Hippophae facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hippophae |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Common sea buckthorn shrub in the Netherlands | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Elaeagnaceae |
| Genus: | Hippophae L. |
| Type species | |
| Hippophae rhamnoides |
|
| Species | |
|
See text |
|
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Hippophae is a group of plants known as sea buckthorns. These are deciduous shrubs, meaning they lose their leaves every year. They belong to the plant family called Elaeagnaceae. Sometimes, people call them sandthorn, sallowthorn, or seaberry.
Sea buckthorns grow orange-yellow berries. For hundreds of years, people in places like Mongolia, Russia, and northern Europe have used these berries. They use them for food, traditional medicines, and even for skin treatments.
This plant is super tough! It can survive very cold winters, even down to -43 degrees Celsius (-45 degrees Fahrenheit). Sea buckthorn plants have strong, wide-spreading roots. Because of this, they are often planted to stop soil erosion (when soil washes away). They also help improve the soil by adding nitrogen. This makes them great for restoring land and creating wildlife habitat.
Contents
What Sea Buckthorn Looks Like
Sea buckthorn shrubs usually grow between 0.5 and 6 meters (about 1.5 to 20 feet) tall. Sometimes, in central Asia, they can grow up to 10 meters (33 feet) tall. Their leaves can be arranged in different ways on the branches.
Here are some of the main types of sea buckthorn:
- Hippophae goniocarpa grows in the mountains of Nepal and China. You can find it on mountain slopes, river banks, and in valleys. It usually grows at very high altitudes, between 2,650 and 3,700 meters (8,700 to 12,100 feet). This type has two subspecies. Its name, goniocarpa, means "with angular fruits."
- Hippophae rhamnoides: This is the most common type of sea buckthorn. It has thick, stiff, and very thorny branches. Its leaves are a light silvery-green color, long and narrow, about 3 to 8 cm (1 to 3 inches) long.
- This plant is dioecious, which means there are separate male and female plants. Male plants produce brownish flowers with pollen that the wind carries. Female plants grow bright orange berries that are about 6 to 9 mm (0.2 to 0.35 inches) wide. These berries are soft, juicy, and full of oils.
- The roots of this plant spread out quickly and widely. They help add nitrogen to the soil around them.
- Hippophae salicifolia (willow-leaved sea buckthorn) is found only in the Himalayas. It grows in dry valleys at high altitudes. It's different from the common sea buckthorn because its leaves are wider and greener, and its berries are yellow. There's also a wild version that grows even higher up in the mountains. This one is a small shrub, less than 1 meter (3 feet) tall, with tiny leaves.
Naming the Plant
The name Hippophae comes from ancient times. People believed that feeding sea buckthorn leaves and young branches to horses helped them gain weight and made their coats shiny. So, the name Hippophae comes from two Greek words: hippo (meaning horse) and phaos (meaning shining).
Where Sea Buckthorn Grows
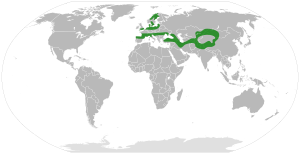
Hippophae rhamnoides, the common sea buckthorn, is the most widespread type. It grows from the Atlantic coasts of Europe all the way to northwestern Mongolia, China, and Pakistan.
In western Europe, you'll mostly find it near the sea. The salt spray from the ocean stops other bigger plants from growing there, so sea buckthorn can thrive. In central Asia, it grows in dry, semi-desert areas where other plants can't survive the dry conditions.
In central Europe and Asia, it also grows as a shrub in mountains, above the tree line. You can also find it in sunny spots like river banks, where it helps stop erosion. Sea buckthorns can handle salt in the air and soil. However, they need lots of sunlight to grow well and don't do well in shady places near larger trees. They usually grow in dry, sandy areas.
More than 90% of the world's natural sea buckthorn areas are in China, India, Pakistan, Mongolia, Russia, northern Europe, Ukraine, and Canada. In these places, the plant is used to help save soil, water, and wildlife. It also helps fight desertification (when land turns into desert) and is used to make products for people.
New Types of Sea Buckthorn
During the Cold War, plant experts in Russia and East Germany created new types of sea buckthorn. These new plants had more nutrients, bigger berries, ripened at different times, and were easier to pick. In the last 20 years, people have also grown experimental crops in the United States and Canada.
Natural Life
Sea buckthorn fruit is an important winter food for some birds, especially fieldfares.
The leaves are eaten by the larva (young stage) of certain moths, like the coastal race of the ash pug moth and the brown-tail moth.
How People Use Sea Buckthorn
Products from Sea Buckthorn
Sea buckthorn berries are safe to eat and full of nutrients. However, they can be quite sour and oily unless they are 'bletted' (frozen to make them less sour) or mixed with sweeter things like apple or grape juice. When the berries are pressed, the juice separates into layers. The top layer is a thick, orange cream, which is good for skin creams. The middle layer has fats that can also be used for skin products. The bottom layer is juice and can be used for things like syrup.
Besides juice, sea buckthorn fruit can be used to make pies, jams, lotions, teas, fruit wines, and liquors. The juice is also used in drinks and cosmetic products like shower gel. Sea buckthorn juice is popular in Germany and Scandinavian countries. It's packed with vitamin C and carotenoids, which are good for you. People even make rich orange-colored ice cream with a melon-like taste from the berries.
In India, the Defence Research Development Organization built a factory to make a special multivitamin drink from sea buckthorn juice. This drink helps their soldiers who face very cold winter temperatures.
The oils from the seeds and fruit pulp of sea buckthorn are also used in many nutritional supplements and cosmetic products.
Using Sea Buckthorn in Landscapes
Sea buckthorn can be used as a landscaping shrub. Its strong root system makes it good for creating barrier hedges and windbreaks. It's also used to stabilize riverbanks and steep slopes, helping to prevent erosion. In colder places, people like them because their colorful berry clusters stay on the plant all winter. Florists sometimes use the branches for decorations.
In northwestern China, sea buckthorn shrubs have been planted in dry riverbeds. This helps the soil hold more water and reduces soil loss. Because the soil holds more moisture and sea buckthorn adds nitrogen, more plants have grown in areas where sea buckthorn has been planted. In Canada, sea buckthorn was once given to farmers for free to use in shelterbelts, which are rows of trees or shrubs that protect against wind.
Traditional Uses and Science
For centuries, sea buckthorn has been used in traditional medicine. However, it's important to know that while scientists are studying its possible effects, there isn't enough strong scientific proof yet to say that sea buckthorn products can prevent or cure human diseases. No national health groups have approved any Hippophae products as prescription drugs.
People sometimes use the berry oil on their skin or take it as a dietary supplement, believing it can soften skin or act as medicine. But again, there isn't enough clear scientific evidence to prove it works. Also, there haven't been many studies on whether Hippophae products are completely safe for everyone.
Organizations That Study Sea Buckthorn
There are organizations that focus on sea buckthorn. For example, the International Seabuckthorn Association was formed in 1988. Its goal is to promote research and development related to sea buckthorn. There's also an active National Association of Seabuckthorn Cultivators and Producers in Mongolia.
See also
 In Spanish: Espino amarillo para niños
In Spanish: Espino amarillo para niños
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |




