Climate of Massachusetts facts for kids
The weather in Massachusetts is mostly a humid continental climate. This means it has hot, sticky summers and cold, snowy winters. It also gets a lot of rain and snow throughout the year. Massachusetts is a state in the New England area of the northeastern United States. Most of its 7 million people live near Boston. The eastern part of this state is mostly cities and suburbs. Massachusetts is the busiest of the six New England states. It ranks third in the country for how many people live in a small area.
Massachusetts gets about 43 inches (1,092 mm) of rain each year. This rain is spread out evenly, but winters can be a bit wetter. Summers are warm, with average high temperatures in July often above 80°F (27°C). Nights are usually above 60°F (16°C) across the state. Winters are cold. However, coastal areas are usually warmer, with highs above freezing even in January. Areas further inland are much colder. Sometimes, the state has extreme temperatures. It can reach 100°F (38°C) in summer. Temperatures below 0°F (-18°C) are also common in winter.
The state often experiences extreme weather. It gets many big winter storms called nor'easters. Summers can bring thunderstorms, happening about 30 days a year. Massachusetts usually has one tornado per year. Like other states on the East Coast, Massachusetts can be hit by hurricanes. Since 1851, Massachusetts has had three direct hits from major hurricanes. This is the same number as Georgia, a state much further south. More often, hurricanes weaken into tropical storms before they reach Massachusetts.
Most of New England, except for southern Connecticut, Cape Cod, and the islands, has a humid continental climate. This means hot summers and cold winters. In the fall, the many deciduous trees turn bright colors. This beautiful fall foliage brings many tourists. Spring is usually wet and cloudy. Rainfall is typically between 39 to 59 inches (1,000 to 1,500 mm) each year. In higher areas, snowfall can often be more than 100 inches (2.5 m) annually.
Contents
What Kind of Climate Does Massachusetts Have?
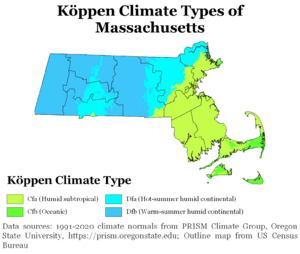
Western, central, and inland northeastern Massachusetts have a continental climate. This climate is found in large land areas in the middle latitudes. Here, cold air from the North Pole meets warm air from the Tropics. The humid continental climate has changing weather patterns. It also has big temperature differences between seasons. Places with at least four months averaging above 50°F (10°C) and a coldest month below 27°F (-3°C) are called continental. They also must not be too dry.
Some areas like Beverly, Lynn, Boston, and the areas southwest of Boston along Interstate 95 are a bit different. They are a transition zone towards subtropical or oceanic climates. These places have slightly warmer winters. The only parts of Massachusetts truly classified as an oceanic climate are Cape Ann, parts of the South Shore and South Coast, Cape Cod, and the islands. These areas are influenced by the North Atlantic current. This current also affects places like Bermuda and the British Isles.
Temperatures Across the State
Massachusetts sees many different temperatures throughout the year. The average high can be 95°F (35°C) in summer. The average low can be -8°F (-22°C) in winter. In Boston, the capital and largest city, July is the hottest month. The average high is 81°F (27°C), and the average low is 66°F (19°C). January is the coldest month. The average high is 36°F (2°C), and the average low is 22°F (-6°C).
Boston has reached 70°F (21°C) twice in February. The highest February temperature was 73°F (23°C) on February 23, 2017. In March, the temperature once hit 90°F (32°C) on March 31, 1998. Spring in Boston can be warm, sometimes reaching the 90s. But it can also be cool, even in late May, if cold ocean water affects the air. July is the hottest month, usually humid. Temperatures above 90°F (32°C) in summer or below 10°F (-12°C) in winter are common but don't last long. Boston's record high is 104°F (40°C) on July 4, 1911. The record low is -18°F (-28°C), set on February 9, 1934.
The highest temperature ever recorded in Massachusetts was 107°F (42°C). This happened on August 2, 1975, in New Bedford. The lowest temperature ever was -40°F (-40°C). This was on January 22, 1984, in Chester.
Coastal areas of Massachusetts have cooler summer temperatures. On Nantucket, July is the warmest month. The average high is 76°F (24°C), and the average low is 64°F (18°C). Winters on the coast are similar to the mainland. In January, Cape Cod has an average high of 37°F (3°C). The average low is 21°F (-6°C).
| City | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boston | 36/22 | 39/24 | 46/32 | 56/40 | 67/50 | 77/59 | 82/66 | 80/64 | 72/57 | 62/46 | 52/38 | 42/28 |
| Worcester | 31/16 | 34/18 | 43/26 | 54/36 | 66/46 | 74/55 | 79/61 | 77/60 | 69/51 | 58/41 | 47/32 | 36/22 |
Extreme Weather Events
What are Nor'easters?
Massachusetts often gets hit by storms called "nor'easters" in winter. These storms are very powerful for two reasons. First, strong winds from the northeast bring humid ocean air. This air drops as heavy rain or wet snow, causing floods inland. Second, the same northeast winds push ocean water onto the shore. This causes very high tides and big waves, leading to coastal flooding and erosion.
The storm is named "nor'easter" because the strong winds that cause problems come from the northeast. This happens in the coastal areas of the Northeastern United States and Atlantic Canada. These storms are a type of low pressure area that forms just off the East Coast. Their winds spin onto land from the northeast. If the same weather pattern happens only over land or only over sea, it's not called a Nor'easter. This is because it doesn't involve the land-sea meeting point, which causes the special problems. Nor'easters can also bring coastal flooding, coastal erosion, very strong winds (like a hurricane), and heavy rain or snow.
Nor'easters can happen any time of year, but they are most famous for winter. Most Nor'easters start as a low-pressure system in the south, often the Gulf of Mexico. They are then pulled towards the Northeast by the jet stream. The jet stream helps the storm grow stronger. The greater the temperature differences between cold and warm air, the more severe the storm can become.
If a nor'easter follows the East Coast, it usually means there's a high pressure area near Bermuda. The storm will reach the North Carolina coast and start to get stronger. At this point, the nor'easter can move slightly offshore, which is the more damaging path. Or it can move slightly inland, which mostly brings rain. If it goes offshore, it gets much stronger very quickly. The effects then start to reach major cities like Boston. The storm keeps getting stronger as it moves north. These storms can sometimes become as strong as a powerful hurricane when they reach Arctic areas. They can then wander around the North Atlantic for several weeks.
Tornadoes in Massachusetts
Massachusetts is not often hit by tornadoes. However, it was part of a very famous event: the Flint-Worcester tornado outbreak sequence on June 9, 1953. The huge Worcester tornado stayed on the ground for almost 90 minutes. It traveled 46 miles (74 km) and grew to be 1 mile (1.6 km) wide. It injured 1,300 people.
At 5:08 P.M., the tornado entered Worcester, the state's second-largest city. It became an amazing one mile wide. The damage in Worcester was huge, some of the worst ever from a U.S. tornado. Areas like Assumption College were hit very hard. The main building's 3-foot (0.9 m) thick brick walls were destroyed. The nearby Burncoat Hill neighborhood also saw heavy damage. The Uncatena-Great Brook Valley neighborhoods were completely leveled. Houses disappeared, and debris was swept away. Forty people died in these areas alone. A 12-ton bus was picked up and thrown against the Curtis Apartments, killing two people. The building plans for the Curtis Apartments were blown 75 miles (121 km) away to Duxbury. Across the street, the Brookside Home Farm was totally destroyed. Six men died there, and all 80 cattle were lost. Wrecked houses and bodies were blown into Lake Quinsigamond. In total, 94 people died in this tornado.
The 2011 New England tornado outbreak created six tornadoes. These storms killed three people, injured over 200, and caused a lot of damage in central and western Massachusetts.
Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes)

Massachusetts has been hit by many important tropical cyclones, also known as hurricanes. One famous storm was the New England Hurricane of 1938. This hurricane killed over 682 people. It damaged or destroyed more than 57,000 homes. The total cost of damage was about $4.7 billion (in 2005 money). Even in 1951, damaged trees and buildings could still be seen.
The center of the storm moved north along the Connecticut River into Massachusetts. The strong winds and flooding killed 99 people there. In Springfield, the river rose 6 to 10 feet (1.8 to 3.0 m) above flood level, causing major damage. Up to 6 inches (152 mm) of rain fell across western Massachusetts. This, combined with earlier rain, caused widespread flooding. People in Ware were stuck for days. They relied on food and medicine dropped from planes. After the flood, the town's Main Street was a deep hole where sewer pipes could be seen. To the east, the storm surge left Falmouth and New Bedford under 8 feet (2.4 m) of water. Two-thirds of all boats in New Bedford harbor sank. The Blue Hills Observatory recorded winds of 121 mph (195 km/h) and a top gust of 186 mph (299 km/h).
Hurricane Gloria brushed past Massachusetts in 1985. On August 19, 1991, Hurricane Bob, a Category 2 hurricane, hit southeastern Massachusetts, Cape Cod, and Martha's Vineyard hard. It killed 18 people and injured 190. It also caused billions of dollars in damage.
Climate Data
| Climate data for Boston (Logan Airport), 1981−2010 normals, extremes 1872−present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 72 (22) |
73 (23) |
89 (32) |
94 (34) |
97 (36) |
100 (38) |
104 (40) |
102 (39) |
102 (39) |
90 (32) |
83 (28) |
76 (24) |
104 (40) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 56.4 (13.6) |
57.7 (14.3) |
67.6 (19.8) |
80.7 (27.1) |
87.3 (30.7) |
92.1 (33.4) |
94.9 (34.9) |
93.3 (34.1) |
87.9 (31.1) |
79.1 (26.2) |
70.5 (21.4) |
61.3 (16.3) |
96.2 (35.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 35.8 (2.1) |
38.7 (3.7) |
45.4 (7.4) |
55.6 (13.1) |
66.0 (18.9) |
75.9 (24.4) |
81.4 (27.4) |
79.6 (26.4) |
72.4 (22.4) |
61.4 (16.3) |
51.5 (10.8) |
41.2 (5.1) |
58.8 (14.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 22.2 (−5.4) |
24.7 (−4.1) |
31.1 (−0.5) |
40.6 (4.8) |
49.9 (9.9) |
59.5 (15.3) |
65.4 (18.6) |
64.6 (18.1) |
57.4 (14.1) |
46.5 (8.1) |
38.0 (3.3) |
28.2 (−2.1) |
44.1 (6.7) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 4.1 (−15.5) |
8.5 (−13.1) |
14.7 (−9.6) |
30.7 (−0.7) |
40.8 (4.9) |
49.6 (9.8) |
57.3 (14.1) |
55.4 (13.0) |
45.8 (7.7) |
34.9 (1.6) |
24.2 (−4.3) |
11.1 (−11.6) |
2.3 (−16.5) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −13 (−25) |
−18 (−28) |
−8 (−22) |
11 (−12) |
31 (−1) |
41 (5) |
50 (10) |
46 (8) |
34 (1) |
25 (−4) |
−2 (−19) |
−17 (−27) |
−18 (−28) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.36 (85) |
3.25 (83) |
4.32 (110) |
3.74 (95) |
3.49 (89) |
3.68 (93) |
3.43 (87) |
3.35 (85) |
3.44 (87) |
3.94 (100) |
3.99 (101) |
3.78 (96) |
43.77 (1,112) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 12.9 (33) |
10.9 (28) |
7.8 (20) |
1.9 (4.8) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
trace | 1.3 (3.3) |
9.0 (23) |
43.8 (111) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 11.3 | 9.8 | 11.6 | 11.2 | 12.0 | 10.9 | 9.6 | 9.4 | 8.6 | 9.4 | 10.6 | 11.6 | 126.0 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 6.7 | 5.3 | 4.2 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 4.6 | 22.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 62.3 | 62.0 | 63.1 | 63.0 | 66.7 | 68.5 | 68.4 | 70.8 | 71.8 | 68.5 | 67.5 | 65.4 | 66.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 163.4 | 168.4 | 213.7 | 227.2 | 267.3 | 286.5 | 300.9 | 277.3 | 237.1 | 206.3 | 143.2 | 142.3 | 2,633.6 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 56 | 57 | 58 | 57 | 59 | 63 | 65 | 64 | 63 | 60 | 49 | 50 | 59 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961−1990) | |||||||||||||