
- Green-skinned slim eggplants include 'Louisiana Long Green' and 'Thai (Long) Green'.
- White-skinned slim eggplants include 'Dourga'.
- Traditional white, egg-shaped eggplants include 'Casper' and 'Easter Egg'.
- Two-toned eggplants with color changes include 'Rosa Bianca' and 'Violetta di Firenze'.
- Striped eggplants include 'Listada de Gandia'.
- In some parts of India, very small eggplants called vengan are popular.
Special Eggplant Varieties
Scientists have also developed some special types of eggplants.
- S. m. var. esculentum – This is the common eggplant we usually eat.
- S. m. var. depressum – This is a dwarf (small) eggplant.
- S. m. var. serpentium – This is called snake eggplant.
Genetically Modified Eggplant
Bt brinjal is a type of eggplant that has been genetically modified. This means scientists added a gene from a soil bacterium called Bacillus thuringiensis to the eggplant. This special gene helps the plant protect itself from certain insects, like the brinjal fruit and shoot borer.
In 2010, India put a stop to growing Bt brinjal for a while to make sure people trusted it. However, in 2013, Bangladesh approved Bt brinjal for farmers to grow.
Cooking and Eating Eggplant
Raw eggplant can sometimes taste a bit bitter. But when it's cooked, it becomes soft and develops a rich, interesting flavor. Eggplant is great at soaking up cooking fats and sauces, which makes dishes very tasty. Some recipes suggest salting, rinsing, and draining sliced eggplant before cooking. This helps to soften it and remove any bitterness, especially from older types of eggplant. However, many modern eggplants don't need this step.
Eggplant is used in cooking all over the world. Because of its texture, it's sometimes used as a meat substitute in vegan and vegetarian cuisines. The inside of the fruit is smooth, similar to a tomato. The many small seeds are soft and safe to eat along with the rest of the fruit. The thin skin is also edible.
Eggplant in East Asia
In Korea and Japan, eggplants usually have thin skins.
-
Chinese yúxiāng-qiézi (fish-fragrance eggplants)
In Chinese cooking, eggplants are called qiézi (茄子). They are often deep-fried and made into dishes like yúxiāng-qiézi, which means "fish-fragrance eggplants."
In Korean cuisine, eggplants are called gaji (가지). They are often steamed, stir-fried, or pan-fried. People eat them as banchan (side dishes), such as namul or jeon.
Eggplant in South Asia
Eggplant is very popular in its home country, India. It's used in dishes like sambar (a lentil stew), dalma (a lentil and vegetable dish), chutney, curry, and achaar (a pickled dish). Because it's so versatile and used in many everyday and special meals, eggplant is often called the "king of vegetables" in India.
A popular dish called baingan bharta is made by roasting, peeling, and mashing eggplant. Then it's mixed with onions, tomatoes, and spices, and cooked slowly. In Bangladesh and eastern India, a similar dish called begun-pora is made by charring eggplant. The mashed eggplant is mixed with raw chopped shallots, green chilies, salt, fresh coriander, and mustard oil.
In Maharashtra, India, there's a dish called bharli vangi. Small eggplants are filled with ground coconut, peanuts, onions, tamarind, and masala spices, then cooked in oil.
Eggplant in the Middle East and Mediterranean
Eggplant is often stewed, like in the French dish ratatouille. It's also often deep-fried, as in the Italian parmigiana di melanzane, the Turkish karnıyarık, or the Greek and Turkish moussaka.
-
Melanzane alla Parmigiana, also known as "eggplant parmesan"
-
Almagro eggplants from Spain
In Iranian cuisine, eggplant is mixed with whey to make kashk e bademjan, or with tomatoes for mirza ghassemi. It can also be made into a stew called khoresh-e-bademjan.
Eggplant can be roasted in its skin until it's charred. Then the soft inside is scooped out and mixed with other ingredients like lemon, tahini, and garlic. This makes dishes like the Arab baba ghanoush and the Greek melitzanosalata.
A mix of roasted eggplant, roasted red peppers, chopped onions, tomatoes, and other vegetables is called zacuscă in Romania. Similar dishes are ajvar or pinjur in the Balkans.
In Spain, a dish called escalivada uses strips of roasted aubergine, sweet pepper, onion, and tomato. In southern Spain, eggplant is often thinly sliced, deep-fried in olive oil, and served hot with honey.
A special dish from the Levant is makdous. This is pickled eggplant stuffed with red peppers and walnuts in olive oil. Eggplant can also be hollowed out and filled with meat, rice, or other ingredients, then baked. In the Caucasus, for example, it's fried and stuffed with walnut paste to make nigvziani badrijani.
Where Eggplants Are Grown
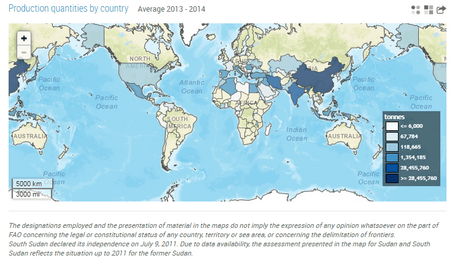
In 2016, the world produced 51.3 million tonnes of eggplants. Almost 1.8 million hectares (4.4 million acres) of land were used to grow eggplants that year. Over 62% of all eggplants came from China alone! Other big producers were India (24.5% of the world's total), Egypt, Turkey, and Iran.
Images for kids
-
Philippine tortang talong, an eggplant omelette
-
Philippine rellenong talong, a type of eggplant omelette stuffed with ground meat
-
Philippine pinakbet, a mixed vegetable dish
See also
 In Spanish: Solanum melongena para niños
In Spanish: Solanum melongena para niños