Sedalia, Missouri facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sedalia, Missouri
|
|
|---|---|
| City of Sedalia | |

Former Third National Bank building located in downtown Sedalia
|
|
| Nickname(s):
Queen City of the Prairie
|
|
Location of Sedalia, Missouri
|
|
| Country | United States |
| State | Missouri |
| County | Pettis |
| Founded | 1857 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 14.32 sq mi (37.09 km2) |
| • Land | 14.29 sq mi (37.00 km2) |
| • Water | 0.03 sq mi (0.09 km2) |
| Elevation | 899 ft (274 m) |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 21,725 |
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
22,086 |
| • Density | 1,520.72/sq mi (587.16/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | Sedalian |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| ZIP codes |
65301-65302
|
| Area code(s) | 660 |
| FIPS code | 29-66440 |
| GNIS feature ID | 2396567 |
| Website | www.cityofsedalia.com |
Sedalia is a city in Missouri, United States. It's about 30 miles (48 km) south of the Missouri River. Sedalia is the main city in the Sedalia Micropolitan Statistical Area, which means it's an important center for the smaller towns around it. In 2020, about 21,725 people lived there.
Sedalia is famous for hosting the Missouri State Fair every August. It's also known for the Scott Joplin International Ragtime Festival, celebrating a famous musician. Two major roads, U.S. Routes 50 and 65, cross paths in the city.
Contents
History of Sedalia
For thousands of years before Europeans arrived, Indigenous peoples lived near the Missouri River. Historians believe the Osage Nation lived in the area where Sedalia is now. Later, some Shawnee people, who had moved from east of the Mississippi River, also lived nearby.
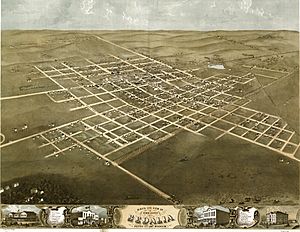
General George Rappeen Smith founded the area that became Sedalia. He officially recorded his plans on November 30, 1857, and first called the place Sedville. The original town plan covered the land from the Missouri Pacific Railroad south to Third Street.
During the American Civil War, the U.S. Army had a base in Sedalia. This brought many merchants and traders, helping the town grow quickly. After the war, two railroads were built, connecting Sedalia to other places. The city grew very fast, becoming a busy place for travelers and cowboys. From 1866 to 1874, it was a major stop for cattle drives, with large areas for livestock.
At the same time, Sedalia built schools, churches, and other community places. Musicians, especially piano players, found work here, leading to a lively music scene. This helped many artists, including the famous ragtime composer Scott Joplin, develop their talents. By 1900, Sedalia had over 15,000 people, making it the fifth-largest city in Missouri.
During World War II, a military base called Sedalia Glider Base was built nearby. After the war, it became Whiteman Air Force Base, named after a Sedalia man who died at Pearl Harbor. This base later became important for ICBMs, though these were removed in the 1990s.
Why the Name Sedalia?
The city was first called Sedville when it was planned in 1857. However, when it officially became a city in 1860, the name was changed to Sedalia. People say the town council changed it because "towns that end in -ville don't amount to anything."
Railroad History
The railroad reached Sedalia in January 1861. Sedalia's early success was closely linked to the railroad industry. Many people worked maintaining tracks and in the large machine shops of the Missouri Pacific Railroad and the Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad (known as the "KATY").
Sedalia was a key railhead for the huge Texas cattle drive of 1866. It had stockyards to receive and ship cattle for much of the 1800s. For almost 100 years, Sedalia's economy depended on the railroads. The KATY railroad had many buildings and workers in the city, including shops, stockyards, and a hospital for its employees.
After the KATY railroad reduced its operations, its old tracks through Missouri were turned into a 225-mile paved trail. This trail, called the KATY Trail, is now used by bikers, walkers, and horseback riders. It's one of the largest "Rails to Trails" projects in the country.
Sedalia During the Civil War
Even with Union soldiers guarding the railroad, Confederate forces almost took Sedalia during the Civil War. On October 15, 1864, about 1,500 cavalry soldiers from Confederate General Joseph O. Shelby surrounded Sedalia. They defeated the Union militia and started to loot the town. However, when Confederate General M. Jeff Thompson arrived, he ordered his men to stop and leave, keeping Sedalia in Union hands.
The Civil War did slow down some development, but Sedalia was the end of the railroad line for three years. After the war, many Union soldiers who had been stationed there saw its potential and decided to move to Sedalia. This caused the population to grow very quickly.
The Salvation Army in Sedalia
The Salvation Army opened its doors in Sedalia in 1886. William Booth, who founded the Salvation Army, even traveled from London to be there. When asked why he chose Sedalia, Captain George Parks of the Salvation Army said, "Because Sedalia is a desperately wicked city and if souls can be won to Christ in Sedalia, they can be won to Christ anywhere." Sadly, Parks was later badly beaten in downtown Sedalia and died almost a year later from his injuries. He is considered the first martyr for The Salvation Army in the United States.
Geography
Sedalia is located at 38°42'11" North and 93°13'52" West. The city covers a total area of about 13.32 square miles (34.50 km2). Most of this area, 13.29 square miles (34.42 km2), is land, and a very small part, 0.03 square miles (0.08 km2), is water.
Population and People
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 4,560 | — | |
| 1880 | 9,561 | 109.7% | |
| 1890 | 14,068 | 47.1% | |
| 1900 | 15,231 | 8.3% | |
| 1910 | 17,822 | 17.0% | |
| 1920 | 21,144 | 18.6% | |
| 1930 | 20,806 | −1.6% | |
| 1940 | 20,428 | −1.8% | |
| 1950 | 20,354 | −0.4% | |
| 1960 | 23,874 | 17.3% | |
| 1970 | 22,847 | −4.3% | |
| 1980 | 20,927 | −8.4% | |
| 1990 | 19,800 | −5.4% | |
| 2000 | 20,339 | 2.7% | |
| 2010 | 21,387 | 5.2% | |
| 2020 | 21,725 | 1.6% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 22,086 | 3.3% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||

In 1860, Sedalia had about 300 people. By 1865, it had grown to about 1,000 residents. Recently, many immigrants from Russia and other former Soviet countries have moved to Sedalia. They make up a good portion of the population. Most of these immigrants belong to one of the seven Pentecostal Churches in the city.
Population in 2020
The 2020 United States census counted 21,725 people living in Sedalia.
- About 77.12% of the people were white.
- About 5.37% were black or African-American.
- About 12.9% of the population were Hispanic or Latino (who can be of any race).
- The rest of the population included Native American, Asian, Pacific Islander, and people of two or more races.
The average age in Sedalia was 35.5 years. About 24.6% of the population was under 18 years old.
Arts and Culture
Carnegie Library
The Sedalia Public Library was the first library in Missouri to receive a grant from Andrew Carnegie. The grant of $50,000 was given in 1899. After getting the land and voter approval for a tax to support it, the library's cornerstone was laid in 1900. The building was finished and opened in July 1901. It is now listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Museums
Sedalia is home to the Daum Museum of Contemporary Art. This museum is named after Harold Daum, a radiologist and art collector from Sedalia who was a major supporter. The museum is located on the State Fair Community College campus. It displays works by many famous artists like Dale Chihuly, Sam Francis, Helen Frankenthaler, and Andy Warhol.
The museum is 16,000 square feet (1,486 m2) and has three floors of gallery space. It features both permanent art collections and temporary exhibits from artists around the world.
Sedalia also has The Pettis County Museum and Historical Society. It's located at 228 Dundee Ave. The building used to be a Jewish Synagogue. It holds many historical items from all periods of Pettis County's past.
Missouri State Fair
Since 1901, the Missouri State Fair has been held in Sedalia every August. The only times it didn't happen were in 1943 and 1944 because of World War II. Many singers and actors visit the fair each year. Presidents like Ronald Reagan and George W. Bush have also given speeches on the fairgrounds, though not during the fair itself.
In 1974, the Missouri State Fairgrounds hosted the Ozark Music Festival. This was one of the biggest music festivals of the 1970s. While only about 50,000 tickets were planned to be sold, around 184,000 fans (and some estimates say up to 350,000) showed up! This huge crowd and many rock bands put a lot of pressure on the fairgrounds and the city. The festival was hosted by Wolfman Jack and attracted people from all over.
Historic Places to Visit
Several places in Sedalia are listed on the National Register of Historic Places because of their historical importance:
- Hotel Bothwell
- C.C. Hubbard High School
- Missouri, Kansas and Texas Railroad Depot
- Missouri State Fairgrounds Historic District
- Sedalia Public Library
- And many historic homes and commercial buildings.
Little Sister of Liberty
In 1950, the Boy Scouts of America celebrated their 40th anniversary with the theme "Strengthen the Arm of Liberty." To mark this, they gave out 200 copper copies of the Statue of Liberty, each 8 feet 6 inches (260 cm) tall. These were called the "Little Sisters of Liberty."
One of these 200 copies was given to Sedalia. It was placed at the County Courthouse.
Education
Sedalia School District 200 manages five elementary schools, one middle school, and two high schools: Whittier High School and Smith-Cotton High School. There are also private schools like Sacred Heart High School and St. Paul's Lutheran School.
State Fair Community College is a public two-year college that offers courses after high school.
A historically black college called George R. Smith College operated in Sedalia from 1894 until it burned down in 1925.
Media
Newspapers
Several newspapers have been published in Sedalia over the years. Today, you can read The Sedalia Democrat and The Sedalia News-Journal.
Radio Stations
Sedalia has several local radio stations:
- KSDL 92.3FM
- KSIS 1050 AM
- KXKX 105.7 FM
- KDRO 1490 AM
- KPOW 97.7 FM
Television Stations
- KMOS-TV (Channel 6)
- K11OJ-TV (Channel 11)
Transportation
Air Travel
- Sedalia Regional Airport
Train Travel
- Sedalia (Amtrak station) is a stop for passenger trains.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sedalia (Misuri) para niños
In Spanish: Sedalia (Misuri) para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |