London Borough of Harrow facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
London Borough of Harrow
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Salus populi suprema lex
(The well-being of the people is the highest law) |
|||
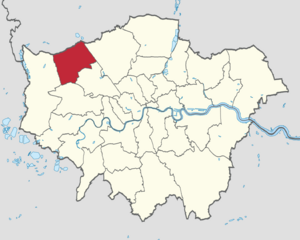
Harrow shown within Greater London
|
|||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||
| Constituent country | England | ||
| Region | London | ||
| Ceremonial county | Greater London | ||
| Created | 1 April 1965 | ||
| Admin HQ | Civic Centre Station Road Harrow |
||
| Government | |||
| • Type | London borough council | ||
| • Body | Harrow London Borough Council | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 19.49 sq mi (50.47 km2) | ||
| Area rank | 270th (of 326) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 251,160 | ||
| • Rank | 70th (of 326) | ||
| • Density | 12,888.9/sq mi (4,976.4/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) | ||
| Postcodes |
HA, NW, UB
|
||
| Area code(s) | 020 | ||
| ISO 3166 code | GB-HRW | ||
| ONS code | 00AQ | ||
| GSS code | E09000015 | ||
| Police | Metropolitan Police | ||
| Website | http://www.harrow.gov.uk/ | ||
The London Borough of Harrow is a special area in northwest London, England. It is part of Outer London. It shares borders with four other London boroughs. These are Barnet to the east, Brent to the southeast, Ealing to the south, and Hillingdon to the west. It also borders the Hertfordshire areas of Three Rivers and Hertsmere to the north.
The local government for Harrow is called Harrow London Borough Council. The London borough was created in 1965. Its boundaries were set in 1934. Harrow includes three main towns: Harrow, Pinner, and Stanmore. It also covers parts of Edgware.
Contents
History of Harrow
The area that is now Harrow used to be three old church areas. These were Harrow on the Hill, Great Stanmore, and Little Stanmore (also known as Whitchurch). All of these were historically in the county of Middlesex. Harrow on the Hill was the biggest of the three. Pinner was part of Harrow on the Hill until 1766. Then it became its own separate church area.
Early Local Government
In 1850, the central part of Harrow on the Hill became a "local board district." An elected board was in charge of public health and building things like roads. This district included the original village on the hill and nearby small settlements. These were Roxeth, Sudbury, and Greenhill. Greenhill later grew into the modern town centre of Harrow. This happened after the Harrow-on-the-Hill station opened there in 1880.
Changes in the 19th and 20th Centuries
In 1894, these local districts became "urban districts." This meant they had more powers to manage local services. Parts of the old Harrow on the Hill area outside this urban district were split into new areas. These new areas were Harrow Weald, Wealdstone, and Wembley. Wealdstone and Wembley also became urban districts.
In 1934, the Harrow urban district became much larger. It took in Wealdstone and the areas of Harrow Weald, Pinner, Great Stanmore, and Little Stanmore. The district was renamed simply 'Harrow' at this time. On May 4, 1954, Harrow Urban District became a "municipal borough." This gave it even more local power. By 1961, Harrow was the most populated local area in Middlesex. It had 209,080 people.
Becoming a London Borough
In 1965, Harrow became part of Greater London under a new law. It kept the same borders but was renamed the London Borough of Harrow. It was one of the 32 new London Boroughs. Harrow was the only London borough that kept its exact previous borders. There was a small change in 1993. The village of Elstree was fully placed into Hertfordshire.
How Harrow is Governed
The local government for Harrow is called Harrow Council. They hold meetings at the Harrow Arts Centre in Pinner. Their main offices are at the Council Hub in Wealdstone.
Representation in London
Since 2000, Harrow is part of the Brent and Harrow area for elections to the London Assembly. The London Assembly helps oversee the Mayor of London and other city-wide issues.
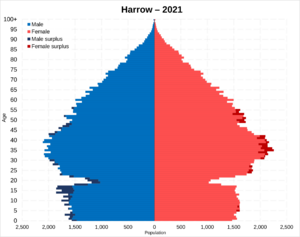
People and Population
Harrow is a great place to live because it's near green spaces. It's also easy to get to central London by train. This has led to many older houses being rebuilt.
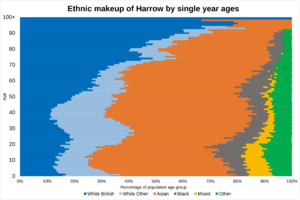
Diverse Communities in Harrow
Harrow is a very diverse borough. About 63.8% of its people are from Black and Minority Ethnic (BME) communities. The largest group is of Indian background, especially from Gujarat and South India. Harrow also has the largest number of Sri Lankan Tamils in the UK and Ireland. It also has the highest number of Gujarati Hindus in the UK.
The areas with the most White British people are Pinner, Pinner South, and Stanmore Park. The areas with fewer White British people are Kenton East and Queensbury.
Since 2005, Harrow Council holds a festival called Under One Sky. It happens on the last Sunday in June. This festival celebrates all the different communities in Harrow. It features dance, music, sports, food, and a carnival parade.
Religion in Harrow
Faith in Harrow (2021) Christian (33.9%) Hindu (25.8%) Muslim (15.9%) No Religion (10.6%) Jewish (2.8%) Jain (2.4%) Buddhist (1.1%) Sikh (1.1%) Other Religions (0.5%) Religion not Stated (5.9%)
Harrow is known for having many different religions. In fact, it's the most religiously diverse local area in the UK. The 2011 census showed that 25.3% of Harrow's population were Hindu. This is the highest percentage in the UK. Many Jewish people live in Stanmore and Hatch End. The Stanmore and Canons Park Synagogue is the largest synagogue in all of Europe. Harrow also has a large Muslim community.
Arts and Culture in Harrow
The Usurp Art Gallery & Studios opened in West Harrow in 2010. It is the first and only contemporary art gallery in Harrow run by artists. It helps artists and offers public art studios. It's an important project supported by Arts Council England.
Harrow has 289 listed buildings. These are buildings with special historical or architectural importance. More than 80 are in Harrow-on-the-Hill and over 50 in Pinner. Important buildings include the Church of St Lawrence, Stanmore and Headstone Manor. Other listed buildings are Bentley Priory, Grim's Dyke, and Harrow and Wealdstone station.
Economy and Jobs
Some of the big employers in Harrow have included Kodak, the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, and Ladbrokes. Ladbrokes, a betting company, used to have its main offices in Harrow.
Sports and Fun Activities
Harrow has four non-league football clubs. These include Wealdstone FC, Harrow Borough F.C., and Rayners Lane F.C.. Barnet F.C. also plays in Harrow. Five of the 30 cricket clubs in the Middlesex County Cricket League are in Harrow. These are Harrow, Harrow St Mary's, Harrow Town, Kenton, and Stanmore.
Harrow also had a professional rugby league team, the London Broncos, in 2014 and 2015. They played at The Hive Stadium.
Education in Harrow
Harrow is known for its good schools. It has many state-funded primary and secondary schools. There are also several large colleges.
Secondary Schools and Colleges
For a long time, secondary schools in Harrow did not have their own sixth forms. Students leaving school had to go to colleges like Harrow College and Stanmore College. This system started in 1987. However, some people felt the colleges didn't keep up the same high standards as the secondary schools.
Eventually, the council changed things again. They created the Harrow Sixth Form Collegiate. This is a group of secondary schools working together. This allowed schools to have their own sixth forms again starting in 2008. Some Catholic schools, like Salvatorian College and Sacred Heart Language College, were not affected. Their students could still go to St Dominic's Sixth Form College.
Since September 2010, primary school students now move to secondary school at age 11. This is similar to other London Boroughs.
Harrow has a Music Service that teaches music to many students. About 15% of all state school pupils in Harrow learn an instrument. This is higher than the national average.
Independent Schools
Harrow has famous independent schools. These include Harrow School and John Lyon School for boys. North London Collegiate School is a top school for girls. These schools are often ranked among the best in the country. Other notable independent primary schools are Orley Farm School and Reddiford School.
Special Needs and Other Schools
There are also "voluntary aided" schools in Harrow. These include Salvatorian College (Catholic, boys), Sacred Heart Language College (Catholic, girls), and Moriah Jewish Day School (Jewish, mixed).
Harrow has two high schools for students with special needs: Kingsley High School and Shaftesbury High School.
Other state secondary schools in Harrow include Whitefriars High School, Bentley Wood High School, Canons High School, Harrow High School, Hatch End High School, Nower Hill High School, Park High School, Rooks Heath School, and Whitmore High School.
Student Voice
All students in Harrow can be elected to the Harrow Youth Parliament. This group of about 50 young people works on projects that help other young people. They also speak for young people to the council.
Transport in Harrow
Harrow has many train and tube stations. This is because it was historically part of an area called "Metro-land". Four different London Underground lines serve the area. The Bakerloo and Jubilee lines end in Harrow. The Piccadilly and Metropolitan lines pass through the south of the borough. The Northern line ends just outside Harrow.
The London Overground also serves Harrow. It shares tracks with the Bakerloo line. It goes beyond Harrow & Wealdstone station to Watford Junction.
Stations in Harrow
The many train and tube stations in Harrow include:
- Canons Park
- Harrow & Wealdstone
- Harrow-on-the-Hill
- Hatch End
- Headstone Lane
- North Harrow
- Pinner
- Rayners Lane
- South Harrow
- Stanmore
- Sudbury Hill
- Sudbury Hill Harrow
- West Harrow
In 2011, most residents traveled to work by driving a car or van (27.5%). Other popular ways were by tube, bus, or train.
Town Twinning
Harrow is twinned with the town of Douai in France. This means they have a special friendship and cultural exchange.
Harrow's Coat of Arms
Harrow Urban District Council received its coat of arms in 1938. A coat of arms is a special design that represents a place or family. When Harrow became a municipal borough in 1954, it was given "supporters" for its arms. These are figures on either side of the shield. When it became a London Borough in 1965, it kept the same coat of arms. The football club Harrow Borough F.C. also uses these arms. The motto is "Salus Populi Suprema Lex." This is Latin for "The well-being of the people is the highest law."
Freedom of the Borough
The "Freedom of the Borough" is a special honor given to people or groups. It recognizes their great service to Harrow.
Individuals Honored
- Sir Winston Churchill: December 30, 1955.
- Sir Roger Bannister: May 2004.
- Keith Toms: November 26, 2020.
Military Units and Organizations Honored
- 131 Independent Commando Squadron, Corps of Royal Engineers: March 10, 1983.
- 47 (Middlesex Yeomanry) Signal Squadron: March 10, 1983.
- 257 (Southern) General Hospital Royal Army Medical Corps: March 10, 1983.
- RAF Stanmore Park: October 20, 1988.
- RAF Bentley Priory: October 20, 1988.
- Roxeth & Harrow Company, Church Lads' & Church Girls' Brigade: October 20, 1994.
- Royal British Legion (Harrow Branch): July 18, 1996.
- Girls' Brigade North West London District: May 1, 2014.
- 1454 (Harrow) Squadron Air Training Corps: May 1, 2014.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Municipio de Harrow (Londres) para niños
In Spanish: Municipio de Harrow (Londres) para niños