Middle Paleolithic facts for kids
| Period | Stone Age |
|---|---|
| Dates | 300,000 to 50,000 BP |
| Preceded by | Lower Paleolithic |
| Followed by | Upper Paleolithic |
| The Paleolithic |
|---|
|
↑ Pliocene (before Homo) |
| Lower Paleolithic (c. 3.3 Ma – 300 ka)
(300–45 ka)
(50–10 ka)
|
| ↓ Mesolithic ↓ Stone Age |
The Middle Paleolithic is the second part of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. This period is understood differently in various parts of the world. In Europe, Africa, and Asia, it broadly lasted from about 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. However, the exact dates can change depending on the region. For example, in Great Britain, the early Middle Paleolithic was around 325,000 to 180,000 years ago. The late Middle Paleolithic there was about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago.
During this time, anatomically modern humans, like us, started moving out of Africa. This happened around 125,000 years ago. They began to live alongside or replace older human groups, such as the Neanderthals and Homo erectus.
Contents
How Humans Became More Modern
The first signs of modern human behavior appeared during the Middle Paleolithic. This means people started showing more complex ways of thinking and living. However, clear evidence of these modern behaviors became much more common later, in the Upper Paleolithic period.
Early Burials and Beliefs
Some ancient burial sites show that Middle Paleolithic people might have had early forms of religious beliefs. For example, at Krapina in Croatia (about 130,000 years ago) and the Qafzeh and Es Skhul caves in Israel (about 100,000 years ago), human remains were found buried. Some experts think these burials suggest a belief in an afterlife. Other experts believe the burials were for practical, non-religious reasons.
Art and Cooperation
The earliest clear evidence of art from the Stone Age comes from Middle Paleolithic sites. For instance, at Blombos Cave, people made bracelets and beads. They also used ochre (a type of colored earth) for body paint or in rituals. Even older examples of art might exist, like the Venus of Tan-Tan.
During this period, people started working together more. They caught large fish and hunted big animals using special tools. This shows they had better teamwork and more organized societies.
Early Trade
Humans also began to trade over long distances during the Middle Paleolithic. This started as early as 120,000 years ago. They traded for rare items like ochre, which was often used for religious purposes. They also traded for raw materials. Trading between groups helped them survive. It allowed them to share resources and goods, especially when food or materials were scarce.
How People Lived Together
Evidence from old sites and studies of modern hunter-gatherers show that Middle Paleolithic people lived in small groups. These groups were likely very equal, meaning everyone had a similar status. Both Neanderthal and early modern human societies took care of older members of their groups.
Some scientists think that this equality helped groups share food and other resources fairly. This would have prevented hunger and kept everyone fed.
Roles of Men and Women
It was once thought that women always gathered plants and firewood, while men hunted. However, some researchers now suggest that this clear division of labor by sex did not exist before the Upper Paleolithic. They believe that men and women might have shared more tasks. This division of labor may have developed later to help humans get food and other resources more efficiently.
What People Ate
Most of the food during the Middle Paleolithic came from gathering plants and hunting animals. But people also started to add seafood to their diet. They also learned to smoke and dry meat to keep it longer.
For example, about 90,000 years ago, people in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo hunted large catfish using special barbed fishing tools. Neanderthals and early modern humans in Africa also began to collect and cook shellfish. This is shown by shellfish remains found at sites in Italy (about 110,000 years ago) and Pinnacle Point in Africa.
Tools and Technology
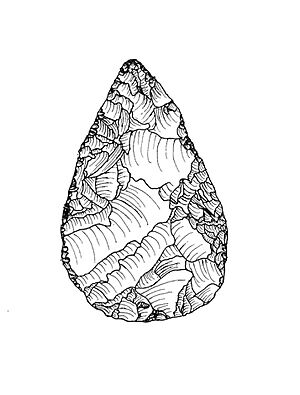
Around 200,000 years ago, a new way of making stone tools appeared. It was called the prepared-core technique. This method was more advanced than earlier techniques. It allowed people to make more controlled and consistent flakes (sharp pieces of stone).
This new method helped Middle Paleolithic humans create stone-tipped spears. These were the first tools made from different parts joined together. Groups like the Neanderthals used these tools. They were good at hunting large animals, just like later modern humans. Neanderthals might have also used projectile weapons, but they mostly hunted by ambushing animals and attacking them with thrusting spears.
The Use of Fire
The use of fire became common for the first time during the Middle Paleolithic. Humans started cooking their food around 250,000 years ago. Some scientists think that early humans began cooking frozen meat to make it easier to eat. This would have helped them survive in cold places.
Some scientists even believe that dogs might have been first tamed during the Middle Paleolithic, possibly around or before 100,000 BCE. This idea is based on studies of dog DNA.
Important Sites
Cave Sites
Western Europe
- Axlor, Spain
- Grotte de Spy, Spy, Belgium
- La Cotte de St Brelade, Jersey
- Le Moustier, France—see also Mousterian
- Neandertal (valley), Germany
- Petralona, Greece
Middle East and Africa
- Aterian, North Africa
- Bisitun Cave, Iran
- Daş Salahlı, Azerbaijan
- Wezmeh, Iran
Open-Air Sites
- Biache-Saint-Vaast, France
- Maastricht-Belvédère, The Netherlands
- Veldwezelt-Hezerwater, Belgium
See also
 In Spanish: Paleolítico medio para niños
In Spanish: Paleolítico medio para niños

