Çifte Minareli Medrese in Erzurum
Seljuk architecture is the special style of buildings created by the Seljuks. They were a powerful group who ruled much of the Middle East and a place called Anatolia. This happened between the 1100s and 1200s. After the 11th century, a new group, the Seljuks of Rum, grew from the main Great Seljuk Empire. They created their own unique building style. Their main city was Konya. Their designs were inspired by the Armenians, Byzantines, and Persians.
Great Seljuk Empire Buildings
You can find Seljuk buildings in a huge area. This area stretches from the Hindu Kush mountains to eastern Anatolia. It also goes from Central Asia to the Persian Gulf. The first Seljuk buildings were made in Turkmenistan and Iran. Sadly, many of these early buildings were destroyed. This happened during the Mongol invasions. Only a few of them still stand today. In 1063, Isfahan became the main city of the Great Seljuk Empire. This was under the ruler Alp Arslan.
Changes in Building Design
A very important change happened in the early 12th century. Mosques (places of worship) started to look different. They changed from a simple hall (called a hypostyle plan) to a four-iwan plan. An iwan is a vaulted hall or space, open on one side. The Shah Mosque is a good example of this style. Another new type of mosque was the kiosk mosque. This was a domed space with three open sides. It had a wall with a mihrab (a special niche showing the direction of prayer).
Memorial Tombs
Buildings from this time also included many memorial tombs. These tombs were usually octagonal (eight-sided) buildings. They had domed roofs. These special tombs were called Kümbet or Türbe. A great example is the mausoleum of Sultan Sanjar. It is located in Merv. This is a huge building, about 27 meters (89 feet) square. It has a massive double dome. The dome rests on special supports called squinches and muqarnas.
Related pages
Gallery
-
-
-
-
Tomb of Zubaidah bint Ja`far in Baghdad
-
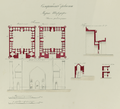
four-iwan plan, section, and elevation
-
Mausoleum of Sultan Sanjar
Images for kids
-
Combination of brickwork and tile decoration on the Gonbad-e Kabud Tomb in Maragha (1196–1197)
-
Mihrab of carved stucco decoration in the Jameh Mosque of Ardestan (circa 1160)
-
Muqarnas in the southern iwan of the Jameh Mosque of Isfahan (early 12th century)
-
Stone-carved decoration in the entrance portal of the Ince Minareli Medrese in Konya (c. 1265)
-
Kızıl Kule (Red Tower) built between 1221–1226 by Kayqubad I in Alanya
-
Malabadi Bridge (1147) near Silvan
-
A double-headed eagle relief, 13th-century, Divriği Great Mosque and Hospital
-
Head of a dragon carved on the façade of the Çifte Minareli Medrese in Erzurum
-
Pair of mirrored sirens above a niche on the Tomb of Hudavend Hatun
-
Head of a bull, one of the animals of the zodiac, carved onto the Tomb of Emir Saltuq
-
Kharraqan Towers, mausoleums of Seljuk princes, built in 1068 and 1093 in Iran
-
Entrance portal of the Ribat-i Malik caravanserai on the road between Bukhara and Samarkand (c. 1068–1080)
-
-
Courtyard of the Friday Mosque in Isfahan, with its four-iwan layout dating from the early 12th century
-
Ribat-i Sharaf caravanserai in Khorasan (northeastern Iran), built in 1114–1115
-
Toghrol Tower in Rayy, south of present-day Tehran (Iran), built in 1139 as the tomb of the Seljuk sultan Tughril
-
-
Citadel Mosque in Divrigi (1180–1181)
-
Interior of the Citadel Mosque in Erzurum (12th century)
-
Great Mosque of Sivas (1197)
-
Great Mosque of Diyarbakir (founded in 7th century, reconstructed in 12th century)
-
Details of the decorated eastern courtyard façade in the Great Mosque of Diyarbakir
-
Façade of the Great Mosque (Ulu Cami) of Kızıltepe, begun by the Artuqids in 1204
-
Alaeddin Mosque of Niğde (1223)
-
The portal of the Divriği Great Mosque in Divriği (1228–1229)
-
Interior of the Divriği Great Mosque
-
Domed area (originally a small open court) in the centre of the Hunat Hatun Mosque in Kayseri (1237–1238)
-
Great Mosque (Ulu Cami) of Afyonkarahisar (1272), an example of a wooden hypostyle mosque
-
Eşrefoğlu Mosque in Beyşehir (1297), another wooden column mosque
-
Tiled mihrab of the Eşrefoğlu Mosque
-
Interior of the Great Mosque (Ulu Cami) of Manisa, built by the Saruhanids around 1371
-
Isa Bey Mosque in Selçuk (1374)
-
-
Gevher Nesibe Medrese (or Çifte Medrese) in Kayseri (c. 1205)
-
Portal of the Darüşşifa (hospital) in the Divriği mosque complex (1228–29)
-
Interior of the hospital in the Divriği mosque complex
-
Interior of the Çifte Minareli Medrese
-
Entrance portal of the Karatay Madrasa in Konya (c. 1251), with muqarnas and ablaq decoration
-
Tile decoration inside the Karatay Madrasa
-
Ince Minareli Medrese in Konya (c. 1265)
-
Façade of the Gök Medrese at Tokat, Turkey built ca. 1270
-
Entrance and minarets of the Gök Medrese in Sivas (1271–2)
-
Buruciye Medrese in Sivas (1271–2)
-
Courtyard of the Buruciye Medrese
-
Yakutiye Medrese in Erzurum (1310)
-
Interior of the Yakutiye Medrese, with central muqarnas vault
-
Tomb of Kiliç Arslan II in the Alaeddin Mosque of Konya (c. 1190)
-
Tomb of Sitte Melik in Divriği (before 1197)
-
Tomb of Emir Saltuq in Erzurum (late 12th century)
-
Tomb of Melike Mama Hatun in Tercan (early 13th century)
-
Outer wall and entrance portal to the Mama Hatun tomb
-
Decorated brick and tile façade of the tomb of Izz al-Din Kayka'us I in Sivas (1217–1218)
-
Döner Kümbet in Kayseri (1276), the tomb of a Seljuk princess
-
Hudavend Hatun Tomb in Niğde (1312)
-
Muqarnas portal (partly reconstructed) of the Alayhan, possibly circa 1190
-
Sultan Han caravanserai, built in 1229 on the road between Aksaray and Konya
-
Courtyard of the Sultan Han caravanserai
-
Covered hall of the Sultan Han
-
Elevated prayer room in the centre of the Sultan Han near Kayseri (1236–1237)
-
Courtyard of the Ağzıkara Han, completed in 1240
-
Courtyard of the Kırkgöz Han (between 1237 and 1246)
-
-
Courtyard and entrance to the covered hall of Karatay Han (c. 1240)
-
Minbar of the Alaeddin Mosque, Konya (1155–6)
-
Details of the kündekâri work on the Alaeddin Mosque's minbar
-
Front part of the Alaeddin Mosque's minbar
-
Minbar of the Ulu Cami of Siirt (13th century), now housed in the Ethnography Museum of Ankara
-
Minbar of the Great Mosque of Divriği (1228–9)
-
Detail of the Divriği minbar: the lines between the wooden boards mounted side-by-side are visible, while the surface itself is carved with motifs imitating kündekâri work
-
Detail from the front of the minbar of the Great Mosque of Sivirhisar (1275)
-
Front part of the minbar of the Eşrefoğlu Mosque, Beyşehir (1297–9)
See also
 In Spanish: Arquitectura selyúcida para niños
In Spanish: Arquitectura selyúcida para niños
 In Spanish: Arquitectura selyúcida para niños
In Spanish: Arquitectura selyúcida para niños