Minute and second of arc facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Arcminute |
|
|---|---|
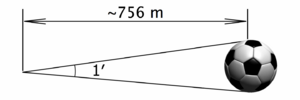
An illustration of the size of an arcminute (not to scale). A standard association football (soccer) ball (with a diameter of 22 cm or 8.7 in) subtends an angle of 1 arcminute at a distance of approximately 756 m (827 yd).
|
|
| General information | |
| Unit system | Non-SI units mentioned in the SI |
| Unit of | Angle |
| Symbol | ′ or arcmin |
| In units | Dimensionless with an arc length of approx. ≈ 0.29091000 of the radius, i..e. 0.2909 mmm |
| Conversions | |
| 1 ′ in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| degrees | 160° = 0.016° |
| arcseconds | 60″ |
| radians | π10800 ≈ 0.000290888 rad |
| milliradians | π·100010800 ≈ 0.2909 mrad |
| gons | 9600g = 0.015g |
| turns | 121600 |
An arcminute (also called a minute of arc or arc min) is a way to measure angles. Imagine a circle. A full circle is 360 degrees. An arcminute is a very small part of a degree. It is equal to 160 of one degree. This means there are 60 arcminutes in one degree.
A second of arc (also called an arcsecond or arc sec) is even smaller! It is 160 of an arcminute. So, there are 60 arcseconds in one arcminute. This also means there are 3,600 arcseconds in one degree (60 arcseconds × 60 arcminutes).
These tiny units are used in many areas. They are especially useful when measuring very small angles. You will find them in astronomy, optometry (eye care), navigation, and even when talking about firearm accuracy.
To measure even smaller angles, scientists use SI prefixes. For example, a milliarcsecond (mas) is one-thousandth of an arcsecond. A microarcsecond (μas) is one-millionth of an arcsecond.
Contents
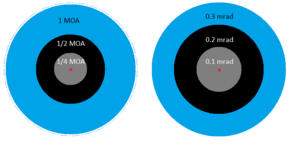
Symbols and Abbreviations
We use special symbols for arcminutes and arcseconds.
- The symbol for an arcminute is ′ (a single prime symbol). So, 1 arcminute is written as 1′.
- The symbol for an arcsecond is ″ (a double prime symbol). So, 1 arcsecond is written as 1″.
You might also see abbreviations:
- arcmin or amin for arcminute.
- arcsec or asec for arcsecond.
Here is a table showing how these units relate to each other:
| Unit | Value | Symbol | Abbreviations | In radians, approx. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree | 1360 turn | ° | Degree | deg | 17.4532925 mrad |
| Arcminute | 160 degree | ′ | Prime | arcmin, amin, am, MOA | 290.8882087 μrad |
| Arcsecond | 160 arcminute = 13600 degree | ″ | Double prime | arcsec, asec, as | 4.8481368 μrad |
| Milliarcsecond | 0.001 arcsecond = 13600000 degree | mas | 4.8481368 nrad | ||
| Microarcsecond | 0.001 mas = 0.000001 arcsecond | μas | 4.8481368 prad | ||
In celestial navigation (finding your way using stars), people often use degrees and decimal parts of a minute. For example, 42° 25.32′ means 42 degrees and 25.32 arcminutes. This is also how many GPS devices show location.
Common Examples of Size
These units help us understand how small some angles are.
- The full Moon looks about 31 arcminutes wide in the sky. That's about half a degree.
- Your eye can usually see details that are about one arcminute apart. This is called resolution.
- A U.S. dime coin (about 18 mm wide) held 4 kilometers (about 2.5 miles) away looks about one arcsecond wide.
- One milliarcsecond is like seeing a half dollar coin from the distance between the Washington Monument and the Eiffel Tower.
- One microarcsecond is like seeing a tiny period at the end of a sentence on a book left on the Moon, from Earth!
Here are some other examples from space:
- The Hubble Space Telescope can see details as small as 0.1 arcseconds.
- The planet Venus can appear between 10 and 60 arcseconds wide, depending on where it is in its orbit.
History of These Units
The idea of dividing a circle into degrees, minutes, and seconds came from ancient Babylon. The Babylonians were great astronomers and mathematicians. They divided the sky into 360 degrees. Then, they divided each degree into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds. This system, based on the number 60 (called sexagesimal), is still used today for angles and time.
How Arcminutes and Arcseconds are Used
In Astronomy

Astronomers use arcminutes and arcseconds all the time. They help measure the exact positions of stars and planets. They also measure how big objects look in the sky (their angular diameter). For example, they use these units to describe:
- The apparent size of planets.
- How much stars move over time (their proper motion).
- The distance to stars using parallax. Parallax is the small shift in a star's position as Earth orbits the Sun. The unit of distance called the parsec comes from "parallax of one arcsecond."
The European Space Agency's Gaia satellite, launched in 2013, is incredibly precise. It can measure star positions down to 7 microarcseconds!
When looking at stars from Earth, our atmosphere can make them look blurry. This is called atmospheric blurring. It can make a star appear about 0.5 arcseconds wide. Special tools like Adaptive optics can help telescopes on the ground see more clearly, sometimes down to 0.05 arcseconds. Space telescopes, like the Hubble Space Telescope, are not affected by the atmosphere.
Arcminutes and arcseconds are also important for making maps (cartography) and for navigation.
- At sea level, one arcminute along the equator is almost exactly one nautical mile. A nautical mile is about 1.852 kilometers.
- Locations on Earth are often given using degrees, minutes, and seconds of latitude (north or south of the equator) and longitude (east or west of the Prime Meridian). For example, a lighthouse might be at 50° 39.734′ N, 001° 35.500′ W.
In Firearms
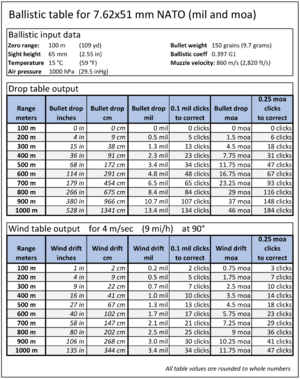
In the world of firearms, especially for rifles, the arcminute is called minute of angle (MOA). It helps measure how accurate a rifle is.
- At 100 yards, 1 MOA covers a circle about 1.047 inches wide. This is often rounded to just 1 inch.
- If a rifle is called a "1 MOA rifle," it means it can usually shoot groups of shots that fit into a 1-inch circle at 100 yards. This shows how precise the rifle is.
Many rifle scopes can be adjusted in small steps, like 12, 14, or 18 MOA per "click." This makes it easier for shooters to adjust their aim. For example, if your shots are 3 inches too high at 100 yards, you would adjust your scope 3 MOA "down." If your scope adjusts in 14 MOA clicks, you would turn it 12 clicks down (3 MOA × 4 clicks/MOA).
Another system used in firearms is the milliradian (mrad or 'mil').
- 1 mrad is about 3.44 MOA.
- A common adjustment on mrad scopes is 110 mrad. This equals exactly 1 centimeter at 100 meters. This makes it very easy to adjust for distance in metric units.
| Increment, or click |
(mins of arc) |
(milli- radians) |
At 100 m | At 100 yd | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | (cm) | (in) | (in) | |||
| style="text-align:center;" | 0.083′ | 0.024 mrad | 2.42 mm | 0.242 cm | 0.0958 in | 0.087 in |
| style="text-align:center;" | 0.086′ | 0.0985 in | 0.09 in | |||
| style="text-align:center;" | 0.036 mrad | 3.64 mm | 0.36 cm | 0.144 in | 0.131 in | |
| style="text-align:center;" | 0.167′ | 0.0485 mrad | 4.85 mm | 0.485 cm | 0.192 in | 0.175 in |
| style="text-align:center;" | 0.172′ | 0.197 in | 0.18 in | |||
| style="text-align: center;" | 0.073 mrad | 7.27 mm | 0.73 cm | 0.29 in | 0.26 in | |
| style="text-align:center;" | 0.344′ | 0.39 in | 0.36 in | |||
| style="text-align:center;" | 0.145 mrad | 14.54 mm | 1.45 cm | 0.57 in | 0.52 in | |
| style="text-align: center;" | 0.516′ | 0.59 in | 0.54 in | |||
| style="text-align: center;" | 0.688′ | 0.79 in | 0.72 in | |||
| style="text-align: center;" | 0.291 mrad | 29.1 mm | 2.91 cm | 1.15 in | 1.047 in | |
| style="text-align: center;" | style="text-align: right;" | 3.9 in | 3.6 in | |||
In Human Vision
When we talk about 20/20 vision, it means a person can see details that are separated by an angle of one arcminute from 20 feet away. This shows how sharp human eyesight can be.
In Manufacturing
Some very precise measuring tools use arcminutes and arcseconds. For example, in optical engineering, the slight tilt between two surfaces might be measured in arcseconds. This helps make sure parts are made perfectly.
See also
 In Spanish: Minuto y segundo de arco para niños
In Spanish: Minuto y segundo de arco para niños
- Gradian
- Degree (angle) § Subdivisions
- Sexagesimal § Modern usage
- Square minute
- Square second
- Steradian
- Milliradian
 | Stephanie Wilson |
 | Charles Bolden |
 | Ronald McNair |
 | Frederick D. Gregory |