Elías Piña Province facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Elías Piña |
||
| Province | ||
|
||
| Country | ||
|---|---|---|
| Development region | El Valle (VII) | |
| Capital | Comendador | |
| - elevation | 395 m (1,296 ft) | |
| - coordinates | 18°53′0″N 71°42′0″W / 18.88333°N 71.70000°W | |
| Highest point | La Tasajera del Chivito | |
| - location | Sierra de Neiba | |
| - elevation | 2,179 m (7,149 ft) | |
| Area | 1,395.5 km² (539 sq mi) | |
| Population | 84,632 (2014) | |
| Density | 61 /km² (158 /sq mi) | |
| Province since | 1942 | |
| Subdivisions | 6 municipalities 7 municipal districts |
|
| Congresspersons | 1 Senator 2 Representatives |
|
| Timezone | EST (UTC-4) | |
| Area code | 1-809 1-829 1-849 | |
| ISO 3166-2 | DO-07 | |
Elías Piña is a Dominican province located in the western part of the country. It shares a border with Haiti. The main city and capital of this province is Comendador.
The province was first created in 1942 and was called San Rafael. Later, in 1965, its name changed to Estrelleta. Finally, in 1972, it received its current name, Elías Piña. Before 1942, this area was part of the San Juan province.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The province of Elías Piña is named after a brave officer from the Dominican army. He fought during the Dominican-Haitian War. Elías Piña was born near Comendador. He sadly passed away in 1845 during a battle close to Bánica.
Where is Elías Piña Located?
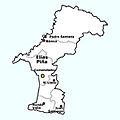
Elías Piña province is surrounded by other provinces. To its northwest is Dajabón. To the northeast, you'll find Santiago Rodríguez. The San Juan province is to its east. To the south, it borders the Independencia province. On its western side, Elías Piña shares a border with the country of Haiti.
 |
Dajabón province | Santiago Rodríguez province |  |
|
| Haiti | San Juan province | |||
| Independencia province |
A Look Back: History of Elías Piña
During colonial times, not many people lived in the territory of Elías Piña. This was because it was right on the border between the French colony of Saint-Domingue and the Spanish colony of Santo Domingo. After 1844, this area became part of the border between the newly independent Haiti and the Dominican Republic.
The only town established during the colonial period was Bánica. It was located in the eastern part of a large area of savannas called Oncéano by the Spanish. Most of this area is now in Haiti. After the Dominican Republic became independent, Comendador and Hondo Valle were important military outposts along the border. The rest of the province had very few people until after the Restoration War ended in 1865. That's when families from other parts of the country started to move here.
During the Dominican-Haitian War (1844-1856), Haitian soldiers often passed through this region. This led to many battles. The most famous battle was the La Estrelleta Battle. It took place in a savanna east of Comendador.
For a long time, this territory was part of the Azua province. Then, in 1938, it became part of the Benefactor province. This province is now known as the San Juan province.
The Elías Piña province was officially created in 1942. It included the municipalities of Elías Piña and Bánica. The new province was named San Rafael, and its capital was the city of Elías Piña. In 1965, the province's name changed to La Estrelleta. Later, in 1972, it was changed again to Elías Piña, and the capital got its old name back, Comendador.
Over the years, more towns became municipalities within the province:
- Pedro Santana joined in 1952.
- El Llano became a municipality in 1974.
- Hondo Valle joined in 1978.
- Juan Santiago became a municipality in 2005.
The municipal districts were added later:
- 1992: Río Limpio
- 2004: Sabana Larga
- 2005: Guanito and Sabana Cruz
- 2006: Guayabo, Sabana Higüero and Rancho de la Guardia
How Many People Live Here?
According to the last national census in 2014, there were about 84,632 people living in Elías Piña province. Only about 30,429 people (which is 36% of the total) lived in towns and cities. The population density was about 60.6 people per square kilometer. This is one of the lowest densities in the Dominican Republic.
The province's population makes up about 0.9% of the country's total population. Elías Piña is ranked as the 28th most populated province out of 31 provinces and the National District.
As of As of 2016[update], the estimated total population of the province is 63,449 people.
The largest city in the province is Comendador. It is the capital city. In 2010, its urban population was about 12,400 people.
Exploring the Geography
The Elías Piña province covers a total area of about 1,395.5 km2 (538.8 sq mi). This means it makes up about 2.9% of the total area of the Dominican Republic. It is ranked as the 14th largest province in the country.
Roads and Travel
There are two main roads in the province:
- The Carretera Sánchez (Sánchez National Road) runs through the middle of the province from east to west. This is a very important road that connects Santo Domingo to Comendador in the western part of the country.
- The second main road goes from south to north. It starts at Matayaya (in San Juan province) and passes through Bánica and Pedro Santana. It then continues through the Dajabón and Monte Cristi provinces, ending in San Fernando de Monte Cristi on the north coast. For several kilometres north of Pedro Santana, this road actually forms the border between the Dominican Republic and Haiti. That's why it's called the "International Road."
There are also other smaller roads. One connects Comendador to Hondo Valle. From there, it crosses the Sierra de Neiba mountain range into the Independencia province.
Mountains and Peaks
Two large mountain ranges stretch across the province from east to west and continue into Haiti.
- The Cordillera Central ("Central mountain range") is in the northern part of the province.
- The Sierra de Neiba runs through the southern half.
Between these two mountain ranges, you'll find several valleys. These valleys were formed by the Artibonite River and its smaller streams, called tributaries. There are also many low mountains, or hills, in this area.
The highest mountain in Elías Piña is the Loma La Tasajera del Chivito. It stands at about 2,179 m (7,149 ft) above sea level in the Sierra de Neiba. The second highest mountain is Nalga de Maco, which is about 1,990 m (6,529 ft) high. It's located in the northeast corner of the province, near the Santiago Rodríguez province. It is the highest peak in the western part of the Cordillera Central.
Rivers and Waterways
The most important river in the province is the Artibonite. In some places, this river actually marks the border between the Dominican Republic and Haiti. Other rivers in the province include Macasías, Tocino, Joca, and Vallecito. All of these are tributaries that flow into the Artibonite river. The Caña river is also important, especially in the southern part of the province. It flows from south to north and is a tributary of the Macasías river.
Climate: What's the Weather Like?
The climate in Elías Piña province is tropical. This means it's generally hot for most of the year. However, it gets cooler in the higher mountain areas.
Cities and Towns: Municipalities
Elías Piña province has 6 main municipalities. Each municipality might also have smaller areas called municipal districts (M.D.). Here are the main municipalities:
| Municipality | Population (2010) |
Area (km2) |
Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comendador | 25,924 | 256.2 | 394 |
| Bánica | 6,533 | 266.3 | 277 |
| El Llano | 8,344 | 100.0 | 544 |
| Hondo Valle | 10,587 | 122.6 | 899 |
| Pedro Santana | 7,281 | 548.3 | 293 |
| Juan Santiago | 4,360 | 102.2 | 807 |
| Total for Elías Piña province | 63,029 | 1,395.5 |
Economy: How People Make a Living
Like other provinces along the border in the Dominican Republic, Elías Piña doesn't have a lot of big industries. However, trade with Haiti is very important, especially in Comendador. In the mountain areas, growing coffee and beans are major activities. Potatos are also grown in the southern part of the province, in the Sierra de Neiba.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Provincia de Elías Piña para niños
In Spanish: Provincia de Elías Piña para niños