Ilam province facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Ilam Province
استان ایلام (Persian)
|
|
|---|---|

A beautiful landscape in Ilam Province
|
|
Where Ilam Province is located in Iran
|
|
| Country | Iran |
| Region | Region 4 |
| Founded | 1974 |
| Capital | Ilam |
| Counties | 12 |
| Area | |
| • Province | 20,164.11 km2 (7,785.41 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 30.13 km2 (11.63 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 22nd |
| Latest measurement in 2019 | |
| Highest elevation
(Kan Seifi Peak)
|
2,775 m (9,104 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 36 m (118 ft) |
| Population
(2016)
|
|
| • Province | 580,158 |
| • Estimate
(2024)
|
904,000 |
| • Rank | 31st (last) |
| • Density | 28.77181/km2 (74.51865/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 395,263 |
| • Rural | 184,444 |
| Time zone | UTC+03:30 (IRST) |
| Postal code |
69311–69991
|
| Area code(s) | +98 84 |
| ISO 3166 code | IR-16 |
| Vehicle registration | Iran 98 |
| Main language(s) | Persian (official) local languages: Kurdish Luri Arabic |
| HDI (2017) | 0.815 very high · 8th |
| Website | Ilam Portal |
Ilam Province (Persian: استان ایلام) is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital city is Ilam.
This province is located in the western part of Iran. It covers about 20,164 square kilometers. Ilam shares a 425-kilometer border with Iraq. It also borders the Iranian provinces of Kermanshah, Lorestan, and Khuzestan.
Contents
- Etymology: The Meaning of Ilam
- History: A Journey Through Time
- Geography: Mountains, Rivers, and Plains
- Demographics: People of Ilam
- Culture: Traditions and Art
- Economy: How People Make a Living
- Education: Learning in Ilam
- Healthcare: Staying Healthy
- Transportation: Getting Around
- Sports: Active in Ilam
- Notable People
- Images for kids
- See also
Etymology: The Meaning of Ilam
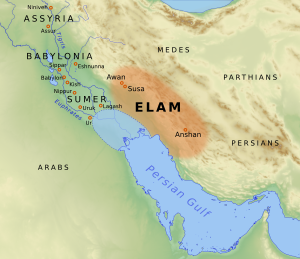
The name "Ilam" comes from "Elam". This was an ancient civilization that lived in southwestern Iran a very long time ago, from around 2700 BC to 539 BC.
History: A Journey Through Time
Ancient Times
People have lived in the Ilam area for a very long time, since about 5000 BC. The name "Ilam" reminds us of the ancient Elam civilization. This civilization was powerful in southwest Iran for many centuries.
Around 639 BC, the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal invaded Elam. Even after this, the Elamite people continued to live in the area. Later, Ilam became part of the Median Empire and then the Achaemenid Empire. During these times, Ilam was an important region due to its location.
Medieval Eras
After the Arab conquests around 640 AD, the area was called the "Land of the Mountains" or "Jibal." Various Arab caliphates ruled the region for several centuries. Later, the Buyid dynasty took control in 945 CE.
Around 1155, Kurdish groups, known as Hazaraspids, began to rule parts of the Zagros Mountains. One group, the Little Lor, controlled areas including present-day Ilam. Another Kurdish group, the Hasanwayhids, also ruled parts of western Iran.
The Khorshidi and Vali Dynasties
The Little Lor rulers, also called the Khorshidi dynasty, governed the area for over 400 years. Their rule ended in 1597. After that, the Vali/Wali dynasty, also known as Feyli Vali, began to govern.
During the Qajar era (1789–1925), the Ilam region was known as Poshtkoh. This name meant "back of the mountain" because of its location in the western Zagros Mountains. The governors of Poshtkoh reported directly to the central government. The famous Vali Castle in Ilam was built in 1908 by Gholamreza Khan Feyli. Today, it is a national heritage site and a museum.
Modern Times
In 1925, the Pahlavi dynasty came to power. They changed the name "Hossein-Abad" to "Ilam" in 1929. Ilam became a county and later, in March 1974, it was officially made a province.
In the 1980s, Ilam was a border area during a conflict. This period caused significant damage to the province's buildings and economy. The people of Ilam worked hard to rebuild and recover in the years that followed.
Geography: Mountains, Rivers, and Plains
Ilam province is the 22nd largest province in Iran. It is located in the southwestern part of the country. The province has two main natural areas:
- The northern and eastern parts are mountainous.
- The southwest has low plains that stretch towards Iraq and Khuzestan.
The mountains in Ilam mostly run from northwest to southeast. They are separated by plains and hills where people grow crops. The most famous mountain is Kabir Kouh, which is 160 km long. The highest point in Ilam is Kan Seifi peak, standing at 2,775 meters above sea level.
Other important mountains include:
- Manesht and Qolarang near Ilam
- Sharah-Zoul and Bankoul in Eywan
- Dinar Kouh in Abdanan
| Peak | Elevation (m) | Elevation (ft) |
|---|---|---|
| Kan Seifi | 2775 | 9104 |
| Manesht | 2629 | 8625 |
| Chaman Ghir | 2578 | 8458 |
| Qolarangh | 2473 | 8114 |
| Ghachan | 2464 | 8084 |
| Bankoul | 2304 | 7559 |
| Melinjeh | 2193 | 7195 |
| Shalam | 2174 | 7133 |
| Sameleh | 2150 | 7054 |
The southern and southwestern plains are much lower, between 50 and 300 meters above sea level. Even with little rain, these areas are farmed thanks to rivers and irrigation systems.
Rivers and Lakes
The Ghamasiab river flows into Ilam and becomes the Seymareh River. It then joins the Kashkan river to form the Karkheh River, one of Iran's longest rivers. Many smaller rivers in Ilam flow into the Seymareh or westward towards Iraq.
Ilam has a few natural springs, like the Siah-Ghav Twin Lakes. There are also four important dams that provide drinking water: Ilam, Seymareh, Eywan, and Doiraj dams.
Flora: Plants of Ilam
About 31% of Ilam is covered with forests, mostly Persian oak trees. You can also find wild almond, hawthorn, and Persian turpentine trees. The Arghavan Canyon is famous for its beautiful pink Judas-trees that bloom in spring.
Fauna: Animals of Ilam
Ilam is home to many animals, including 32 types of mammals and 183 types of birds. In the mountains, you might see wild goats, Asiatic mouflon, and even the endangered Persian leopard. Other animals include Caracals, Asian black bears, wolfs, and wild boars. Smaller animals like Caucasian squirrels and rabbits also live here.
Ilam province is the only place in the world where the unique spider-tailed horned viper can be found!
Nature Conservatories
About 13% of Ilam province is protected to help preserve its nature. There are four main protected areas:
- Kabir Kouh Protected Area near Darreh Shahr
- Dinar Kouh near Abdanan
- Manesht and Qolarangh near Ilam
- Koulak near Mehran
Other special places include the "Arghavan Valley forest reserve," known for its pink Judas trees, and the "Razyaneh Canyon," a deep, narrow canyon. There's also an area near Dehloran with hot water springs and 'bat caves.'
Landslides
Ilam Province is known for one of the largest landslides ever recorded. This huge event happened in the Kabir Kuh mountain range. Scientists believe an earthquake might have caused this massive slide, moving a vast amount of rock.
Climate: Weather in Ilam
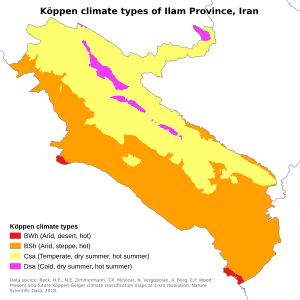
Ilam's climate is very varied due to its mountains and plains. Air from the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea brings rain in autumn and winter. Hot air from Iraq and Saudi Arabia causes very hot summers.
Ilam has three main climate types:
- Cold Climate: The northern and northeastern mountains have long, cold winters. Temperatures can drop to -15 to -20°C.
- Dry Hot Climate: The western and southwestern plains have very hot, dry summers. Temperatures can go above 52°C.
- Warm Climate: Other areas have hot summers and mild winters.
| Town | July daily maximum | January daily maximum | Annual precipitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ilam | 38.2 °C (100.8 °F) | 10.5 °C (50.9 °F) | 585.4 mm (23.05 in) |
| Mehran | 45.6 °C (114.1 °F) | 16.3 °C (61.3 °F) | 230.4 mm (9.07 in) |
| Dehloran | 48.1 °C (118.6 °F) | 16.5 °C (61.7 °F) | 280.4 mm (11.04 in) |
| Darreh Shahr | 46.4 °C (115.5 °F) | 15 °C (59 °F) | 482.1 mm (18.98 in) |
| Eyvan | 38.8 °C (101.8 °F) | 11 °C (52 °F) | 704.1 mm (27.72 in) |
| Sarableh | 41.4 °C (106.5 °F) | 11.2 °C (52.2 °F) | 510.7 mm (20.11 in) |
| Abdanan | 42.5 °C (108.5 °F) | 12.9 °C (55.2 °F) | 613.7 mm (24.16 in) |
| Lumar | 45.2 °C (113.4 °F) | 13.2 °C (55.8 °F) | 460.3 mm (18.12 in) |
Floods and Dust Storms
Heavy rainstorms can sometimes cause floods in Ilam. This happens because of the steep mountains and certain soil types. Many towns are built near rivers, which increases the risk. In March and April 2019, Ilam experienced significant flooding, which damaged bridges like the Gavmishan bridge.
Ilam also sometimes experiences dust storms, especially in summer. These storms are more common now due to droughts and conflicts in nearby countries. Cities like Mehran and Dehloran are most affected.
Demographics: People of Ilam
Languages and Ethnic Groups
Ilam Province has a mix of languages because it's located where different language groups meet. The main language is Kurdish, with various dialects spoken. Luri is spoken in the southern parts of the province. You can also find some smaller communities where Arabic is spoken near the border with Khuzestan.
| Ilam linguistic composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| language | percent | |||
| Kurdish | 80.66% | |||
| Luri | 14.74% | |||
| Arabic | 3.43% | |||
| Other | 1.16% | |||
The northern parts of Ilam are mostly home to Kurdish tribes like the Kalhuri and Feyli.
Population
| Ilam Province Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1956 | 110,067 | — |
| 1966 | 148,307 | +34.7% |
| 1976 | 246,024 | +65.9% |
| 1986 | 382,091 | +55.3% |
| 1991 | 440,693 | +15.3% |
| 1996 | 487,886 | +10.7% |
| 2006 | 545,787 | +11.9% |
| 2011 | 557,599 | +2.2% |
| 2016 | 580,158 | +4.0% |
| Est. 2020 | 602,000 | +3.8% |
| Notes: As Ilam Census Area in 1956 and Ilam General Governorate in 1966. Source: Statistical Center of Iran | ||
In 2016, the population of Ilam Province was 580,158 people. It is currently the least populated province in Iran. The capital city, Ilam, has about 194,030 residents.
Administrative Divisions
Ilam province is divided into 12 counties, which are like large districts. These counties are further divided into smaller areas.
| Counties | 2006 | 2011 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abdanan | 45,830 | 46,977 | 47,851 |
| Badreh | — | — | 15,614 |
| Chardavol | 73,422 | 72,167 | 57,381 |
| Chavar | — | — | — |
| Darreh Shahr | 56,346 | 59,551 | 43,708 |
| Dehloran | 58,993 | 66,399 | 65,630 |
| Eyvan | 47,380 | 48,833 | 49,491 |
| Holeylan | — | — | — |
| Ilam | 193,222 | 213,579 | 235,144 |
| Malekshahi | — | 22,587 | 21,138 |
| Mehran | 55,271 | 27,506 | 29,797 |
| Sirvan | — | — | 14,404 |
| Total | 530,464 | 557,599 | 580,158 |
Cities
More than 68% of Ilam's population lives in cities. The capital, Ilam, is the largest city.
| Rank | Town | Pop. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ilam | 194,030 |
| 2 | Dehloran | 32,941 |
| 3 | Eyvan | 31,299 |
| 4 | Abdanan | 23,946 |
| 5 | Darrehshahr | 21,900 |
| 6 | Mehran | 17,435 |
| 7 | Sarableh | 12,393 |
| 8 | Arkavaz | 11,977 |
Culture: Traditions and Art
Ilam's culture is a mix of different groups who have lived there over time, including Kurds, Lurs, Laks, and Arabs. This blend makes the local culture very rich and interesting.
Handicrafts

One of the most important handicrafts in Ilam is the Embossed Kilim. This is a special type of rug that combines simple weaving with carpet knots, creating a raised pattern. It became famous thanks to a weaver named Sahar Chalanghar. Today, thousands of people in Ilam make these beautiful kilims. Ilam is even known as the national capital of embossed kilim.
Cuisine
Ilam's food is a delicious mix of Kurdish and Luri cooking. Some traditional dishes include:
- Bersaq
- Kala-Konji
- Tarkhineh
- Chezenak-Reqo
- Shola-Keena
- Mountain Leek Stew
- Kangar
- Jeghar-Vaz
- Saj bread
- Qala Masoua
- Qoyerma
- Makash
Economy: How People Make a Living
Ilam is still developing compared to some other parts of Iran. Most people in rural areas work in farming and raising animals. In cities, people work in various services and skilled trades.
Agriculture
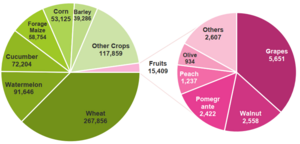
Farming is the biggest part of Ilam's economy. Over 55,000 farmers work here, and about half of all families are involved in agriculture. Farmers grow crops like wheat, barley, corn, watermelon, and cucumber. They also grow fruits such as grapes, walnuts, pomegranates, and olives.
Industry
| Rank. Province | Count |
|---|---|
| 1. Tehran |
6,806
|
| 2. Isfahan |
3,892
|
| 3. R. Khorasan |
2,164
|
| 29. S. Khorasan |
139
|
| 30. Kohgiluyeh |
65
|
| 31. Ilam |
52
|
Ilam's industry is not as developed as in some other provinces. There are fewer large factories here. However, efforts are being made to encourage new businesses by building industrial towns and offering benefits like cheaper land. Some of the larger companies include Ilam Cement Company and Ilam Petrochemical Company.
Energy
Ilam is rich in natural resources, holding a lot of Iran's gas and oil reserves. It ranks 2nd in gas and 3rd in oil reserves in the country. This makes Ilam an important energy center for western Iran. There are several plants that process oil and gas in the province.
Mining
Ilam has many non-metallic minerals. You can find large amounts of gypsum, limestone, and bitumen. Ilam's gypsum is very pure, and the Dehloran Gypsum Factory produces high-quality products. The province is also 2nd in Iran for bitumen production and reserves. The "Dehloran Bitumen Spring" is a natural monument where liquid bitumen seeps from the ground.
Education: Learning in Ilam
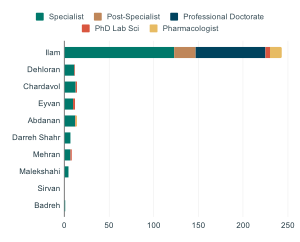
Ilam has many schools for elementary and secondary education. For higher education, there are several universities and institutes. As of 2019, there were 1,778 schools and over 112,503 students in Ilam province. The literacy rate for men was 89.1% and for women was 80.6% in 2016.
Some of the higher education institutes include:
- Ilam University of Medical Sciences
- Ilam University
- Islamic Azad University of Ilam
- Payame Noor University of Ilam
Healthcare: Staying Healthy
Ilam has a good number of doctors and dentists compared to its population. However, most of the medical facilities and specialists are located in the capital city, Ilam.
Some of the main hospitals in the province are:
- Imam Khomeini Hospital
- Mostafa Khomeini Hospital
- Ayatollah Taleghani Hospital
Transportation: Getting Around
Air Travel
The Ilam Airport is the only airport in the province. It has regular flights to cities like Tehran and Mashhad. In 2016, it also started international flights to Najaf.
Road Travel
Ilam province has a network of roads, including highways that connect it to other parts of Iran. Important roads include Road 17, which links Eslamabad-e Gharb to Mehran, and Road 64, connecting Mehran to Dehloran.
There are also several road tunnels in Ilam, helping cars travel through the mountains. The Ghalajeh tunnel is 2,583 meters long, and the Kabir Kouh Tunnel is under construction and will be 6,250 meters long.
Sports: Active in Ilam
Football
Ilam has a women's football team called Palayesh Gas Ilam. They compete in Iran's top professional league, the Kowsar Women Football League.
Powerlifting
Mojtaba Maleki is a famous powerlifter from Ilam. He has won gold medals in World Powerlifting Championships and many Asian gold medals. He is known for being one of only two people in the world to squat 500 kg raw with wraps.
Notable People
- Darioush Rezaeinejad, nuclear energy scientist
- Navid Mohammadzadeh, Iranian actor
- Mojtaba Maleki, Iranian strongman
- Zabihollah Pourshab, Iranian karateka
- Ali Shadman, Iranian actor
- Said Lotfi, Iranian footballer
- Pouria Norouzian, Iranian sport shooter
- Armina Sadeghian, Iranian sport shooter
- Ali Hashemi, Iranian weightlifter
- Jahangir Asgari, Iranian footballer
- Behrouz Boochani, Iranian-Kurdish writer and filmmaker
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Provincia de Ilam para niños
In Spanish: Provincia de Ilam para niños
- Elam
- Ethnic minorities in Iran