Prince Creek Formation facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Prince Creek FormationStratigraphic range: Early Maastrichtian 70.6–69.1Ma |
|
|---|---|
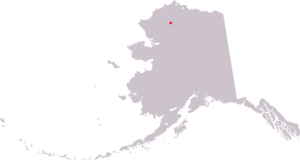
General location of the Prince Creek Formation, in red
|
|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Colville Group |
| Sub-units | Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry, Kogosukruk Tongue, Ocean Point, Coleville River Bluff |
| Underlies | Sagavanirktok Formation |
| Overlies | Schrader Bluff Formation |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sandstone, mudstone |
| Other | siltstone, carbonaceous shale, ash-fall |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 70°00′N 151°30′W / 70.0°N 151.5°W |
| Approximate paleocoordinates | 83°12′N 115°54′W / 83.2°N 115.9°W |
| Region | |
| Country | |
The Prince Creek Formation is a special place in Alaska where scientists find amazing fossils. It's like a giant time capsule made of rock! These rocks formed a very long time ago, during a period called the Early Maastrichtian. Many incredible dinosaur remains have been discovered here, giving us clues about what life was like in ancient Alaska.
Contents
When Did the Prince Creek Formation Form?
The rocks of the Prince Creek Formation were laid down between about 80 and 61.7 million years ago. Most of the dinosaur fossils come from a spot called the Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry. This part of the formation is about 70.6 to 69.1 million years old.
Some older parts, like the Kogosukruk Tongue, date back to 72 to 71 million years ago. The very youngest part, Ocean Point, goes into the Paleogene period. This means it formed right after the dinosaurs disappeared.
What Was the Ancient Habitat Like?

When the Prince Creek Formation was forming, Earth was much warmer. It was a "greenhouse" phase, meaning there was no ice at the poles. The area was a muddy coastal plain, close to a large body of water.
Scientists know this because they found gypsum and pyrite in nearby rocks. These minerals often form near water. The land was full of plants, like leafy plants, roots, and pollen. There's even evidence that dinosaurs walked all over the plants!
The Prince Creek Formation was likely a cool, polar woodland. It didn't have ground ice, even though it was far north. Tall flowering plants and trees grew everywhere. Dinosaurs were the main animals roaming this ancient forest.
The average temperature was around 5 to 6 degrees Celsius (41 to 43 degrees Fahrenheit). In colder months, it was about 2 to 4 degrees Celsius (36 to 39 degrees Fahrenheit). Warmer months saw temperatures of 10 to 12 degrees Celsius (50 to 54 degrees Fahrenheit). It rained quite a bit, too, with about 500 to 1500 millimeters (20 to 59 inches) of rain each year.
Amazing Ancient Animals (Vertebrate Paleofauna)
Many different kinds of animals lived in the Prince Creek area long ago. Scientists have found fossils of dinosaurs and even tiny mammals!
Dinosaurs
Meat-Eating Dinosaurs (Theropods)
Scientists have found teeth from large meat-eating dinosaurs called tyrannosaurids. These teeth come from different fossil sites like Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry.
Color key
|
Notes Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; |
| Theropods | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
D. cf albertensis |
Liscomb Quarry, Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry, Byers Bed |
Fossilized teeth |
A dromaeosaur, a type of fast, meat-eating dinosaur. | ||
|
Gruipeda |
G. vegrandiunis |
Denali Park |
Footprints from a small ancient bird. |
||
|
Saurornitholestinae indet. |
Indeterminate |
Pediomys Point - Liscomb Quarry |
Small jawbone tip from a young dinosaur. |
A new type of dromaeosaurid, similar to Saurornitholestes. |
|
|
N. hoglundi |
Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry |
One partial skull, including parts of the upper and lower jaw. |
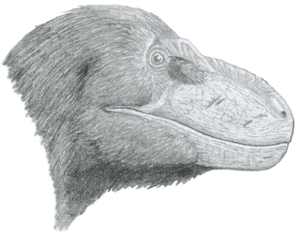
Nanuqsaurus was a smaller tyrannosaurid. It was related to famous dinosaurs like Tyrannosaurus. |
||
|
Saurornitholestes |
S. cf. langstoni |
Old Bone Beach |
Teeth |
Another type of dromaeosaur. | |
|
T. sp |
Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry, Liscomb Quarry, Byers Bed, Magical Mystery Bar |
Teeth and braincases have been found. |
These Troodon remains are about 50% larger than those found elsewhere. It was the most common meat-eating dinosaur here. |
||
Plant-Eating Dinosaurs (Ornithischians)
Color key
|
Notes Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; |
| Ornithischians of the Prince Creek Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
A. gangloffi |
Kogosukruk Tongue |
A skull bone and part of its head dome. |
This was the first pachycephalosaur (a dinosaur with a thick, bony skull dome) found in Alaska. |
||
|
P. perotorum |
Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry |
Lots of bones, including a young dinosaur. |
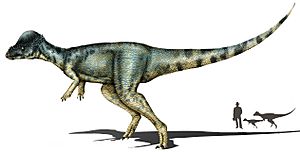
This is the youngest species of Pachyrhinosaurus, a horned dinosaur. It was found very far north. Scientists learned how its head crest grew by studying a young Pachyrhinosaurus. |
||
|
E. sp |
Liscomb Bonebed, Kikak-Tegoseak Quarry |
Young dinosaurs |
These duck-billed dinosaurs were once thought to be a different genus, but recent studies show they are young Edmontosaurus. |
||
| Lambeosaurinae indet. | Indeterminate | Liscomb Bonebed | A supraoccipital bone (part of the skull). | This was the first confirmed lambeosaurine (another type of duck-billed dinosaur with a crest) found in the Prince Creek Formation. | |
Ancient Mammals
Small mammals also lived alongside the dinosaurs in the Prince Creek Formation.
| Mammals of the Prince Creek Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Abundance | Notes | Images |
| Unnuakomys | U. hutchisoni | Pediomys Point | Lower Maastrichtian | Over 60 specimens | A small ancient mammal, similar to a marsupial. | |
Ancient Plants
The Prince Creek Formation was home to many different types of plants. These plants helped create the environment where dinosaurs lived. Scientists find their pollen and leaf fossils.
Color key
|
Notes Uncertain or tentative taxa are in small text; |
| Plants of the Prince Creek Formation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Abundance | Notes | Images |
|
Parataxodium |
P. wigginsii |
Kogosukruk Tongue |
A conifer tree that was common in the ancient forests. |
||
|
Hollickia |
H. quercifolia |
Kogosukruk Tongue |
Leaves |
An angiosperm (flowering plant) known from its leaves. |
|
|
Quereuxia |
Q. angulata |
Kogosukruk Tongue |
An aquatic flowering plant that lived in the water. |
||
|
Equisetites |
E. sp. |
Kogosukruk Tongue |
A type of horsetail plant. |
||
|
Botryococcus |
B. braunii |
Coleville River Bluff |
Pollen |
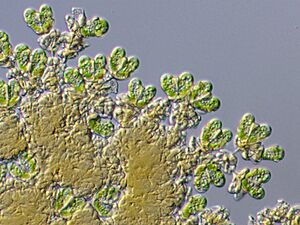
A type of green algae, also found in the Schrader Bluff Formation. |
|