Uinta Basin facts for kids
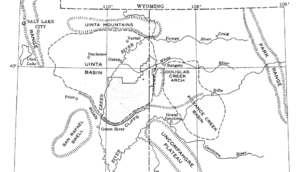
The Uinta Basin is a special area in eastern Utah. It's part of a much larger region called the Colorado Plateau. This basin is a big dip in the land, shaped by geology. It sits east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains.
Many rivers and creeks flow into the Uinta Basin from the Uinta Mountains. These include the Strawberry River, Currant Creek, and Lake Fork River. They all join the Duchesne River, which then flows into the Green River. The Green River is a major branch of the Colorado River.
The Uinta Mountains form the northern edge of the Uinta Basin. They are home to Kings Peak, Utah's highest point. This peak reaches 13,528 feet (4123 meters) above sea level! The Uinta Basin has a dry climate, and winters can be very cold.

Contents
History of the Uinta Basin
People have lived in the Uinta Basin for a very long time. In September 1776, a Spanish explorer named Father Escalante visited the area.
Later, from 1822 to 1840, French Canadian trappers came to the basin. They included Étienne Provost and Antoine Robidoux. They used the Old Spanish Trail to enter the basin. These trappers became rich by catching many beavers and trading with the local Uintah tribe.
In 1861, the Northern Ute Indian Reservation was created by the President of the United States. This land was set aside for the Ute people. In 1905, the United States allowed other people to settle on parts of the reservation.
During the early 1900s, new ways to bring water to farms were built. These included the Uinta Indian Irrigation Project and the Moon Lake Project. These projects helped both Native and non-Native farmers.
Communities and Fun Places

The biggest town in the Utah part of the Uinta Basin is Vernal. In 2010, about 9,089 people lived there. Other towns in the area include Duchesne, Roosevelt, Altamont, and Tabiona. There are also many smaller communities.
The Uinta Basin is also home to the Uintah and Ouray Indian Reservation. This is where the Ute Tribe of the Uintah and Ouray Agency lives. The Ute Tribe is so important that the state of Utah is named after them!
There are many cool places to visit in the Uinta Basin:
- Dinosaur National Monument: See real dinosaur bones!
- Starvation Reservoir State Park: Great for boating and fishing.
- Flaming Gorge National Recreation Area: Beautiful canyons and a huge reservoir.
- Raven Ridge and Fantasy Canyon: Unique rock formations that look like something from another world.
The local economy used to be mostly about farming and mining. Now, it has grown to include energy production and tourism. To help move oil out of the region, a new railroad is planned. Also, Utah State University has campuses in Vernal and Roosevelt. This helps more students in the area get a college education.
Land Features of the Uinta Basin
The Uinta Basin is the northernmost part of the Colorado Plateau. The land here is generally between 5,000 and 10,000 feet (1,500 to 3,000 meters) above sea level. South of the basin, the land rises sharply. Then it drops about 3,000 feet (900 meters) in two big steps. These steps are called the Roan Cliffs and the Book Cliffs.
The Green River flows south from the Uinta Mountains, right through the Uinta Basin. It carves a very deep canyon called Desolation Canyon, which is about 5,000 feet (1,500 meters) deep! The Colorado River also crosses the eastern part of this area. It cuts through a large section of land, leaving behind high, flat-topped mountains like Grand Mesa and Battlement Mesa.
How the Uinta Basin Formed
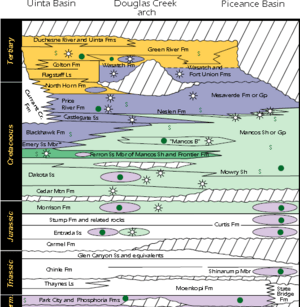
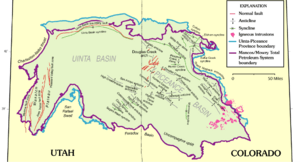
The Uinta Basin is a special type of structural basin in geology. This means the rock layers have bent downwards, forming a bowl shape. This basin is a major source of oil and natural gas.
The basin formed a long time ago during a period of mountain building called the Laramide Orogeny. At that time, the land where the basin is now started to sink. This created a huge ancient lake. Rivers brought sand and mud into this lake, forming layers of rock. These layers mixed with organic material from plants and animals in the lake. Over millions of years, this organic material turned into oil and gas.
The Uinta Basin is also famous for its unique solid hydrocarbons. These are like natural asphalt or tar found in cracks in the rocks. They include substances like gilsonite and ozocerite.
People discovered oil in the Uinta Basin in 1948. The first big oil discovery was at Ashley Valley. Later, more oil fields were found, like the Red Wash Field and Duchesne Field in 1951. The Bluebell Field was found in 1967, and the Altamont Field in 1970. These discoveries helped the region's economy grow.
Images for kids
-
Uinta Basin structural map
-
Freedom Bridge over Starvation Reservoir on U.S. Route 40 in Duchesne County, Utah.
-
Blue Mountain, east of Jensen, Utah.
-
The Uinta Mountains form the northern boundary of the Uinta Basin.
-
Uinta-Piceance Basins geologic map