Solar energy facts for kids
Solar energy is power that comes from the Sun. People have used it for thousands of years in many ways. The oldest uses of solar energy were for heating, cooking, and drying things. Today, it is also used to make electricity. This is very helpful in places far from cities or in outer space, where other power sources are not available.
Making electricity from solar energy is becoming cheaper. Because the Sun always provides energy, solar power is a renewable energy source. This means it will not run out, unlike coal and oil.
Contents
How We Use Solar Energy
Solar energy is used in many ways today:
- To make hot water and heat buildings.
- For cooking food.
- To create electricity using solar cells or special engines.
- To remove salt from seawater.
- To dry clothes and towels in the sun.
- Plants use it for photosynthesis, which helps them grow.
- In special solar cookers for cooking food.
Sunlight's Power

After sunlight travels through Earth's atmosphere, most of its energy is in the form of visible light and infrared light (heat). Plants use sunlight to make their own food through a process called photosynthesis. Humans use this stored energy when they burn wood or fossil fuels. We also get this energy by eating plants and animals.
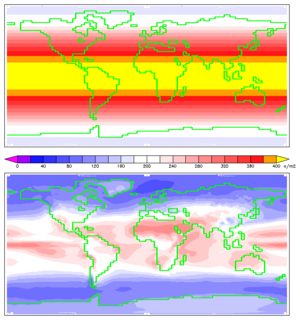
Solar radiation reaches Earth's upper atmosphere with a power of 1366 watts for every square meter. Because Earth is round, areas closer to the poles are angled away from the Sun. This means they get much less solar energy than areas closer to the equator.
Today, solar cell panels can turn about 15% of the sunlight that hits them into electricity. Imagine if we covered a small part of the Earth with efficient solar panels. This area could produce enough electricity for the whole world's needs!
Solar Technologies
Many technologies have been created to use the Sun's energy. Some of these use solar energy directly for light or heat. Others turn sunlight into electricity.
Solar Power Plants
Solar power plants change sunlight into electricity. They do this in two main ways:
- Photovoltaics (PV): These use solar cells to turn light directly into electric current.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP): These systems use special lenses or mirrors. They focus a large area of sunlight into a small, powerful beam. This beam then creates heat to make electricity.
Solar Cookers
Solar cooking uses the Sun's energy instead of fuels like charcoal or gas. Solar cookers are cheap and good for the environment. They are becoming popular in places where wood is scarce or fuel is expensive. They also help prevent fires. Solar cookers often have a glass cover. They use mirrors to focus the Sun's rays, which makes them get hotter.
Solar Heaters

The Sun can be used to heat water instead of using electricity or gas. There are two main types of solar heating systems:
- Liquid-based systems: These heat water or a special liquid in a "hydronic" collector.
- Air-based systems: These heat air in an "air collector."
Both types can help heat buildings that use forced air systems.
Solar Cells
Solar cells are devices that turn light energy into electrical energy. Sometimes, "solar cell" means a device that specifically uses sunlight. "Photovoltaic cell" is a broader term for any cell that turns light into electricity.
Solar cells are used in many places. They are great for situations where there is no regular power from the grid. This includes remote areas, Earth-orbiting satellites, and space probes. You can also find them in small items like calculators and wrist watches. Many solar cells are put together to form a solar panel. These panels can make enough electricity for practical use. The electricity from solar panels can be stored in special rechargeable batteries for later use.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The source of solar power: the Sun
-
Solar water heaters facing the Sun to get the most energy.
-
MIT's Solar House #1, built in 1939, used stored heat for year-round heating.
-
This large dish in Auroville, India, uses the Sun to make steam for cooking.
-
Darmstadt University of Technology, Germany, won a competition in 2007 with this energy-efficient house.
-
Greenhouses like these in the Netherlands grow vegetables, fruits, and flowers.
-
Thermal energy storage. The Andasol plant stores solar energy in tanks of molten salt.
-
In 2016, Solar Impulse 2 was the first solar-powered aircraft to fly around the world.
See also
 In Spanish: Energía solar para niños
In Spanish: Energía solar para niños