Jacques-Cartier Lake facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Jacques-Cartier Lake |
|
|---|---|

A beach of Jacques-Cartier Lake
|
|
| Location | Lac-Jacques-Cartier, La Côte-de-Beaupré Regional County Municipality |
| Coordinates | 47°35′07″N 71°12′26″W / 47.5852°N 71.2073°W |
| Lake type | Natural |
| Primary inflows | (clockwise from the mouth) Décharge du lac Plamondon et décharge des lacs Nadreau, Grandpré et "lac Petit Pré". |
| Primary outflows | =Jacques-Cartier River |
| Basin countries | Canada |
| Max. length | 9.2 km (5.7 mi) |
| Max. width | 1.8 km (1.1 mi) |
| Average depth | 69 m (226 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 783 m (2,569 ft) |
Jacques-Cartier Lake is a large glacial lake in Quebec, Canada. It is the main source of the Jacques-Cartier River. This beautiful lake is found in the Laurentides Wildlife Reserve. It is about 90 km north of Quebec City.
The lake is in an area called Lac-Jacques-Cartier. This area is part of the La Côte-de-Beaupré Regional County Municipality. It is also in the Capitale-Nationale region of Quebec.
You can reach the lake by Route 175. This road runs along its western side. The road is used for both logging and tourism. Logging is the main activity here. Tourism is also very important.
The lake's surface usually freezes from early December to late March. It is generally safe to walk on the ice from mid-December to mid-March.
Contents
About the Lake's Location
This section explains where Jacques-Cartier Lake is located. It also describes the rivers and lakes nearby.
Rivers and Lakes Nearby
Many rivers and lakes are close to Jacques-Cartier Lake. They are grouped by direction:
- North side: Pikauba River, Lac des Pas Perdus, Verchères Lake, Jacqueline Lake, Franchère Lake.
- East side: Montmorency River, Malbaie River, Malbaie Lake, Neiges Lake, rivière du Gouffre, rivière à la Loutre.
- South side: Montmorency River, Sept-Îles Lake, Jacques-Cartier River, Jacques-Cartier North-West River, Sautauriski River.
- West side: Beauséjour lake, Launières River, Banville lake.
The lake is in the unorganized territory of Lac-Jacques-Cartier. The Nadreau Lake is where the Jacques-Cartier River begins. Nadreau Lake gets water from two smaller lakes. These are Plamondon Lake (844 m high) and another unnamed lake (862 m high).
Nadreau Lake flows north into Lake Grandpré (847 m high). Lake Grandpré then flows west into "Petit Pré lake". This lake is 440 m long and 838 m high.
From "Petit Pré lake", the Jacques-Cartier River flows northwest. It travels 15.6 km to reach Jacques-Cartier Lake.
Size and Features
Jacques-Cartier Lake is the biggest lake in the Laurentides Wildlife Reserve. It is 9.2 km long and 1.8 km wide. The lake is also 69 m deep.
The lake is about 795 m above sea level. To its east is Mont Camille-Pouliot, which is 1006 m high. At the south end of the lake, there is a dam. It was built in 1922 to control water flow.
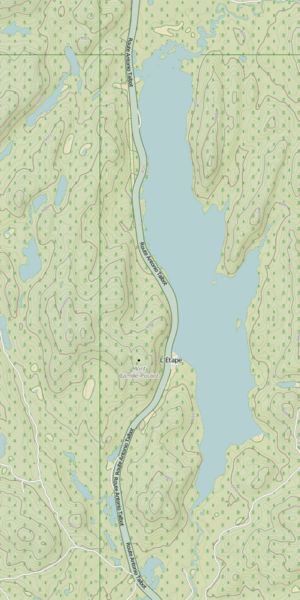
Between the lake and the mountain, you will find Route 175. There is also a highway rest area called L'Étape.
Fun Things to Do
Jacques-Cartier Lake is a great place for outdoor activities.
Fishing
You can go fishing in this lake. A popular fish to catch here is the gray trout, also known as lake trout.
Other Lakes
There is also a "Petit lac Jacques-Cartier" (Small Jacques-Cartier Lake). This is why the main lake was often called "Great Jacques-Cartier Lake". This helped people tell the two lakes apart.
How the Lake Got Its Name
The lake is named after a famous explorer.
Jacques Cartier, the Explorer
The lake is named after Jacques Cartier. He was an explorer and navigator from Saint-Malo, France. He lived from 1491 to 1557. Cartier made three trips to Canada between 1534 and 1542.
In 1534, King François I sent him to find gold and a way to Asia. He explored Anticosti Island and the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. On July 24, he put up a cross in Gaspé Bay. This showed that France claimed the land.
In 1535, Cartier sailed up the St. Lawrence River. He reached Hochelaga (now Montreal). He spent a hard winter in Stadaconé (now Quebec City).
In 1541, Cartier tried to start the first French colony in America. He set up a settlement at the mouth of the Cap-Rouge river. He named it Charlesbourg-Royal. Cartier left the colony in June 1542. He met Roberval, another explorer, in Newfoundland. Cartier then decided to return to Saint-Malo.
Jacques Cartier was the first person to map the St. Lawrence River. He also realized that the "gold" and "diamonds" he found were actually iron pyrite and quartz.
Official Naming
The name "lac Jacques-Cartier" became official on December 5, 1968. This was done by the Commission de toponymie du Québec.
Images for kids
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |