Later Han (Five Dynasties) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Han
漢
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 947–951 | |||||||||||
Later Han
|
|||||||||||
| Capital | Bian (Kaifeng) | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Chinese | ||||||||||
| Religion | Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism, Chinese folk religion | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||||
|
• 947–948
|
Emperor Gaozu | ||||||||||
|
• 948–951
|
Emperor Yin | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period | ||||||||||
|
• Established in Taiyuan
|
March 10, 947 | ||||||||||
|
• Coup d'etat, surrender of Bian; Emperor Yin killed (de facto end)
|
January 1; January 2, 951 | ||||||||||
|
• Guo Wei proclaimed Emperor (de jure end)
|
February 13 951 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Chinese cash, Chinese coin, copper coins etc. | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||||
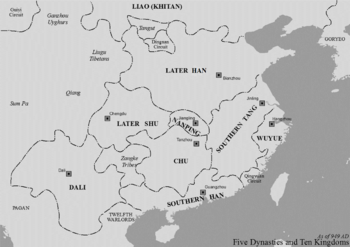
The Later Han (also known as Han) was a very short-lived empire in China. It lasted only about four years, from 947 to 951 AD. It was the fourth of the "Five Dynasties" during a time in Chinese history called the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. This period was a bit chaotic, with many different rulers and kingdoms. The Later Han was founded by a leader named Liu Zhiyuan.
Contents
How the Later Han Dynasty Began
Liu Zhiyuan was a powerful military leader. He controlled an area around Taiyuan, which is in modern-day Shanxi province. He served a dynasty called the Later Jin. However, the Later Jin was weak and controlled by the Khitan Liao dynasty from the north.
When the Later Jin tried to fight back, the Liao dynasty sent an army south. This army destroyed the Later Jin. The Liao emperor, Emperor Taizong of Liao, reached the Yellow River. He then decided to return to his home base near modern-day Beijing.
But on his way back, Chinese forces kept attacking his army. The Liao emperor died in May 947. This created a big power vacuum, meaning there was no strong ruler in charge. Liu Zhiyuan saw this chance and stepped in. He founded the Later Han dynasty.
Historians have different ideas about the background of the Later Han emperors. Some say they were from the Shatuo people. Others say the emperors claimed to be from the Han Chinese people.
Where the Later Han Ruled
Liu Zhiyuan made his capital at Bian, which is now Kaifeng. The Later Han controlled mostly the same land as the previous Later Jin dynasty. Its southern border was near the East China Sea. It stretched between the Yellow River and the Yangtze River.
The border then went south towards the Yangtze and turned northwest. It followed the northern edge of Sichuan and reached as far west as Shaanxi. In the north, it included much of Shaanxi and Hebei. However, it did not include the Sixteen Prefectures. These lands were lost to the Liao Dynasty by the Later Jin.
A Very Short Reign
The Later Han was one of the shortest dynasties in China's long history. Liu Zhiyuan died just one year after starting the dynasty. His teenage son took over as emperor.
But the dynasty was overthrown only two years later. A Han Chinese general named Guo Wei led a military takeover. He then declared himself emperor of a new dynasty, the Later Zhou.
The Northern Han Kingdom
After the Later Han fell, some of its remaining forces went back to the Shatuo homeland in Shanxi. There, they created a new kingdom called the Northern Han. It is sometimes called the Eastern Han.
The Northern Han was protected by the powerful Liao dynasty. This protection helped it stay independent from the Later Zhou. Later, the Song Dynasty rose to power in 960 AD. The Song Dynasty became a very strong force in northern China.
The Song Dynasty successfully took control of the southern states by 978. But the Northern Han managed to hold out because the Liao Dynasty kept helping them. The Northern Han's continued existence was a big problem for the relationship between the Liao and Song dynasties. Finally, in 979, the Song Dynasty took over the Northern Han. This mostly completed the reunification of China. Only the Sixteen Prefectures remained under the control of the Liao dynasty.
Later Han Rulers
| Temple names | Posthumous names | Personal names | Reign | Era names |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gāozǔ (高祖) | Emperor Ruìwén Shèngwǔ Zhāosù Xiào (睿文聖武昭肅孝皇帝) | Liu Zhiyuan (劉知遠) | 947–948 | Tiānfú (天福) 947 Qiányòu (乾祐) 948 |
| None | Emperor Yǐn (隱皇帝) | Liu Chengyou (劉承祐) | 948–951 | Qiányòu (乾祐) 948–951 |
Later Han and Northern Han Emperors Family Tree
| The family tree of the Later Han and Northern Han rulers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
– Later Han emperors; – Northern Han emperors
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Monarchy of China
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |


