Basque Country (autonomous community) facts for kids
The Basque Autonomous Community (which is also called the Basque Country) is a special region in northern Spain. It's like a state within Spain that has its own government and rules. This area includes three provinces: Álava, Biscay, and Gipuzkoa.
The Spanish Constitution of 1978 recognized the Basque Country as a unique "nationality" within Spain. This means it has a strong cultural identity. Another nearby region, Navarre, chose to be a separate autonomous community instead of joining the Basque Country.
Even though it doesn't have one official capital city, Vitoria-Gasteiz in Álava is very important. It's where the Basque Parliament (like a regional congress) and the Basque Government meet. The President of the Basque Autonomous Community also lives there. The main court for the region is in Bilbao. Vitoria-Gasteiz is the largest city by land area, while Bilbao has the most people.
Sometimes, when people say "Basque Country," they are talking about a larger cultural area called Euskal Herria. This bigger region is the traditional home of the Basque people and includes the autonomous community.
Contents
Exploring the Basque Country's Geography
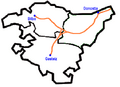
The Basque Autonomous Community is made up of three main areas, each with its own capital city:
- Álava (also called Araba in Basque), with its capital Vitoria-Gasteiz.
- Biscay (Bizkaia in Basque), with its capital Bilbao.
- Gipuzkoa (Guipúzcoa in Spanish), with its capital Donostia-San Sebastián.
Mountains and Rivers
The Basque Country is surrounded by different regions. To the west, it borders Cantabria and the Burgos province. The Bay of Biscay is to the north. To the east, you'll find France and Navarre. To the south, it touches La Rioja, near the Ebro River.
The region has three main parts, separated by the Basque Mountains. These mountains act like a natural wall, dividing the rivers that flow towards the Atlantic Ocean from those that flow towards the Mediterranean Sea. The highest point in these mountains is in the Aizkorri area, which is 1,551 meters (about 5,089 feet) high.
Atlantic Side
On the northern side of the mountains, rivers like the Nervión, Urola, and Oria flow down short valleys into the Bay of Biscay. The coast here is rugged, with tall cliffs. Important coastal areas include the Bilbao Abra Bay and the Estuary of Bilbao, the Urdaibai estuary, and the Bidasoa-Txingudi Bay, which forms the border with France.
Central Plains
Between the two main mountain ranges, there's a high, flat area called Llanada Alavesa (the Álava Plains). This is where Vitoria-Gasteiz is located. Rivers in this area flow south from the mountains towards the Ebro River. The main rivers here are the Zadorra River and Bayas River.
Ebro River Valley
The Ebro is a large river that starts in Cantabria and flows through the southern part of the Basque Autonomous Community. This area is known as the Ebro Valley. It's famous for its delicious wine.
Weather and Climate
The Basque Mountains also play a big role in the region's climate. They create different weather patterns:
- Northern Valleys: Areas like Biscay, Gipuzkoa, and the Ayala valley in Álava are part of "Green Spain." They get a lot of rain, making them very green and lush.
- Central Area: The climate in the middle part of the Basque Country is more like central Spain. This means warm, dry summers and cold winters, often with snow.
- Ebro Valley: The Ebro Valley has a climate similar to central Spain. Winters are cold and dry, and summers are very hot and dry. Most of the rain falls in spring and autumn, but overall, this part of the region doesn't get much rain.
Who Lives in the Basque Country?
Almost half of the 2.1 million people in the Basque Autonomous Community live in the area around Bilbao, known as Greater Bilbao. Many of the biggest cities in the region are part of this large urban area, including Bilbao itself, Barakaldo, Getxo, Portugalete, Santurtzi, and Basauri.
Many people living in the Basque Country were born somewhere else. About 28% of the population moved there from other places. For a long time, most of these people came from other parts of Spain, like Galicia or Castile and León. Recently, many have moved back to their home regions. Now, more people are moving to the Basque Country from other countries, especially from South America.
The main religion in the Basque Country is Roman Catholicism. In 2012, about 58.6% of Basques said they were Roman Catholic. However, many people don't follow a religion: 24.6% said they were non-religious, and 12.3% said they were atheist.
Major Cities in the Basque Country
| Rank | Pop. | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bilbao | 351,629 |
| 2 | Vitoria-Gasteiz | 245,036 |
| 3 | San Sebastián | 186,409 |
| 4 | Barakaldo | 100,369 |
| 5 | Getxo | 80,026 |
| 6 | Irun | 61,102 |
| 7 | Portugalete | 47,756 |
| 8 | Santurtzi | 47,129 |
| 9 | Basauri | 41,971 |
| 10 | Errenteria | 39,324 |
Images for kids
-
Basque coast near Mundaka
-
Basque coast near Mundaka, Biscay
-
Urkiola mountain range seen from Mañaria
-
Monument to the Battle of Vitoria, part of the Spanish Independence War against French rule.
-
Churruca's death at the Battle of Trafalgar. Basque navigators were very important for the navy of Castile and later the Spanish Navy.
-
BBVA head-office building in Bilbao
-
Garaia technology center in Mondragón, one of several science parks in the Basque Country
-
AP-8 in Eibar
-
Pelota (jai alai) court in Sara, Lapurdi.
See also
 In Spanish: País Vasco para niños
In Spanish: País Vasco para niños