Sui dynasty facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sui
隋
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 581–618 | |||||||||||
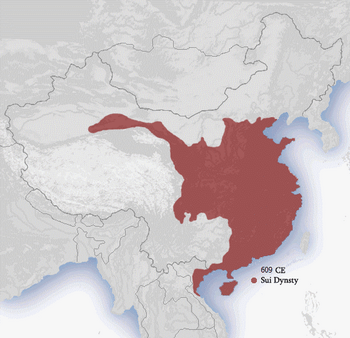
Sui dynasty c.609
|
|||||||||||
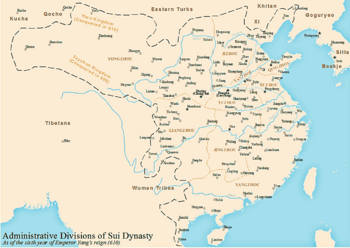
Administrative division of the Sui dynasty circa 610 AD
|
|||||||||||
| Capital | Daxing (581–605), Luoyang (605–618) | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Middle Chinese | ||||||||||
| Religion | Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism, Chinese folk religion, Zoroastrianism | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||
|
• 581–604
|
Emperor Wen | ||||||||||
|
• 604–617
|
Emperor Yang | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Postclassical Era | ||||||||||
|
• Ascension of Yang Jian
|
4 March 581 | ||||||||||
|
• Abolished by Li Yuan
|
23 May 618 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 589 est. | 3,000,000 km2 (1,200,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
|
• 609
|
est. 46,019,956 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Chinese coin, Chinese cash | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | China Vietnam |
||||||||||
| Sui dynasty | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

"Sui dynasty" in Chinese characters
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 隋朝 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Sui dynasty (Chinese: 隋朝; pinyin: Suí cháo) was a short but very important imperial dynasty in Chinese history. It lasted from 581 to 618 AD. This dynasty brought China back together after a long time of being split into many smaller kingdoms. It also helped bring back Chinese culture and rule to the whole country. The Sui dynasty set the stage for the famous Tang dynasty that came after it.
Contents
Founding the Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty was started by Emperor Wen of Sui, whose real name was Yang Jian. He became emperor in 581 AD. The first capital city was Chang'an, which was renamed Daxing. Later, the capital moved to Luoyang in 605 AD.
Important Leaders and Their Changes
Two main emperors ruled during the Sui dynasty: Emperor Wen and Emperor Yang. They made many big changes to how China was run.
- Fair Land System: They introduced the equal-field system. This system aimed to give land to farmers more fairly. It helped reduce differences in wealth and made farming better.
- New Government System: They set up the Three Departments and Six Ministries system. This was a new way to organize the government. It made the government more efficient and powerful.
- Standard Money: They made sure that all the money used across the empire was the same. This helped with trade and made the economy stronger.
- Buddhism: The emperors also encouraged Buddhism to spread throughout the empire.
By the middle of the Sui dynasty, China was doing very well. There was plenty of food, and the population grew quickly.
Amazing Building Projects
The Sui dynasty is famous for its huge building projects. These projects changed China forever.
The Grand Canal
One of the most important projects was the Grand Canal. This massive waterway connected different parts of China.
- Connecting Cities: It linked the capital cities of Chang'an and Luoyang to important farming areas in the east. It also reached the northern border near modern Beijing.
- Reasons for Building: The canal was first built to move food to the capital. It also helped transport soldiers and military supplies.
- Long-Term Benefits: Over time, the Grand Canal made it easier to trade goods within China. It also helped people travel and share ideas for hundreds of years.
Other Big Projects
Besides the Grand Canal, the Sui emperors also extended the Great Wall. They also built the new eastern capital city of Luoyang. These huge projects needed millions of workers. Many people were forced to work on them, and it was very hard labor.
Why the Sui Dynasty Ended
The Sui dynasty lasted only 37 years. It ended because of several big problems.
Costly Wars
Emperor Yang started many expensive and unsuccessful wars. The most damaging were the wars against Goguryeo, a kingdom in Korea. These wars were very costly and ended in defeat by 614 AD.
Heavy Taxes and Revolts
The huge building projects and wars cost a lot of money. The emperors made people pay very high taxes and forced them to work on these projects. This made many people angry. Widespread revolts started across the empire.
The End of the Dynasty
Finally, in 618 AD, Emperor Yang was killed by his own ministers. After his death, there was a short civil war. This led to the end of the Sui dynasty and the start of the Tang dynasty.
Sui Dynasty's Lasting Impact
Even though it was short, the Sui dynasty was very important. It is often compared to the earlier Qin dynasty. Both dynasties unified China after long periods of division. The Sui dynasty's reforms and building projects had a lasting impact. They helped create a strong foundation for the powerful Tang dynasty that followed.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
A Sui dynasty pilgrim flask made of stoneware.
-
A Sui dynasty stone statue of the Avalokitesvara Boddhisattva (Guanyin).
-
Chinese swords of the Sui dynasty, about 600, found near Luoyang. The P-shaped furniture of the bottom sword's scabbard is similar to and may have been derived from sword scabbards of the Sarmatians and Sassanians.
-
Model of a Pipa Player, Sui Dynasty
See also
 In Spanish: Dinastía Sui para niños
In Spanish: Dinastía Sui para niños






