History of Google facts for kids
Google is a very famous company that helps millions of people around the world find information online every day. It was officially started in 1998 by two smart students, Larry Page and Sergey Brin. They created Google Search, which quickly became the most popular way to search the internet.
Larry Page and Sergey Brin were students at Stanford University in California. In 1996, they developed a special way to search the internet, which they first called "BackRub." Their idea was so good that their company grew very fast. They moved their main offices several times, finally settling in Mountain View in 2003.
Google continued to grow rapidly. In 2004, the company offered its shares to the public for the first time, becoming one of the world's largest technology companies. Over the years, Google launched many useful products, like Google News in 2002, Gmail for email in 2004, Google Maps to help you find your way in 2005, and the Google Chrome web browser in 2008. They also created a charitable group called Google.org in 2005 to help with good causes. In 2015, Google became the main part of a bigger company called Alphabet Inc..
The name "Google" comes from a playful misspelling of the word "Googol." A googol is a huge number: a 1 followed by 100 zeros! This name was chosen to show that the search engine aimed to organize and provide a massive amount of information from the internet.
Contents
The Story of Google: How It All Began
Starting with "BackRub" at Stanford
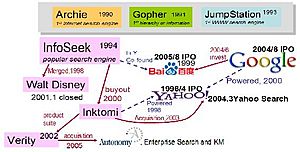
The idea for Google began in 1996 with a research project called "BackRub." This project was started by Larry Page and Sergey Brin while they were PhD students at Stanford University in California. They wanted to find a better way to organize all the information on the World Wide Web.
Larry Page thought about how important research papers are often cited by many other papers. He believed that web pages could be ranked similarly: pages with more links pointing to them from other important pages might be more useful. Sergey Brin soon joined the project, and together they developed a special system to make this idea work.
They created an algorithm called PageRank. This algorithm looked at the links between web pages to figure out which pages were most important and relevant. They realized that a search engine using PageRank would give much better results than older search engines, which mostly just counted how many times a search word appeared on a page. The first version of their search engine was launched on the Stanford website in August 1996.
Becoming an Official Company
After their successful project, Larry Page and Sergey Brin decided to turn their idea into a real company. The internet address google.com was registered on September 15, 1997. They officially started their company, named Google, on September 4, 1998. Their first office was in a friend's garage in Menlo Park, California.
At first, Larry and Sergey weren't sure about having advertisements on their search engine. However, they soon decided to allow simple text ads. These ads helped Google earn money while keeping the search page clean and fast to load. By the end of 1998, Google had already indexed about 60 million web pages, showing how quickly it was growing.
In March 1999, the company moved to bigger offices in Palo Alto, California. As Google continued to expand, it moved again in 2003 to a large campus in Mountain View, Santa Clara County, California. This campus is now famously known as the Googleplex, a fun name that sounds like the huge number "googolplex" (a 1 followed by a googol of zeros!).
Google's Growth and Innovations in the 2000s
Google's simple design and excellent search results quickly made it popular with internet users. In 2000, Google started selling advertisements that appeared next to search results. These ads were text-only, which helped keep the pages loading quickly and looking neat.
Google had a famous motto: "Don't be evil." This meant they believed in doing good things for the world, even if it meant not making the most money in the short term.
In 2004, Google made a big step by having its initial public offering (IPO). This meant that people could buy shares in the company. The IPO was very successful, and Google's value grew a lot. After this, the founders and CEO even chose to take a salary of just $1 each year, because their main earnings came from owning parts of the company.
The word "to google" became so common that it was added to dictionaries in 2006. This showed how much Google had changed the way people search for information online.
Google also faced competition from other big technology companies, like Microsoft with its Bing search engine. Both companies offered similar services, such as email and online maps. Google even created its own web browser, Google Chrome, to compete with others.
To make its advertising more effective, Google started using information about people's browsing habits in 2007. This helped them show ads that were more relevant to what users were interested in.
Google in the 2010s and Beyond
In the 2010s, Google continued to expand its reach. By 2014, it had over 70 offices in more than 41 countries around the world.
A big change happened in 2015 when Google reorganized itself under a new parent company called Alphabet Inc.. Google became the main part of Alphabet, focusing on internet-related services.
Google also explored new areas, like video games, by launching a cloud gaming platform called Google Stadia in 2019.
However, as Google grew, governments around the world started to look closely at its business practices. In 2019, the United States Department of Justice began investigating Google for concerns about fair competition. This led to lawsuits, with some governments arguing that Google had too much control over the search and advertising markets.
Recent Developments in the 2020s
The early 2020s brought new challenges and changes for Google. During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Google made some cost-cutting decisions, like slowing down hiring. Google also worked with Apple to develop tools for contact tracing on smartphones to help fight the pandemic.
There were also some temporary outages of Google services in 2020, affecting things like YouTube and Google Drive, but these were quickly fixed.
Governments in countries like Australia and Canada introduced new laws that would require Google to pay news organizations for showing their content. Google responded by removing Canadian news links from its services in June 2023.
The antitrust cases continued. In September 2024, the European Commission fined Google 2.42 billion euros for unfair practices related to its shopping service. In October and November 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice proposed significant changes to Google's business, including potentially forcing it to sell parts of its company or share data with competitors. Google disagreed with these proposals, calling them excessive.
In December 2024, Google offered its own ideas for changes, suggesting a shorter ban on exclusive deals where it pays device makers to make Google its default search engine.
The legal discussions continued into 2025. In April 2025, a trial began in Washington, D.C., to decide on these proposed changes. In September 2025, the court ruled that Google would not have to sell its Chrome browser or Android operating system. However, the court did say that Google could no longer make exclusive deals for its search engine and would need to share some of its search data with other companies to encourage more competition.
How Google Got Its Funding
The very first money for Google as a company came in August 1998, when Andy Bechtolsheim, a co-founder of Sun Microsystems, invested $100,000.
In June 1999, Google received another $25 million from big investment firms. Larry Page and Sergey Brin were careful about giving up control of their company, but they knew they needed more money to grow. They eventually hired Eric Schmidt as Google's first CEO in August 2001.
In January 2004, Google announced its plans for an initial public offering (IPO). This meant they would sell shares of the company to the public. The IPO happened on August 19, 2004, with shares selling for $85 each. This sale raised about $1.67 billion and made Google worth over $23 billion! Many Google employees became very wealthy overnight.
Google's shares are traded on the NASDAQ stock exchange under the symbol GOOG. When Alphabet Inc. was created, it kept Google's stock history and symbol.
The Meaning Behind the Name "Google"
The name "Google" came from a simple mistake in spelling the word "googol." A googol is a huge number: a 1 followed by one hundred zeros (10100). Larry Page and Sergey Brin chose this name because it fit their goal of building a search engine that could handle and organize a massive amount of information on the internet.
The word "google" became so widely used that it was added to the Merriam Webster Collegiate Dictionary and the Oxford English Dictionary in 2006. It means "to use the Google search engine to obtain information on the internet." This shows how much Google has become a part of our everyday language and how it helps us explore the vast world of online information.
Working with Other Companies: Google's Partnerships
Google has often worked with other companies and organizations to improve its products and services. These partnerships help Google innovate and reach more people.
For example, in 2005, Google started a long-term research partnership with NASA. They planned to work together on managing large amounts of data and exploring new technologies.
Google also teamed up with media companies like Time Warner's AOL unit and News Corp. to expand its advertising reach. In 2007, Google became a key partner for the fun NORAD Tracks Santa program, using Google Earth to show Santa's journey in 3D.
In 2013, Google partnered with car companies like Kia Motors and Hyundai to integrate Google Maps into new car models. Google also joined the Alliance for Affordable Internet (A4AI) in 2013, working with companies like Facebook and Microsoft to make internet access more affordable for everyone, especially in developing countries.
These partnerships show how Google collaborates across different industries to bring new and exciting services to users around the globe.
See also
- Timeline of Google Search
- Criticism of Google
- Google logo
- List of Google Easter eggs
- Timeline of Mountain View, California, headquarters of Google since 1999