Geography of Guatemala facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Geography of Guatemala |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Continent | North America |
| Region | Central America |
| Coordinates | 15°30′N 90°15′W / 15.500°N 90.250°W |
| Area | Ranked 105th |
| • Total | 108,889 km2 (42,042 sq mi) |
| • Land | 98.41% |
| • Water | 1.59% |
| Coastline | 400 km (250 mi) |
| Borders | total: 1,667 km (1,036 mi) |
| Highest point | Tajumulco Volcano 4,220 m or 13,845 ft} |
| Lowest point | Pacific Ocean 0 m |
| Longest river | Motagua River 486 km (302 mi) |
| Largest lake | Lake Izabal 589.6 km2 (227.6 sq mi) |
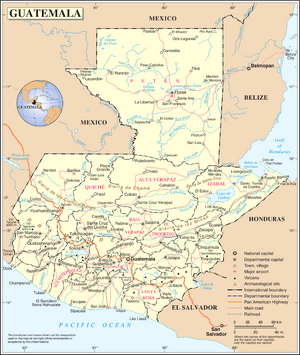
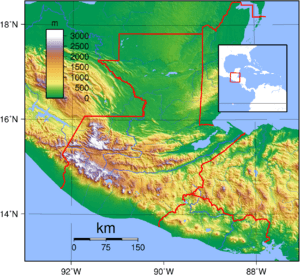
Guatemala is a country in Central America. It has many mountains, but also flat areas along the southern coast. In the north, you'll find large lowlands called Petén.
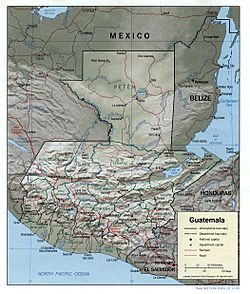
Guatemala shares borders with Mexico to the north and west. To the northeast, it borders Belize and the Gulf of Honduras. Honduras is to the east, and El Salvador is to the southeast. The Pacific Ocean is to the south.
Two main mountain ranges cross Guatemala from west to east. These ranges divide the country into three major parts:
- The highlands, where the mountains are located.
- The Pacific coast, which is south of the mountains.
- The Petén region, a flat limestone area north of the mountains.
These areas have different climates, elevations, and landscapes. You can find hot, humid tropical lowlands and cool mountain peaks and valleys.
Contents
Exploring Guatemala's Regions
The Western Highlands and Volcanoes
The southern part of Guatemala's western highlands has a mountain range called the Sierra Madre. This range starts near the border with Mexico and goes southeast towards El Salvador. It has many steep volcanoes.
Tajumulco Volcano is the highest point in Guatemala and all of Central America. It stands at 4,220 meters (13,845 feet) tall. Guatemala has 37 volcanoes in total. Three of them are active: Pacaya, Santiaguito, and Fuego. All these volcanoes are found in this mountain range.
Northern Mountains and Rivers
Another mountain chain starts near the Mexican border with the Cuchumatanes range. It then stretches east through other mountain ranges like the Chuacús and Chamá sierras. It reaches the Santa Cruz and Minas sierras, close to the Caribbean Sea.
The northern and southern mountains are separated by the Motagua valley. The Motagua River flows through this valley. It collects water from the highlands and empties into the Caribbean Sea. The lower part of the river can be used by boats and forms part of the border with Honduras.
Guatemala's rivers are different depending on where they flow. Rivers on the Pacific side are usually short and shallow. Rivers flowing towards the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico are larger and deeper. Examples include the Polochic, which flows into Lake Izabal, and the Río Dulce. The Sarstún River forms the border with Belize. The Usumacinta River forms part of the border with Mexico.
Major Cities and Lakes
Most of Guatemala's big cities are located in the highlands.
- Guatemala City is the capital, located in the Central Highlands at 1,500 meters (4,921 feet) elevation.
- Antigua Guatemala is also in the Central Highlands, at 1,530 meters (5,020 feet).
- Quetzaltenango is in the Western Highlands, at a higher elevation of 2,350 meters (7,710 feet).
- Puerto Barrios is an important city on the Caribbean coast.
The largest lake in Guatemala is Lago de Izabal (589.6 square kilometers or 227.6 square miles). It is close to the Caribbean coast.
A major earthquake hit Guatemala on February 4, 1976. It caused a lot of damage and sadly, more than 23,000 people died in the Central Highlands.
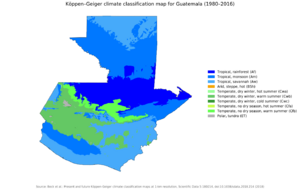
Guatemala's Climate Zones
Guatemala has different climates depending on the region:
- The Pacific and Petén Lowlands are hot and humid.
- The highlands have a more moderate or temperate climate.
- The highest parts of the Cuchumatanes range can get freezing cold.
- The easternmost areas are hot and drier.
Because Guatemala is located between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, it can be affected by hurricanes. For example, Hurricane Mitch in 1998 and Hurricane Stan in October 2005 caused a lot of damage. The main problem was not the strong winds, but the severe flooding and landslides that happened.
| Climate data for Guatemala City (1990-2011) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 30.0 (86.0) |
32.1 (89.8) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.9 (93.0) |
33.9 (93.0) |
31.2 (88.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
30.2 (86.4) |
29.8 (85.6) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.9 (85.8) |
28.8 (83.8) |
33.9 (93.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 24.3 (75.7) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.1 (80.8) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.1 (77.2) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
23.9 (75.0) |
25.5 (77.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.7 (65.7) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
20.8 (69.4) |
21.0 (69.8) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.3 (68.5) |
19.4 (66.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 13.2 (55.8) |
13.6 (56.5) |
14.6 (58.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.3 (61.3) |
16.5 (61.7) |
16.4 (61.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
14.7 (58.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
15.4 (59.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
7.8 (46.0) |
8.4 (47.1) |
8.6 (47.5) |
12.3 (54.1) |
11.2 (52.2) |
12.1 (53.8) |
13.5 (56.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
11.4 (52.5) |
9.4 (48.9) |
7.6 (45.7) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 2.8 (0.11) |
5.4 (0.21) |
6.0 (0.24) |
31.0 (1.22) |
128.9 (5.07) |
271.8 (10.70) |
202.6 (7.98) |
202.7 (7.98) |
236.6 (9.31) |
131.6 (5.18) |
48.8 (1.92) |
6.6 (0.26) |
1,274.8 (50.18) |
| Average rainy days | 1.68 | 1.45 | 2.00 | 4.73 | 12.36 | 21.14 | 18.59 | 19.04 | 20.82 | 14.59 | 6.18 | 2.64 | 125.22 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74.3 | 73.4 | 73.2 | 74.3 | 77.3 | 82.4 | 80.8 | 80.9 | 84.5 | 82.0 | 79.2 | 76.0 | 77.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 248.4 | 236.2 | 245.6 | 237.9 | 184.4 | 155.3 | 183.4 | 191.8 | 159.0 | 178.0 | 211.7 | 209.2 | 2,440.9 |
| Source: Instituto Nacional de Sismologia, Vulcanologia, Meteorologia, e Hidrologia | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Villa Nueva | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 25.2 (77.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
27.4 (81.3) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.5 (81.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.4 (77.7) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
26.1 (78.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 19.4 (66.9) |
19.8 (67.6) |
20.9 (69.6) |
21.7 (71.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.3 (70.3) |
21.2 (70.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
20.9 (69.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.7 (69.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 13.6 (56.5) |
13.6 (56.5) |
14.5 (58.1) |
15.7 (60.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
16.4 (61.5) |
16.4 (61.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
14.8 (58.6) |
13.8 (56.8) |
15.4 (59.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 1 (0.0) |
3 (0.1) |
5 (0.2) |
26 (1.0) |
126 (5.0) |
253 (10.0) |
217 (8.5) |
182 (7.2) |
244 (9.6) |
130 (5.1) |
16 (0.6) |
5 (0.2) |
1,208 (47.5) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Cobán | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 21.7 (71.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.3 (75.7) |
23.4 (74.1) |
22.3 (72.1) |
21.6 (70.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.1 (61.0) |
17.3 (63.1) |
18.3 (64.9) |
19.4 (66.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.3 (68.5) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
19.8 (67.6) |
18.9 (66.0) |
17.6 (63.7) |
16.7 (62.1) |
18.7 (65.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 10.5 (50.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
12.1 (53.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
14.9 (58.8) |
16.0 (60.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
15.4 (59.7) |
15.4 (59.7) |
14.4 (57.9) |
13.0 (55.4) |
11.8 (53.2) |
13.7 (56.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 108 (4.3) |
86 (3.4) |
99 (3.9) |
93 (3.7) |
169 (6.7) |
293 (11.5) |
262 (10.3) |
231 (9.1) |
302 (11.9) |
288 (11.3) |
216 (8.5) |
126 (5.0) |
2,273 (89.6) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org Instituto Nacional de Sismología, Vulcanología, Meteorología e Hidrología de Guatemala |
|||||||||||||
Understanding Climate Change in Guatemala
Key Geographic Facts about Guatemala
Here are some important facts about Guatemala's geography:
- Location: It's in Central America, with coordinates around 15°30′N 90°15′W.
- Total Area: Guatemala covers about 108,889 square kilometers (42,042 square miles). Most of this is land (107,159 km²).
- Land Borders: The total length of its land borders is 1,667 kilometers (1,036 miles).
- It shares 266 km with Belize.
- It shares 199 km with El Salvador.
- It shares 244 km with Honduras.
- It shares 958 km with Mexico.
- Coastline: Guatemala has 400 kilometers (249 miles) of coastline.
- Ocean Claims:
- It claims a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22 km).
- It has an Exclusive economic zone of 114,170 square kilometers (44,081 square miles). This zone extends 200 nautical miles (370 km) from its coast.
- Highest Point: Volcán Tajumulco is the highest point at 4,220 meters (13,845 feet).
- Lowest Point: The lowest points are the Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea at 0 meters (sea level).
- Natural Resources: Guatemala has natural resources like oil, nickel, rare woods, fish, and hydropower.
- Land Use:
- About 14.32% of the land is used for growing crops (arable land).
- 8.82% is used for permanent crops like fruit trees.
- The rest (76.87%) is for other uses (2012 estimate).
- Natural Dangers: Guatemala faces several natural dangers:
- It has many active volcanoes.
- It experiences occasional strong earthquakes.
- The Caribbean coast can be hit by hurricanes and tropical storms, which cause flooding, mudslides, and landslides.
- Environmental Issues: Some current environmental problems include deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Geografía de Guatemala para niños
In Spanish: Geografía de Guatemala para niños
- Guatemala Biodiversity
- List of earthquakes in Guatemala
- List of national parks of Guatemala
- List of places in Guatemala
- List of rivers of Guatemala
- List of volcanoes in Guatemala
- Water resources management in Guatemala
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |