List of the prehistoric life of New Mexico facts for kids
This article explores the amazing prehistoric life found in New Mexico. Scientists have discovered many fossils here, showing us what ancient plants and animals lived in this area long, long ago. From tiny sea creatures to giant dinosaurs and early mammals, New Mexico has a rich history of life!
Contents
Ancient Life: The Precambrian Era
The very first era of Earth's history is called the Precambrian. So far, scientists haven't found any fossils from this super ancient time in New Mexico. This means either no life existed here then, or their remains were too soft to fossilize.
Life in the Paleozoic Era
The Paleozoic Era was a time when many different kinds of life appeared. In New Mexico, fossils from this era show us a world filled with sea creatures and early land animals.
Some of the interesting animals found include:
- †Adelophthalmus: This was a type of "sea scorpion," an ancient creature that lived in the water.
- †Dimetrodon: A famous "mammal precursor" with a large sail on its back. It wasn't a dinosaur, but an early relative of mammals.

- †Edaphosaurus: Another mammal precursor, also with a sail on its back, but it was a plant-eater.
- †Eryops: A large, crocodile-like amphibian that lived both in water and on land.
- †Ophiacodon: One of the earliest and largest mammal precursors, known for its long, narrow skull.
- †Platyhystrix: An amphibian with a tall, sail-like structure on its back, similar to Dimetrodon.
- †Sphenacodon: Another mammal precursor, closely related to Dimetrodon, also found in New Mexico.
Many types of ancient plants also grew here, such as:
- †Annularia: A plant related to modern horsetails.
- †Calamites: Another large, tree-like horsetail.
- †Lepidodendron: A type of scale tree, which were huge trees with diamond-shaped patterns on their trunks.
- †Neuropteris: An ancient fern-like plant.
Other interesting creatures from this time include:
- †Aviculopecten: An ancient type of scallop, a shellfish.
- †Composita: A common type of brachiopod, which are marine animals with two shells.
- †Metalegoceras: A type of ammonoid, a shelled creature related to modern squids and octopuses.
- †Stethacanthus: An unusual shark known for its anvil-shaped dorsal fin.
Life in the Mesozoic Era (Age of Dinosaurs)
The Mesozoic Era is often called the "Age of Dinosaurs." New Mexico was home to many amazing dinosaurs and other reptiles during this time.
Here are some of the famous dinosaurs and other reptiles:
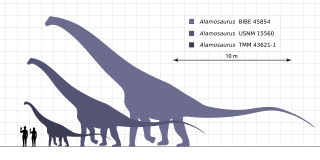
- †Alamosaurus: A giant, long-necked plant-eating dinosaur (sauropod) from the Late Cretaceous period. It was one of the last sauropods to live.
- †Allosaurus: A large, meat-eating dinosaur from the Late Jurassic.
- †Anasazisaurus: A duck-billed dinosaur (hadrosaur) from the Late Cretaceous.
- †Bistahieversor: A type of tyrannosaur, a large meat-eating dinosaur, found in New Mexico.
- †Camarasaurus: Another long-necked sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic.
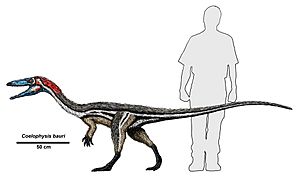
- †Coelophysis: One of the earliest known dinosaurs, a small, fast meat-eater from the Late Triassic. Many fossils of this dinosaur have been found in New Mexico.
- †Daemonosaurus: An early meat-eating dinosaur from the Late Triassic.
- †Diplodocus: A very long sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, known for its whip-like tail.

- †Kritosaurus: Another duck-billed dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous.
- †Nothronychus: An unusual feathered dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous, known for its large claws and plant-eating diet.
- †Ornithomimus: A "ostrich dinosaur," which looked like a modern ostrich but was a dinosaur.
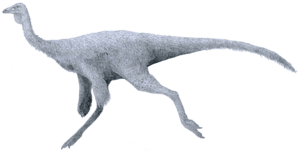
- †Parasaurolophus: A duck-billed dinosaur famous for its long, hollow crest on its head.
- †Pentaceratops: A large horned dinosaur (ceratopsian) from the Late Cretaceous, with a huge frill and five horns.

- †Saurornitholestes: A small, agile, meat-eating dinosaur (dromaeosaurid) from the Late Cretaceous, related to Velociraptor.
- †Stegoceras: A dome-headed dinosaur (pachycephalosaur) from the Late Cretaceous.

- †Tawa: One of the earliest meat-eating dinosaurs, found in New Mexico.
- †Titanoceratops: A very large horned dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous.
- †Triceratops: The famous three-horned dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous.

- †Tyrannosaurus: The mighty "king" of the dinosaurs, a huge meat-eater from the Late Cretaceous. Footprints of this dinosaur have been found in New Mexico.

- †Ziapelta: An armored dinosaur (ankylosaur) from the Late Cretaceous, known for its bony plates and club tail.
- †Zuniceratops: An early horned dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous, important for understanding how horned dinosaurs evolved.
Other interesting animals from this era include:
- †Angistorhinus: A large, crocodile-like reptile called a phytosaur.
- †Baculites: A straight-shelled ammonoid, a type of ancient marine creature.
- †Chinlea: An ancient coelacanth fish from the Late Triassic.
- †Deinosuchus: A giant alligator relative from the Late Cretaceous, much larger than modern alligators.

- †Effigia: A distant crocodile relative from the Late Triassic that walked on two legs and looked like an ostrich.
- †Exogyra: A type of foam oyster, a common shellfish from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
- †Hesperosuchus: An early crocodile relative from the Late Triassic.
- †Ichthyornis: A toothed bird from the Late Cretaceous, showing how birds evolved.

- †Inoceramus: A very large marine bivalve (shellfish) from the Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous.
- †Machaeroprosopus: Another type of phytosaur, a large crocodile-like reptile.
- †Meniscoessus: A multituberculate mammal, an early type of mammal from the Late Cretaceous.
- †Mortoniceras: A type of ammonoid cephalopod from the Early Cretaceous.
- †Platecarpus: A mosasaur, a large marine reptile from the Late Cretaceous that swam in ancient seas.
- †Redondasaurus: Another phytosaur, a crocodile-like reptile from the Late Triassic.
Ancient trees and plants from this era include:
- †Araucarioxylon arizonicum: A type of petrified wood, showing ancient conifer trees.

- †Sequoia: Ancestors of today's giant redwood trees.

Life in the Cenozoic Era (Age of Mammals)
The Cenozoic Era is the "Age of Mammals," and New Mexico has many fossils from this time, showing how mammals grew and changed after the dinosaurs disappeared.
Some of the fascinating mammals found include:
- †Aepycamelus: A "long-necked camel" from the Miocene epoch, much taller than modern camels.
- †Amphicyon: Known as a "beardog," this was a large, powerful predator from the Miocene and Pliocene epochs.
- †Arctodus: The giant short-faced bear, one of the largest bears that ever lived.
- †Camelops: A large, extinct camel that lived in North America during the Pliocene and Holocene epochs.

- †Canis dirus: The dire wolf, a large wolf that lived during the Ice Age.
- †Capromeryx: A small, dwarf pronghorn from the Pleistocene epoch.
- †Ceratogaulus: A unique horned gopher from the Miocene and Pleistocene epochs.
- †Coryphodon: A large, heavy mammal from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs, similar to a hippopotamus.
- †Cuvieronius: An elephant relative from the Pliocene and Holocene epochs, with spiral tusks.
- †Duchesneodus: A large, rhino-like mammal called a brontothere from the Eocene epoch.
- †Eohippus: One of the earliest ancestors of modern horses, a small, dog-sized animal.
- †Epicyon: A large, bone-crushing dog from the Miocene epoch.
- †Equus scotti: An extinct species of horse that lived during the Pleistocene epoch.
- †Euceratherium: The shrub ox, a type of bovid (like cattle or goats) from the Pleistocene.
- †Glyptotherium: A large, armored armadillo relative from the Pleistocene epoch.
- †Gomphotherium: Another elephant relative, with four tusks, from the Miocene and Pliocene epochs.
- †Hemiauchenia: A long-legged llama relative from the Pliocene and Pleistocene.
- †Hyaenodon: A creodont, a group of extinct meat-eating mammals, from the Eocene to Miocene epochs.
- †Mammut americanum: The American mastodon, a large elephant relative from the Pleistocene.
- †Mammuthus columbi: The Columbian mammoth, a giant woolly elephant relative from the Pleistocene.
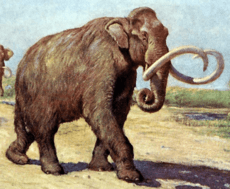
- †Megalonyx: A giant ground sloth from the Pleistocene.
- †Menoceras: A small rhinoceros from the Miocene epoch.
- †Neohipparion: A three-toed horse from the Miocene and Pliocene epochs.
- †Nimravides: A saber-toothed cat from the Miocene epoch.

- †Osbornoceros: An ancient pronghorn from the Miocene.
- †Paramylodon: Another type of ground sloth from the Pliocene and Pleistocene.
- †Platygonus: An extinct peccary (a pig-like animal) from the Miocene and Pleistocene.

- †Protitanotherium: A brontothere, a large rhino-like mammal, from the Eocene epoch.
- †Psittacotherium: A taeniodont mammal from the Paleocene, known for its strong teeth.
- †Rhynchotherium: An elephant relative with a long lower jaw and tusks, from the Miocene and Pliocene.
- †Smilodon: The famous saber-toothed cat from the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs.

- †Stegomastodon: Another elephant relative from the Pliocene and Pleistocene.
- †Teleoceras: A short-legged, barrel-bodied rhinoceros from the Miocene and Pliocene.
- †Tomarctus: An early bone-crushing dog from the Miocene.
- †Ysengrinia: A bear dog from the Miocene.
Many modern animals also have ancient relatives found in New Mexico, including:
- Bison: Ancient bison species like †Bison antiquus and †Bison latifrons.
- Canis: Various ancient dog and wolf species.
- Castor: Ancient beavers.
- Crotalus: Rattlesnakes.
- Desmodus: Vampire bats.
- Falco: Falcons, including the prairie falcon.


- Lynx: Lynx and bobcats.
- Microtus: Voles.

- Mustela: Weasels, including the black-footed ferret.

- Neotoma: Woodrats.
- Peromyscus: Deer mice.

- Puma: Cougars.
- Saniwa: Large monitor lizards.
- Ursus: Bears, including the American black bear.
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |