Ewing Township, New Jersey facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ewing Township, New Jersey
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Township
|
||

Aerial view of Ewing, looking southeast and featuring Trenton–Mercer Airport, Interstate 295, and the Delaware River
|
||
|
||
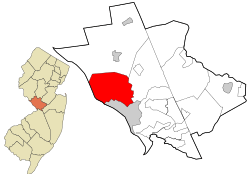
Location of Ewing Township in Mercer County highlighted in red (right). Inset map: Location of Mercer County in New Jersey highlighted in orange (left).
|
||
Census Bureau map of Ewing Township, New Jersey
|
||
| Country | ||
| State | ||
| County | Mercer | |
| Incorporated | February 22, 1834 | |
| Named for | Charles Ewing | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Faulkner Act (mayor–council) | |
| • Body | Township Council | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 15.56 sq mi (40.29 km2) | |
| • Land | 15.21 sq mi (39.38 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.35 sq mi (0.90 km2) 2.24% | |
| Area rank | 174th of 565 in state 8th of 12 in county |
|
| Elevation | 128 ft (39 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 37,264 | |
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
34,753 | |
| • Rank | 64th of 565 in state 3rd of 12 in county |
|
| • Density | 2,450.6/sq mi (946.2/km2) | |
| • Density rank | 255th of 565 in state 5th of 12 in county |
|
| Time zone | UTC−05:00 (Eastern (EST)) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (Eastern (EDT)) | |
| ZIP Codes |
08560, 08618, 08628, 08638
|
|
| Area code(s) | 609 | |
| FIPS code | {{{1}}}-{{{2}}} | |
| GNIS feature ID | 0882128 | |
Ewing Township is a special kind of town called a township in Mercer County, New Jersey. It's located near both the big cities of New York and Philadelphia. In 2020, about 37,264 people lived here. This was the highest number of people ever counted in Ewing Township!
Contents
History of Ewing Township

Long ago, the Lenape Native Americans lived in the area that is now Ewing Township. They lived along the Delaware River, hunting, fishing, making pottery, and farming.
European settlers, mostly from the British Isles, started to move here in 1699. One of the first settlers was William Green. His old farmhouse from 1717 is still standing today at The College of New Jersey.
Ewing Township officially became its own township on February 22, 1834. It was named after Charles Ewing, who was a very important judge in New Jersey. A few years later, in 1838, it became part of the new Mercer County.
In the 1800s, Ewing Township was mostly farmland with small villages. These villages included places like Ewing, Ewingville, West Trenton, and Wilburtha. Over time, especially in the 1900s, Ewing grew into a suburb of Trenton. Today, you can find The College of New Jersey, the New Jersey State Police headquarters, and the Trenton-Mercer Airport here.
From 1953 to 1997, Ewing was home to a United States Navy jet engine test facility. When it closed, many jobs were moved away.
Interestingly, the very first industrial robot used to replace human workers was at a factory in Ewing in 1961.
Geography of Ewing Township

Ewing Township covers about 15.56 square miles (40.29 square kilometers). Most of this area is land, with a small part being water.
The highest point in Ewing Township is about 225 feet (69 meters) above sea level. The lowest point is near the Delaware River, which forms the western border of the township.
The biggest lake completely inside Ewing is Lake Sylva. It's a man-made lake on the campus of The College of New Jersey. The Shabakunk Creek also flows through the township.
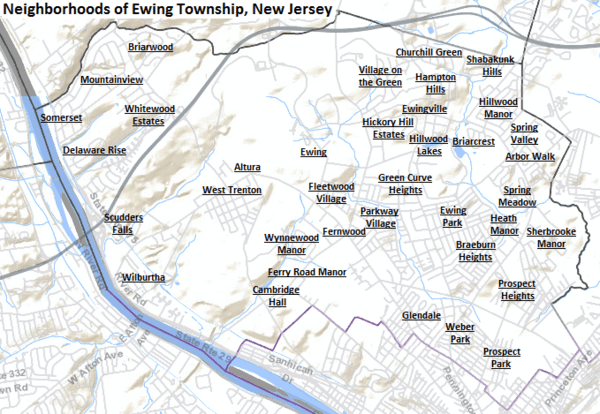
Ewing Township has many different neighborhoods. Some of these include Braeburn Heights, Ewing Park, Ewingville, Fernwood, Hillwood Lakes, Prospect Heights, Scudders Falls, Shabakunk Hills, West Trenton, and Wilburtha.
Ewing Township shares borders with other towns like Hopewell Township, Lawrence Township, and Trenton in Mercer County. It also borders towns in Bucks County, Pennsylvania, across the Delaware River.
Population and People
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 1,017 | — | |
| 1850 | 1,480 | 45.5% | |
| 1860 | 2,079 | 40.5% | |
| 1870 | 2,477 | 19.1% | |
| 1880 | 2,412 | −2.6% | |
| 1890 | 3,129 | 29.7% | |
| 1900 | 1,333 | * | −57.4% |
| 1910 | 1,889 | 41.7% | |
| 1920 | 3,475 | 84.0% | |
| 1930 | 6,942 | 99.8% | |
| 1940 | 10,146 | 46.2% | |
| 1950 | 16,840 | 66.0% | |
| 1960 | 26,628 | 58.1% | |
| 1970 | 32,831 | 23.3% | |
| 1980 | 34,842 | 6.1% | |
| 1990 | 34,185 | −1.9% | |
| 2000 | 35,707 | 4.5% | |
| 2010 | 35,790 | 0.2% | |
| 2020 | 37,264 | 4.1% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 34,753 | −2.9% | |
| Population sources: 1840–1920 1840 1850–1870 1850 1870 1880–1890 1890–1910 1910–1930 1940–2000 2000 2010 2020 * = Lost territory in previous decade. |
|||
In 2010, there were 35,790 people living in Ewing Township. The population was made up of different groups: about 63% White, 27% Black or African American, and smaller percentages of Asian, Native American, and other races. About 7.6% of the population was Hispanic or Latino.
Climate and Environment
Ewing Township has a climate with hot summers. This means it gets warm and humid in the summer, and cold in the winter.
| Climate data for Ewing Twp, Mercer County (40.2626, -74.8027), Elevation 128 ft (39 m), 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981-2022 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 71.5 (21.9) |
77.5 (25.3) |
87.8 (31.0) |
95.3 (35.2) |
95.4 (35.2) |
98.3 (36.8) |
103.6 (39.8) |
100.0 (37.8) |
97.6 (36.4) |
93.5 (34.2) |
80.4 (26.9) |
75.2 (24.0) |
103.6 (39.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 40.2 (4.6) |
42.8 (6.0) |
50.6 (10.3) |
62.9 (17.2) |
72.4 (22.4) |
81.5 (27.5) |
86.2 (30.1) |
84.5 (29.2) |
77.9 (25.5) |
66.0 (18.9) |
55.2 (12.9) |
45.1 (7.3) |
63.9 (17.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 23.3 (−4.8) |
24.7 (−4.1) |
31.7 (−0.2) |
41.6 (5.3) |
51.4 (10.8) |
60.7 (15.9) |
65.9 (18.8) |
64.1 (17.8) |
57.0 (13.9) |
45.4 (7.4) |
35.5 (1.9) |
28.6 (−1.9) |
44.3 (6.8) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −9.3 (−22.9) |
−0.6 (−18.1) |
5.8 (−14.6) |
18.2 (−7.7) |
32.6 (0.3) |
42.8 (6.0) |
49.2 (9.6) |
42.7 (5.9) |
37.3 (2.9) |
25.1 (−3.8) |
12.1 (−11.1) |
0.4 (−17.6) |
−9.3 (−22.9) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.58 (91) |
2.82 (72) |
4.27 (108) |
3.68 (93) |
4.04 (103) |
4.42 (112) |
4.84 (123) |
4.44 (113) |
4.17 (106) |
4.13 (105) |
3.33 (85) |
4.42 (112) |
48.13 (1,223) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 8.1 (21) |
8.4 (21) |
3.9 (9.9) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.6 (1.5) |
3.3 (8.4) |
24.6 (62) |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 21.5 (−5.8) |
22.0 (−5.6) |
27.6 (−2.4) |
37.3 (2.9) |
49.3 (9.6) |
59.4 (15.2) |
64.3 (17.9) |
63.6 (17.6) |
57.7 (14.3) |
46.1 (7.8) |
34.9 (1.6) |
27.3 (−2.6) |
42.7 (5.9) |
| Source 1: PRISM | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOHRSC (Snow, 2008/2009 - 2022/2023 normals) | |||||||||||||
Ewing Township's natural plant life would mostly be Oak trees and other Eastern Hardwood Forest trees.
Economy and Businesses
In 2013, the company Church & Dwight, which makes products like Arm & Hammer, moved its main office to Ewing.
Education in Ewing Township
The Ewing Public Schools system teaches students from pre-kindergarten all the way through twelfth grade. There are five schools in the district. In the 2020-21 school year, about 3,444 students were enrolled.
The schools are:
- W. L. Antheil Elementary School (PreK-5)
- Francis Lore Elementary School (K–5)
- Parkway Elementary School (K–5)
- Gilmore J. Fisher Middle School (6–8)
- Ewing High School (9–12)
A famous court case called Everson v. Board of Education happened in 1946. It was about whether the school district could provide bus transportation for students who went to private religious schools. The Supreme Court of the United States decided that it was okay.
The Ewing Public Education Foundation helps raise money for new and creative educational programs in Ewing Township schools.
Students in eighth grade from all over Mercer County can apply to special high school programs at the Mercer County Technical Schools. These schools offer training in health sciences, STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math), and culinary arts.
The Marie H. Katzenbach School for the Deaf is also in Ewing. It opened in 1883 and moved to West Trenton in 1923. It helps hearing-impaired students learn.
There are also private schools like Villa Victoria Academy, a Catholic school for girls from sixth to twelfth grade.
The College of New Jersey is a large college located right in Ewing Township.
Transportation in Ewing Township
Ewing Township has many roads, a train line, and an airport.
Major Roads and Highways
Several important highways go through Ewing Township:
- Interstate 295 runs through the northwest part of the township. It's a large highway that connects to Philadelphia.
- U.S. Route 206 (Princeton Avenue) is on the southeastern side of the township. It connects to Trenton and Princeton.
- Route 29 (Daniel Bray Highway and River Road) runs along the western edge, next to the Delaware River. This road is part of the Delaware River Scenic Byway.
- Route 31 (Pennington Road) is on the eastern side. It connects to Trenton and other towns to the north.
Public Transportation Options

The West Trenton Station is a train station that mainly serves people traveling to and from Philadelphia. There are also plans for a new train line that would connect West Trenton to other parts of New Jersey.
Ewing Township is home to the Trenton-Mercer Airport (TTN), which opened in 1929. It's one of three commercial airports in New Jersey.
The Delaware and Raritan Canal also runs through Ewing Township near the Delaware River. It used to be important for trade, but now it's part of the Delaware and Raritan Canal State Park, a great place for outdoor activities.
NJ Transit buses also provide service within Ewing Township and to Trenton.
Points of Interest in Ewing Township
- The William Greene Farmhouse is a very old house from 1717. It's listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
- Delaware and Raritan Canal – A historic canal that runs along the western part of Ewing Township.
- Washington Victory Trail – This trail shows the path that George Washington's army took on December 26, 1776, during the American Revolutionary War. This led to a surprise attack on the Hessian troops in Trenton.
- Ewing Presbyterian Church – An old church building from 1867, located in the historic Ewing Church Cemetery.
- Ewing Church Cemetery – One of the oldest cemeteries in the area, with graves of soldiers from many wars, including the Revolutionary War.
- Our Lady of Good Counsel Church – A Roman Catholic church built in the 1960s.
- Louis Kahn's Trenton Bath House – An interesting building designed by a famous architect. It's now part of the Ewing Senior & Community Center.
- The offices and studios of the radio station WKXW, "New Jersey 101.5", are located in Ewing.
Famous People from Ewing Township
Many interesting people have lived in or are connected to Ewing Township:
- Pierre Bernard – A graphic designer and comedian known from the TV show Late Night with Conan O'Brien.
- Al Clark – A former professional baseball umpire for Major League Baseball.
- Hollis Copeland – A former basketball player for the New York Knicks.
- Steve Garrison – A former Major League Baseball pitcher.
- Janis Hirsch – A comedy writer for television.
- Wayne Krenchicki – A former Major League Baseball third baseman.
- William M. Lanning – A politician who served in the U.S. House of Representatives.
- Dick LaRossa – A politician who served in the New Jersey Senate.
- Davon Reed – An NBA basketball player.
- Henry Rowan – An engineer and generous person for whom Rowan University was renamed.
- Bonnie Watson Coleman – A politician who is a U.S. representative for New Jersey. She is the first Black woman from New Jersey to be in Congress.
See also
 In Spanish: Ewing (Nueva Jersey) para niños
In Spanish: Ewing (Nueva Jersey) para niños