Photography facts for kids

Photography is a cool way to make pictures using a special device called a camera. The person who takes these pictures is known as a photographer. And the picture itself? We call it a photograph or simply a photo!
Contents
What is a Camera?
Imagine a camera as a simple box with a small hole in the front. This hole has a special piece of glass called a lens. When you want to take a picture, the lens helps create a tiny image of what you're looking at inside the camera. It does this by gathering and focusing light. Think of a camera lens like the lenses in glasses or a magnifying glass. Some very basic cameras, like a Pinhole camera, don't even have a lens; they just use a tiny hole to focus the light.
To snap a photo, you press a button called the shutter release. This button opens something called the shutter. The shutter is like a little door that covers the hole inside the camera, right behind the lens. When the shutter is closed, no light can get in. When you press the button, the shutter opens and then quickly closes. This happens super fast! The amount of time the shutter stays open is called the shutter speed. It can be as quick as 1/1000th of a second (that's 0.001 seconds!) or even a few seconds. Usually, it's much faster than one second.
Some cameras also have an aperture ring. This ring helps control how much light gets into the camera.
The picture inside the camera is captured either on a special material called film or, in modern digital cameras, by an electronic sensor.
How Film Works
In older cameras, the picture the lens makes is recorded on photographic film. This film is placed inside the camera. When light comes through the lens, passes the aperture, and the shutter opens, it shines onto the film. Photographic film has special chemicals on it that react when light hits them. Letting light shine on the film is called exposing the film.
There are many kinds of photographic film. Some films are for taking color pictures, and others are for black and white photos. They also come in different sizes. The most common size is 35 mm, named because the film is 35 millimeters wide. Most cameras used this size.
Another difference between films is how sensitive they are to light. Films have a special code number called an ISO number. This number tells you how quickly the film reacts to light. For example, you might see ISO 50, ISO 100, ISO 200, ISO 400, ISO 800, or ISO 1600. The ISO number is sometimes also called the ASA number or the film speed.
- When the ISO number is low (like ISO 50), the film takes longer to record the picture. This is called a slow film, meaning the shutter needs to stay open for a longer time.
- When the ISO number is high (like ISO 800), the picture is made very quickly. This is a fast film, so the shutter opens and closes very fast.
Developing Film and Prints
Once the film has been exposed to light, it needs to be processed. This processing must happen in complete darkness, or the film will get too much light and the picture will be ruined. Processing stops the film from reacting to light anymore. After it's processed, you can finally see the pictures on the film!
A photographic print is a photo made on paper. To make a print, you use special light-sensitive paper. The picture on the film is put into a machine called an enlarger. An enlarger shines light through the film, making a bigger picture appear on the light-sensitive paper. A chemical reaction happens in the paper, turning the areas hit by light black when the paper is 'developed'. (More light means a darker area.) Developing makes the picture show up on the paper – now it's a photograph! Then, the paper is put into other chemicals that make it no longer sensitive to light. This step is called "fixing." Finally, the paper is washed to remove any remaining chemicals and then dried. And just like that, your photo is ready!
Digital Photography Today

Digital photography uses a digital camera. Sometimes it's called digital imaging. Just like traditional cameras, a digital camera has a lens, an aperture, and a shutter. But instead of film, the picture the lens makes is recorded by a light-sensitive electronic sensor.
Digital cameras don't use photographic film. Instead, digital photos are saved on storage devices like SD cards. You can then easily move them to a computer. You can also print paper copies from digital pictures. A big advantage of digital cameras is that they are not expensive to use because you don't need to buy film!
Taking a Great Photograph
One of the most important things when taking a photograph is making sure the lens is focused. If the lens isn't focused well, your picture will look blurry. Many modern cameras have autofocus, which means they focus automatically when you press the shutter release button. Older cameras often have manual focus, where you adjust it yourself.
Three other things are super important for how bright or dark your photograph will be:
- The shutter speed: This is how long the shutter stays open. It's written like "1/400," meaning one four-hundredth of a second.
- The aperture: This is how wide the opening in the lens gets. A wider opening lets in more light. It's written like "f/5.6," which describes the size of the opening compared to the lens's focal length.
- The film speed (or ISO): This tells you how quickly the film or digital sensor records the picture. It's written like "400."
Here's how they work together:
- A slower shutter speed, a bigger aperture, and a faster film/higher ISO sensor all make a brighter picture.
- A faster shutter speed, a smaller aperture, and a slower film/lower ISO sensor all make a darker picture.
A good picture is just right – not too bright and not too dark. If a picture is too bright, it's called "overexposed". Many modern cameras can change these settings by themselves when you press the shutter button, making it easier to get a great shot!
Images for kids
-
Earliest known surviving heliographic engraving, 1825, printed from a metal plate made by Nicéphore Niépce. The plate was exposed under an ordinary engraving and copied it by photographic means. This was a step towards the first permanent photograph taken with a camera.
-
View of the Boulevard du Temple, a daguerreotype made by Louis Daguerre in 1838, is generally accepted as the earliest photograph to include people. It is a view of a busy street, but because the exposure lasted for several minutes the moving traffic left no trace. Only the two men near the bottom left corner, one of them apparently having his boots polished by the other, remained in one place long enough to be visible.
-
View from the Window at Le Gras, 1826 or 1827, the earliest surviving camera photograph. Original plate (left) and colorized reoriented enhancement (right).
-
A latticed window in Lacock Abbey, England, photographed by William Fox Talbot in 1835. Shown here in positive form, this may be the oldest extant photographic negative made in a camera.
-
The first color photograph made by the three-color method suggested by James Clerk Maxwell in 1855, taken in 1861 by Thomas Sutton. The subject is a colored, tartan patterned ribbon.
-
Color photography was possible long before Kodachrome, as this 1903 portrait by Sarah Angelina Acland demonstrates, but in its earliest years, the need for special equipment, long exposures, and complicated printing processes made it extremely rare.
-
This image of the rings of Saturn is an example of the application of ultraviolet photography in astronomy
-
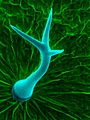
Devices other than cameras can be used to record images. Trichome of Arabidopsis thaliana seen via scanning electron microscope. Note that image has been edited by adding colors to clarify structure or to add an aesthetic effect. Heiti Paves from Tallinn University of Technology.
-
Classic Alfred Stieglitz photograph, The Steerage shows unique aesthetic of black-and-white photos.
-
The Musée de l'Élysée, founded in 1985 in Lausanne, was the first photography museum in Europe.
See also
 In Spanish: Fotograf%C3%ADa para ni%C3%B1os
In Spanish: Fotograf%C3%ADa para ni%C3%B1os