Timeline of the Space Race facts for kids
This page is about achievements specific to the Space Race. For space achievements of all decades and nations, see Timeline of space exploration.
The Space Race was an exciting competition between the Soviet Union (USSR) and the United States. It happened during the Cold War, a time of political tension between the two superpowers. Both countries wanted to be the first to achieve amazing things in space. This timeline highlights the most important "firsts" by the USSR and USA during this period. These achievements were important for showing off new technology and for what people thought about each country's progress.
Contents
Starting the Race
| Date | Country | Achievement | Mission / Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 July 29 | The United States announced it planned to launch an artificial satellite into space. This was for the International Geophysical Year. | / | |
| 1955 August 30 | The Soviet Union decided to launch a 1.5-ton satellite. They planned to use their powerful R-7 ICBM rocket. | / |
1957–1959: Early Milestones

The first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1 (a replica).
| Date | Country | Achievement | Mission / Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 August 21 | First intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) launched. This was a very powerful long-range rocket. | R-7 Semyorka | |
| 1957 October 4 | First artificial satellite in orbit. It also sent the first man-made signals from space. | Sputnik 1 | |
| 1957 November 3 | First mammal in orbit around Earth. This was a dog named Laika. | Sputnik 2 | |
| 1958 March 17 | First satellite powered by solar panels. | Vanguard 1 | |
| 1959 January 2 | First spacecraft to fly past the Moon. It was also the first to leave Earth's orbit. | Luna 1 | |
| 1959 January 4 | First spacecraft to orbit the Sun (a heliocentric orbit). | Luna 1 | |
| 1959 February 28 | First satellite to fly over both poles of Earth (a polar orbit). | Discoverer 1 | |
| 1959 August 7 | First photograph of Earth taken from orbit. | Explorer 6 | |
| 1959 September 14 | First spacecraft to crash-land on another space body (the Moon). | Luna 2 | |
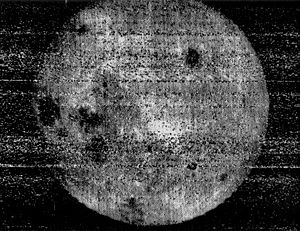
| 1959 October 7 | First photos of the far side of the Moon. This side is never seen from Earth. | Luna 3 |
1960–1969: Humans in Space and Moon Landings

The first human in space, Yuri Gagarin.
| Date | Country | Achievement | Mission / Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 August 11 | First satellite to be recovered whole from orbit. | Discoverer 13 | |
| 1960 August 18 | First spy photography from space. | Discoverer 14 | |
| 1960 August 19 | First animals and plants to return alive from space. These were the dogs Belka and Strelka. | Korabl-Sputnik 2 (Sputnik 5) | |
| 1961 January 31 | First great ape in space. This was Ham, a chimpanzee. | Mercury-Redstone 2 | |
| 1961 February 12 | First launch from Earth orbit into a solar orbit. | Venera 1 | |
| 1961 April 12 | First human spaceflight mission with Yuri Gagarin. He was the first human in space. | Vostok 1 | |
| 1961 May 5 | First pilot-controlled space flight by Alan Shepard. | Freedom 7 | |
| 1961 May 19 | First spacecraft to fly past Venus, though contact was lost. | Venera 1 | |
| 1961 August 6 | First crewed mission to last a full day, with Gherman Titov. | Vostok 2 | |
| 1962 August 12 | First dual crewed spaceflight with two spacecraft flying at the same time. | Vostok 3 / Vostok 4 | |
| 1962 December 14 | First successful mission to fly past Venus. | Mariner 2 | |
| 1963 June 16 | First woman in space, Valentina Tereshkova. She was also the first civilian in space. | Vostok 6 | |
| 1963 June 19 | First spacecraft to fly past Mars, though contact was lost. | Mars 1 | |
| 1963 July 19 | First reusable piloted spacecraft and first spaceplane (suborbital flight). | X-15 Flight 90 | |
| 1963 July 26 | First satellite that stayed in the same spot above Earth (a geosynchronous satellite). | Syncom 2 | |
| 1964 August 19 | First satellite that stayed in a fixed position relative to Earth (a geostationary satellite). | Syncom 3 | |
| 1965 March 18 | First spacewalk outside a spacecraft. | Voskhod 2 | |
| 1965 March 23 | First piloted spacecraft to change its orbit. | Gemini 3 | |
| 1965 July 14 | First successful mission to fly past Mars. | Mariner 4 | |
| 1966 February 3 | First soft landing on another space body (the Moon). It also sent the first photos from the Moon's surface. | Luna 9 | |
| 1966 March 1 | First crash-landing on another planet (Venus). | Venera 3 | |
| 1966 March 16 | First spacecraft to dock with another object in space. | Gemini 8 / ATV | |
| 1966 April 3 | First artificial satellite to orbit another space body (the Moon). | Luna 10 | |
| 1966 September 12 | First direct rendezvous (meeting) in space from the first orbit. | Gemini 11 / ATV | |
| 1967 October 18 | First time a spacecraft analyzed the atmosphere of another planet (Venus). | Venera 4 | |
| 1967 October 30 | First time two remote-controlled spacecraft docked together. | Cosmos 186 / Cosmos 188 | |
| 1968 September 14–21 | First return to Earth after circling the Moon. Also, the first living things to circle the Moon and return safely. | Zond 5 | |
| 1968 December 21 | First return to Earth after orbiting the Moon. This was also the first human mission to enter the Moon's gravity. | Apollo 8 | |
| 1969 January | First parachute to be used on another planet (Venus). | Venera 5 | |
| 1969 January 16 | First time astronauts exchanged places between two docked spacecraft. | Soyuz 4 / Soyuz 5 | |
| 1969 July 20 | First humans to walk on the Moon. Also, the first launch from another space body and first Moon samples brought back. | Apollo 11 | |
| 1969 November 19 | First very precise piloted landing on the Moon. | Apollo 12 |
1970–1979: Rovers and Space Stations

The first lunar rover, Lunokhod 1.
| Date | Country | Achievement | Mission / Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 September 24 | First robotic mission to bring samples back from another space body (the Moon). | Luna 16 | |
| 1970 November 23 | First remote-controlled rover on another space body (the Moon). | Lunokhod 1 | |
| 1970 December 15 | First soft landing on another planet (Venus). It also sent the first signals from another planet's surface. | Venera 7 | |
| 1971 April 19 | First human-crewed space station launched into orbit. | Salyut 1 | |
| 1971 June 29 | First human-crewed orbital observatory in space. | Soyuz 11 / Salyut 1 | |
| 1971 July 31 | First human-driven lunar rover on the Moon. | Apollo 15 | |
| 1971 November 14 | First spacecraft to orbit another planet (Mars). | Mariner 9 | |
| 1971 November 27 | First crash-landing on Mars. | Mars 2 | |
| 1971 December 2 | First soft landing on Mars. It also sent the first signals from Mars' surface. | Mars 3 | |
| 1972 March 3 | First spacecraft sent on a path away from the Sun. | Pioneer 10 | |
| 1972 July 15 | First mission to enter the asteroid belt and leave the inner part of our Solar System. | Pioneer 10 | |
| 1973 December 3 | First spacecraft to fly past Jupiter. | Pioneer 10 | |
| 1974 March 29 | First spacecraft to fly past Mercury. | Mariner 10 | |
| 1975 July 15 | First human-crewed mission involving more than one country. | Soyuz 19 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project |
|
| 1975 October 20 | First spacecraft to orbit another planet (Venus). It also sent the first clear photo from Venus's surface. | Venera 9 | |
| 1979 September 1 | First spacecraft to fly past Saturn. | Pioneer 11 |
1980–1989: Space Shuttles and New Frontiers

The first Space Shuttle launching.
| Date | Country | Achievement | Mission / Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 April 12 | First reusable spaceplane in orbit, the Space Shuttle. | STS-1 | |
| 1984 February 7 | First spacewalk without being tied to the spacecraft, by Bruce McCandless II. | STS-41-B | |
| 1985 June 11 | First balloon (aerostat) released into the atmosphere of Venus. | Vega 1 probe | |
| 1986 January 24 | First spacecraft to fly past Uranus. | Voyager 2 | |
| 1986 February 19 | First part of the first space station built from different modules launched. This began its assembly in orbit. | Mir Core Module | |
| 1989 August 25 | First spacecraft to fly past Neptune. | Voyager 2 | |
| 1990 February 11 | First space station to be lived in continuously for a long time. | Mir |
The Space Race officially ended on December 31, 1991, when the United Nations accepted the breakup of the Soviet Union.
See also
 In Spanish: Anexo:Cronología de la carrera espacial para niños
In Spanish: Anexo:Cronología de la carrera espacial para niños
- List of communications satellite firsts
- List of space exploration milestones, 1957–1969
- Timeline of space exploration
- Timeline of first orbital launches by country
- Timeline of space travel by nationality

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Timeline of the Space Race Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.