Solar power facts for kids
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is a way to turn energy from sunlight into electricity. This can happen in two main ways: directly, using photovoltaics (PV), or indirectly, using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use a special effect called the photovoltaic effect to change light into an electric current. Concentrated solar power systems use special lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a lot of sunlight onto one hot spot. This heat often creates steam, which then spins a steam turbine to make electricity.
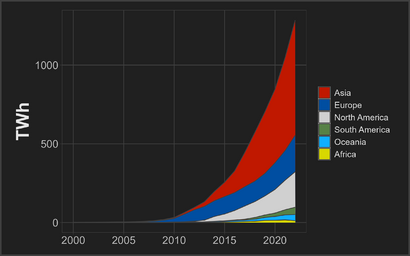
At first, photovoltaics (PV) were only used for small things, like calculators or homes far from the main power grid. Large concentrated solar power plants started being built in the 1980s. Since then, the cost of solar panels has dropped a lot. This has caused the amount of electricity made by solar PV systems connected to the main power grid to grow very quickly. Now, solar power is a huge part of new electricity production, with millions of rooftop installations and very large photovoltaic power stations being built.
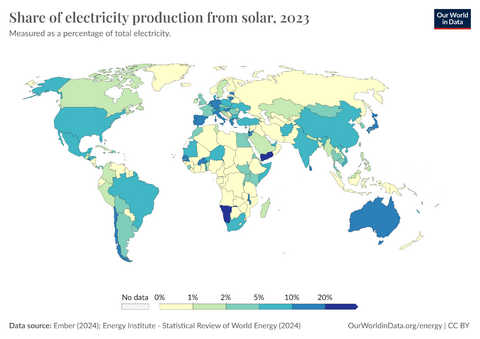
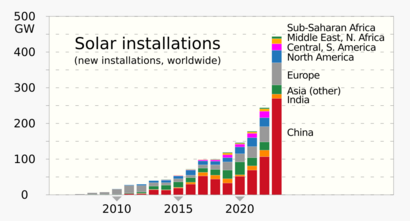
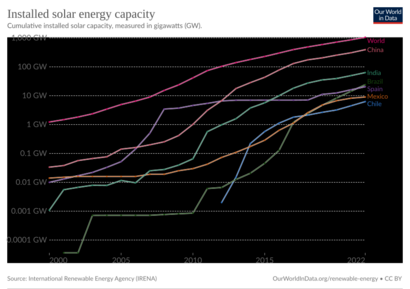
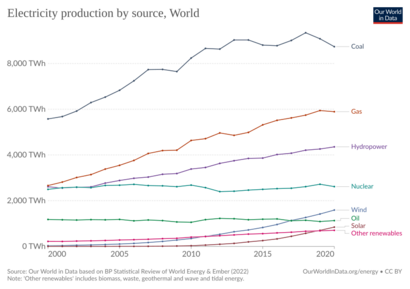
In 2024, solar power made 6.9% of the world's electricity. This was twice as much new electricity as coal. Solar power is now one of the cheapest ways to make new electricity in most countries, along with wind power. By 2023, 33 countries got more than 10% of their electricity from solar. China has been a leader in adding new solar power. Almost half of the solar power installed in 2022 was on rooftops.
We need much more low-carbon power to help with climate change. Experts say that solar power can greatly lower the cost of energy.
How Much Solar Energy Can We Use?
Geography plays a big role in how much solar energy a place can get. Areas closer to the equator usually receive more sunlight. However, solar panels that can follow the Sun's movement can greatly increase the energy collected, even in places farther from the equator. Cloud cover during the day can reduce the sunlight available for solar cells. Also, how much land is available affects how much solar energy can be used.
How Do Solar Technologies Work?
Solar power plants use two main types of technology:
- Photovoltaic (PV) systems use solar panels. These panels can be on rooftops or in large solar farms on the ground. They change sunlight directly into electric power.
- Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight. This creates extreme heat, which makes steam. The steam then spins a turbine to create electricity.
Understanding Photovoltaic Cells
A solar cell, also called a photovoltaic cell, is a device that turns light into electric current. It uses something called the photovoltaic effect. The first solar cell was made by Charles Fritts in the 1880s. Later, in 1954, researchers Gerald Pearson, Calvin Fuller, and Daryl Chapin created the silicon solar cell. These early cells were expensive and not very efficient. Over time, new methods like surface passivation helped make solar cells much better.
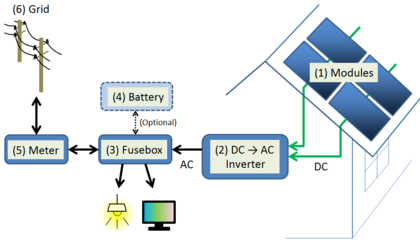
By 2022, most solar panels (over 90%) were made from crystalline silicon. A PV system produces direct current (DC) power. This power changes with how strong the sunlight is. For everyday use, this DC power usually needs to be changed into alternating current (AC) using devices called inverters. Many solar cells are connected inside panels. These panels are then wired together to form larger groups called arrays. The arrays connect to an inverter, which makes the power ready for use.
Many home PV systems are connected to the main power grid, especially in developed countries. In these grid-connected PV systems, storing energy is an option but not always needed. For places like satellites, lighthouses, or homes in remote areas, batteries or extra power generators are often added. These stand-alone power systems allow power to be used at night or when there isn't much sunlight.
New ways to use solar panels include "vertical agrivoltaics". Here, solar cells stand upright on farmland, allowing crops to grow while also making renewable energy. Other ideas include floating solar farms on water, solar covers over parking lots, and panels on roofs.
Thin-Film Solar Cells
A thin-film solar cell is a newer type of solar cell. It is made by putting very thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a base, like glass, plastic, or metal. These thin-film cells are used in different technologies, such as cadmium telluride (CdTe) and amorphous thin-film silicon.
Perovskite Solar Cells
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
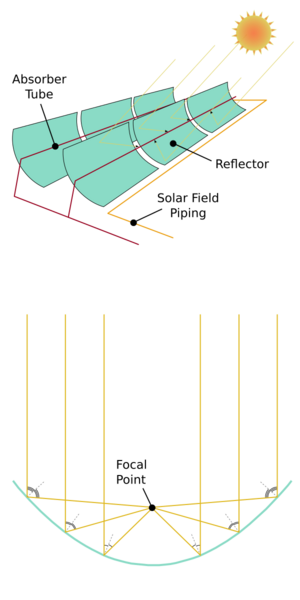
Concentrated solar power (CSP) uses special lenses or mirrors and tracking systems to focus sunlight. This creates very high heat. This heat is then used to generate electricity, usually by making steam that spins a turbine.
By 2022, less than 1% of all solar power came from CSP. This is because the cost of making electricity with CSP is higher than with PV systems.
Hybrid Solar Systems
A hybrid system combines solar power with other ways of making or storing energy. For example, solar can be combined with hydro power, wind power, or batteries. This helps the system provide power more steadily, even when the sun isn't shining. Combining solar panels with existing hydro dams is very useful. Hydro power can be adjusted quickly, and the existing power lines can be used.
How Solar Power Has Grown
The Beginning of Solar Power
People started developing solar technologies in the 1860s. They thought coal might run out soon. Charles Fritts put the world's first rooftop solar array on a New York City roof in 1884. His cells were only 1% efficient. However, solar technology development slowed down in the early 1900s. This was because coal and petroleum became much easier and cheaper to find.
In the 1950s, Bell Telephone Laboratories worked with silicon wafers. They created the "Bell Solar Battery," which was 6% efficient. The first satellite with solar panels was launched in 1957. By the 1970s, solar panels were still too expensive for most uses, except for satellites. But the energy crises of the 1970s made countries around the world look at solar power again.
Governments started programs to encourage solar energy. For example, the US had the Federal Photovoltaic Utilization Program. Japan had the Sunshine Program. Research centers were also created. Between 1970 and 1983, more and more photovoltaic systems were installed.
Solar Power from the 1990s to Today
In the mid-1990s, solar power started growing fast again. This was due to concerns about oil and natural gas supplies, worries about global warming, and solar power becoming more affordable. In the early 2000s, policies like "feed-in tariffs" helped solar power grow a lot in Europe. These policies guaranteed a fixed price for solar electricity.
For many years, Europe led the world in solar PV growth. Then, the focus shifted to Asia, especially China and Japan. Now, solar power is growing in many countries worldwide. China became the largest maker of solar equipment. The cost of large-scale solar PV dropped by 85% between 2010 and 2020. This made it much more popular than concentrated solar power (CSP).
Even with some material costs rising during the 2021–2022 global energy crisis, large solar farms remained the cheapest energy source in many places. This was because other energy sources, like natural gas, became more expensive. In 2022, the world's total solar power capacity went over 1,000 gigawatts (1 TW) for the first time.
Where Solar Power is Now
About half of the solar power installed today is in large utility-scale projects.
What's Next for Solar Power
It is expected that most new renewable energy built between 2022 and 2027 will be solar. Solar power is predicted to become the largest source of installed power capacity, even more than coal. Large solar farms are expected to become the biggest source of electricity in almost all parts of the world by 2050.
A study from 2021 estimated that rooftop solar panels could generate a huge amount of electricity each year. However, this depends on having good ways to store electricity.
Large Solar Power Plants
A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park or solar farm, is a very large system that uses solar panels to make electricity. These big solar farms are connected to the main power grid, which is like a huge network that delivers electricity to homes and businesses. They are different from the smaller solar panels you might see on a house roof because they produce power for a whole city or region, not just one building.
Solar farms mostly use photovoltaic (PV) technology. This means they turn sunlight directly into electricity. There's another type of large-scale solar called concentrated solar power, which uses mirrors to focus sunlight and create heat to make electricity. But PV technology is much more common for big solar farms today.
When we talk about how much power a solar farm can make, we often use terms like megawatt-peak (MWp) or gigawatt (GW). A megawatt is a million watts, and a gigawatt is a billion watts! Most solar parks are at least 1 megawatt in size, and some of the biggest ones can make over 1 gigawatt of power. By the end of 2019, there were about 9,000 large solar farms around the world.
Many of these big solar farms are owned by companies that specialize in making electricity. In the past, these projects often needed special help from governments, like payments for the electricity they produced (called feed-in tariffs) or tax credits. But now, making electricity with solar panels has become much cheaper. It's often as cheap as, or even cheaper than, electricity from other sources, so these special helps are usually not needed anymore.Concentrating Solar Power Stations
Large commercial concentrating solar power (CSP) plants started in the 1980s. The 377 MW Ivanpah Solar Power Facility in California is one of the world's largest. Other big CSP plants are in Spain, like the Solnova Solar Power Station. A big advantage of CSP is that it can store heat. This allows the plant to make electricity even after the sun goes down, or when it's most needed. Many CSP plants use molten salt to store heat for several hours.
The Cost of Solar Power
How Much Does Solar Power Cost?
The cost of solar power includes the panels, the frames that hold them, wiring, inverters, and the cost of installation. It also includes any land needed, connecting to the power grid, and maintenance. Solar panels do not use fuel, and they usually last for 25 to 40 years. This means that most of the cost of solar power comes from the initial setup and financing.
In many countries, solar power is now the cheapest way to get electricity. For example, in Saudi Arabia, a new solar power plant agreed in 2021 to produce electricity for a very low price.
Prices for Installing Solar
The cost of high-power solar panels has dropped a lot over time. In 1982, it cost about $27,000 per kilowatt. By 2006, it was about $4,000 per kilowatt. For a full PV system, the cost dropped from about $16,000 per kilowatt in 1992 to about $6,000 in 2008. In 2021, installing solar on homes in the US cost between $2 and $4 per watt. Large utility solar projects cost around $1 per watt.
Where Solar Power Works Best
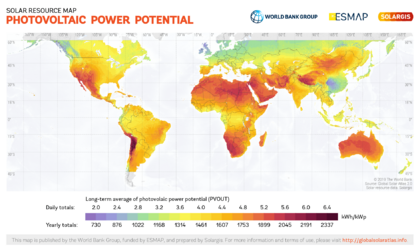
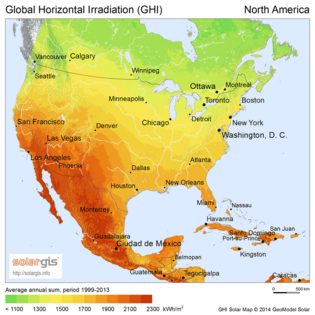
How much electricity solar power can produce in a region depends on how much sunlight it gets. This changes throughout the day and year. It is also affected by how close a place is to the equator and its weather. Other factors like temperature, wind, and dirt on the panels also affect how much power is made.
Wind power is often the cheapest electricity source in places like Northern Europe, Canada, and parts of the US. But in many other parts of the world, solar power is considered the best and cheapest option. Studies suggest that by 2030, solar could be the least expensive energy source almost everywhere.
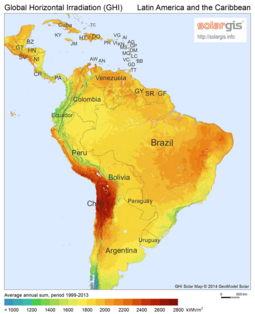
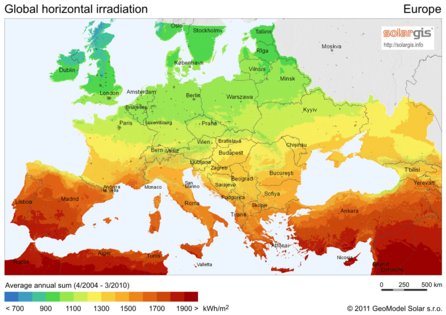
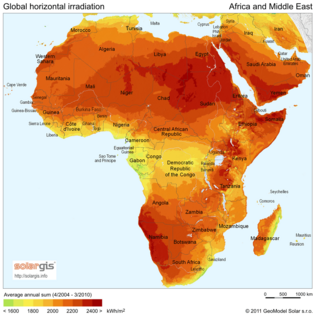
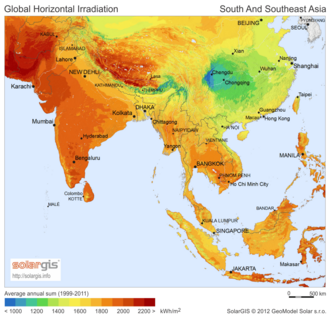
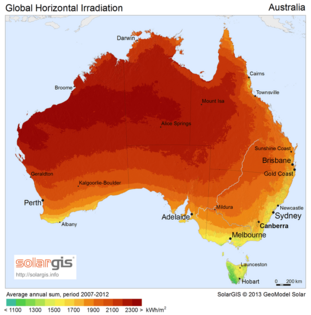
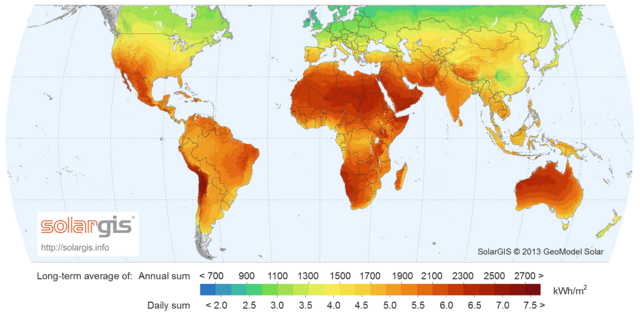
The places with the most sunlight are usually hot, dry areas near the equator. These deserts often have clear skies and many hours of sunshine. This "Global Sun Belt" includes large areas in Africa, Asia, Australia, and parts of North and South America. So, solar power is (or is expected to become) the cheapest energy source in all of Central America, Africa, the Middle East, India, Southeast Asia, and Australia.
Different maps show how much sunlight different areas receive:
Using Your Own Solar Power
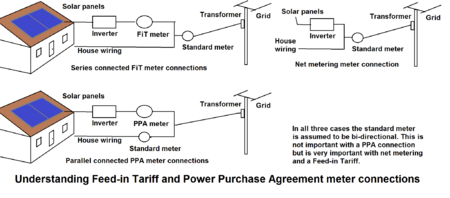
When you use the solar energy you produce yourself, you save money by not buying as much electricity from the grid. Sometimes, you might make more electricity than you need. This extra power can be sent back to the grid. When you need more power than your panels make, you buy it from the grid. The prices for buying and selling electricity affect how much you save. Often, the price you get for selling solar electricity is lower than what you pay to buy it. This encourages people to use more of their own solar power.
You can use more of your own solar power by storing it in batteries or by using electricity when your panels are making the most power. Batteries can be expensive, but they can also help during power outages. Hot water tanks with electric heaters can store solar energy cheaply. You can also run appliances like dishwashers or washing machines when the sun is shining.
Solar Power Incentives
Governments offer incentives to help solar power grow. These policies aim to make solar energy more common, even when it costs more than other energy sources. This helps the solar industry grow and become more affordable. Now that solar power is often cheaper, these policies also help countries become more energy independent and create new jobs.
Financial incentives for solar power are different in various countries, like Australia, China, Germany, India, Japan, and the United States.
What is Net Metering?
With net metering, the price you get for the electricity you produce is the same as the price you pay for electricity from the grid. You are only billed for the difference between what you use and what you produce. This system often works with regular electricity meters. It lets homes and businesses use the main power grid like a giant battery. If you produce more than you use in a month, the extra credit rolls over to the next month.
Community Solar Projects
A community solar project is a solar power system that many people can invest in. This includes individuals, businesses, and other groups. Participants get credit for the electricity produced and can receive tax benefits.
How Solar Power Connects to the Grid
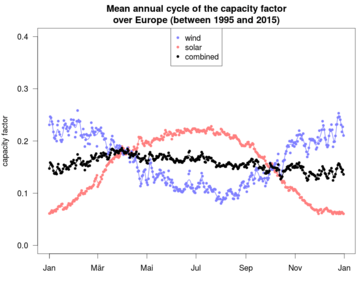
Why Solar Power Can Vary
Most electricity is used right away because traditional power plants can adjust to demand. Solar power and wind power are "variable" sources. This means their output changes depending on the weather and time of day. All the power they produce must be used right away, sent to other places, or stored. Since solar energy isn't available at night, storing it is very important, especially for homes not connected to the main grid.
Solar power changes because of day and night cycles and different weather. However, we can predict solar power somewhat based on the time of day, location, and seasons. Integrating solar power into an electricity system can be challenging. But in places with hot summers, solar power often matches well with the need for air conditioning during the day.
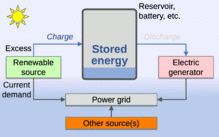
Storing Solar Energy
Concentrated solar power plants can use thermal energy storage to store solar energy. They often use hot molten salts. These salts are good for storage because they are cheap, hold a lot of heat, and can release heat at temperatures that work with power systems. This allows CSP plants to provide power even when the sun isn't shining.
In stand-alone PV systems, rechargeable batteries are used to store extra electricity. For grid-connected photovoltaic power systems, extra electricity can be sent to the electrical grid. Programs like net metering give credit for this electricity. This credit helps offset the cost of electricity taken from the grid when the solar system isn't producing enough. As solar power grows, more ways to balance the grid are needed.
As prices drop, PV systems are using more rechargeable batteries to store extra power for night use. Batteries used for grid-storage can help stabilize the electrical grid by reducing the need for power during peak times. In the future, cheaper batteries could play a big role. They could charge when there's lots of solar power and release energy when demand is high.
Common batteries for home solar systems include lead-acid and lithium-ion. Lithium-ion batteries are becoming more popular as their prices drop. Batteries from electric cars could also be used for storage in the future. Since most cars are parked a lot, their batteries could send electricity to the grid and take it back when needed.
Other Ways to Balance the Grid
Solar power plants usually produce as much power as they can. So, in an electricity system without enough grid energy storage, other power sources like coal, natural gas, or hydroelectricity must adjust their output. They go up and down to match the changes in solar electricity and demand.
Traditional hydroelectric dams work very well with solar power. Water can be held back or released from a reservoir as needed. If there are no suitable dams, pumped-storage hydroelectricity can be used. Solar power pumps water to a high reservoir on sunny days. Then, at night or in bad weather, the water is released through a hydroelectric plant to make electricity.
Combining wind and solar PV is also good because they often produce power at different times of the day and year. This makes the total power generation more steady. Solar power also changes with the seasons, especially far from the equator. This means we might need long-term storage, perhaps using hydrogen or pumped hydro.
How Solar Power Affects the Environment
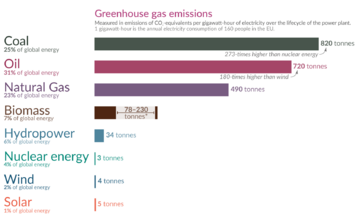
Solar power is much cleaner than electricity from fossil fuels. This makes it better for the environment. Solar power does not create harmful emissions when it is working. However, making the solar panels does create some pollution. The carbon footprint from manufacturing is small, and it is expected to get even smaller as factories use more clean electricity and recycled materials. Solar power has an initial environmental cost during production, but it provides clean energy for its long lifetime (about 30 years).
The total greenhouse gas emissions from solar farms over their whole life are very low. For example, they are much lower than gas or coal power plants. Switching to low carbon power for making and transporting solar equipment will reduce these emissions even more.
Large solar farms need a lot of land. This could lead to removing plants or changing farmland. However, some countries, like South Korea and Japan, use land for agriculture under PV panels. They also use floating solar farms. Overall, the land used for solar power worldwide has a minimal impact on nature. We can also put solar panels on buildings and other built-up areas to reduce land use.
Some materials are used to make solar panels, but usually in small amounts. For example, there are some concerns about lead in perovskite solar cells. The demand for materials like copper, tellurium, and indium is expected to increase as more solar power is built.
Recycling can help manage these materials. Old solar panels are sometimes reused in developing countries. Many countries also have rules for recycling solar panels. Even though maintenance costs are low, some experts want solar systems to be designed so they are easier to repair.
Large solar installations in deserts can increase the local temperature. This effect can be stronger than the heat island effect seen in cities.
A very small part of solar power comes from concentrated solar power. These plants can use a lot of water, which can be a problem in deserts where they are often built.
Solar Power and Global Connections
Once solar power systems are installed, they cannot be cut off by global events, unlike oil and gas. This helps countries have more energy security.
China makes a large amount of the world's polysilicon, which is used in solar panels. Experts believe that even if China's supply was cut off, other countries would have time to build their own manufacturing.
See also
 In Spanish: Producción de electricidad a partir de la luz solar para niños
In Spanish: Producción de electricidad a partir de la luz solar para niños
- 100% renewable energy
- Cost of electricity by source
- Gravity battery
- Index of solar energy articles
- List of cities by sunshine duration
- List of photovoltaic power stations
- List of solar thermal power stations
- List of solar-powered products
- Renewable energy commercialization
- Solar energy
- Solar lamp
- Solar vehicle
- Sustainable energy
- Thin-film solar cell
- Timeline of solar cells