Mediterranean house gecko facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mediterranean house gecko |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Gekkonidae |
| Genus: | Hemidactylus |
| Species: |
H. turcicus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hemidactylus turcicus (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
| Native range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Mediterranean house gecko (Hemidactylus turcicus) is a type of house gecko. It comes from the Mediterranean area. From there, it has traveled to many parts of the world. You can now find it in places like East Africa, South America, the Caribbean, and the Southern and Southeastern United States. People often call it the Turkish gecko because of its Latin name. It's also known as the moon lizard since it usually comes out at night.
These geckos are active at night, especially around 2 AM. They eat insects. They are usually about 15 cm (5.9 in) long. They have big eyes with no eyelids and pupils shaped like slits. Their skin can be purple or tan with black spots. Sometimes, they have stripes on their tails. Their bellies are a bit see-through. We don't know much about how these geckos affect other animals in places where they are new.
The number of Mediterranean house geckos is growing in many parts of the world. Unlike many other reptiles, they seem to be very strong against bug sprays. They might be increasing because they don't have many enemies in new places. They also like to hide in small spaces in human homes, like inside walls. Because they live close to people, their numbers have grown, much like rodents. In some countries like Turkey and Cyprus, people believe it's wrong to hurt these geckos. They are often kept as pets because they are harmless.
Contents
What Does the Mediterranean House Gecko Look Like?

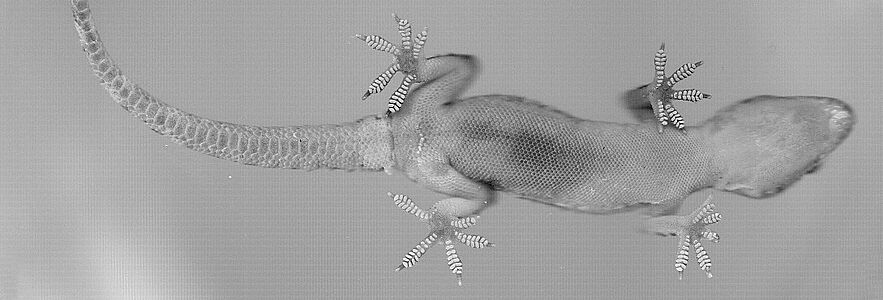
The Mediterranean gecko is a small lizard. It is usually about 10–13 cm (4–5 inches) long. It has sticky pads on its toes, which help it climb. Its eyes are large and have pupils that are vertical, like a cat's. It does not have eyelids.
Its nose area is rounded. The distance from its eye to its ear is about the same length as its nose. The top of its head is a little bit curved inward. Its ear opening is shaped like an oval. It is about half the size of its eye.
The gecko's body and legs are of average size. Its toes have different lengths. The inner toe is always well-formed. There are 6 to 8 sticky pads (called lamellae) under the inner toes. There are 8 to 10 pads under the fourth finger and 9 to 11 under the fourth toe.
The top of its body has tiny bumps mixed with larger, round bumps. These larger bumps are usually bigger than the spaces between them. They are arranged in 14 or 16 neat rows. The scales on its belly are small, smooth, and round.
Male geckos have a short row of 4 to 10 (sometimes 2) special pores near their tail. The tail is round, a bit flat, and gets thinner towards the end. It has tiny scales on top and rows of large, bumpy scales. The underside of the tail has large, wide plates.
These geckos are light brown or grayish on top. They have darker spots. Many of their bumps and their undersides are white. Some geckos can be almost see-through, except for their spots. Others are darker in color. They often look for dark places when they are trying to escape. You might see them alone or in groups of up to five.
Where Do Mediterranean House Geckos Live?
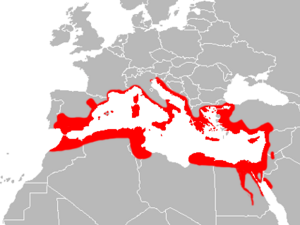
The "Med gecko" comes from the Mediterranean area. It is one of the most successful gecko types in the world. It has spread to many places far from its original home. It has created new groups there. This gecko is not considered in danger or threatened.
You can find it in countries with Mediterranean weather. These include Portugal, Spain, France, Italy, Greece, Israel, Turkey, and many more. It also lives in parts of Africa and Asia.
By 2016, it was found in parts of the Southwestern United States. This includes Arizona, California, Nevada, and New Mexico. It is more common in the Southern United States. Here, it lives in states like Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Texas. It is especially common in states along the Gulf Coast. Recently, it has also been seen in Pennsylvania and Tennessee. In 2019, it was reported in Indiana. We don't know yet if it has made a permanent home there.
In Mexico, these geckos have been found in many states. Some of these are Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Yucatán, and Baja California.
What Kind of Homes Do Geckos Like?
Mediterranean house geckos live in many different places. They often live near people. You can find them on university campuses, in cemeteries, near the coast, and in bushy areas. In cities or towns, they are often seen in the cracks of old brick buildings.
They can also live in other places, like mountain cliffs and caves. They might build their nests in piles of trash. You can also find their nests in attics or under the baseboards of buildings.
How Do Mediterranean House Geckos Behave?
Mediterranean house geckos are active at night. They make a special, high-pitched sound. It sounds a bit like a squeak or a bird's chirp. They might use this sound to tell other geckos to stay out of their area. Because adults can be aggressive, young geckos usually stay away from them.
These geckos are very good at hunting. They eat moths and small cockroaches. They are often drawn to outdoor lights. This is because the lights attract the insects they like to eat. They are also attracted to the calls of male crickets. Even though male crickets are usually safe in their burrows, female crickets attracted to the call can be caught and eaten by the geckos.
The Life Cycle of Mediterranean House Geckos
Mediterranean house geckos become adults and can have babies when they are between four months and one year old. Male geckos make clicking sounds to find a partner. Female geckos answer with their own squeaks.
The time for laying eggs is usually from April to August each year. Eggs are laid from mid-May to August. A female usually lays two eggs at a time. Female geckos can store sperm. This means they can get pregnant even after some time has passed since mating. Because of this, we don't know exactly how long they are pregnant, but it's thought to be around 40 days.
Neither the male nor the female gecko takes care of the babies. In fact, male geckos have been seen biting young geckos.
What Do Mediterranean House Geckos Eat?
Mediterranean house geckos mainly eat insects and other small creatures. Their favorite foods include crickets, grasshoppers, cockroaches, spiders, beetles, moths, butterflyes, ants, isopods, and snails.
These geckos hunt by seeing their prey. They prefer to eat living prey rather than dead ones.
Gallery
-
A close-up of a Mediterranean house gecko's foot and toe pads in Paphos, Cyprus.
-
A gecko with a longhorn beetle (its prey) on a wall in Messenia, Greece.
See also
- List of reptiles of Italy