Sumbawa facts for kids
 |
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 8°47′S 118°5′E / 8.783°S 118.083°E |
| Archipelago | Lesser Sunda Islands |
| Area | 15,323.77 km2 (5,916.54 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 57th |
| Highest elevation | 2,850 m (9,350 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Tambora |
| Administration | |
|
Indonesia
|
|
| Province | West Nusa Tenggara |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Sumbawan |
| Population | 1,626,517 |
| Pop. density | 106.14 /km2 (274.9 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Sumbawans, Bima people |

Sumbawa is a large island in Indonesia. It's part of the Lesser Sunda Islands, with Lombok to its west and Flores to its east. Together with Lombok, Sumbawa forms the West Nusa Tenggara province.
Long ago, Sumbawa was known for its special wood called sappanwood, as well as honey and sandalwood. The island has a savanna-like climate with big grasslands. This makes it a great place to raise horses and cattle, and even to hunt deer.
Sumbawa is about 15,323 square kilometers, which is three times bigger than Lombok. About 1.6 million people live there. The island is like a border between islands influenced by cultures from India (like Hinduism and Islam) and those less influenced. People from outside call the whole island "Sumbawa." But locals often call the western part "Sumbawa" and the eastern part "Bima." This is because the two parts have different geography, cultures, and languages.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name "Sumbawa" comes from older names like Cumbava or Cimbava. These names likely came from the local word Sambawa. Some people think the name might even come from an old Sanskrit word, śāmbhawa, which means 'related to Shiva', a Hindu god.
Island History
In the 1300s, old writings mention several small kingdoms on Sumbawa, like Dompu and Bima. Four kingdoms in western Sumbawa were connected to the powerful Majapahit Empire on Java. Because Sumbawa had many natural resources, different groups often tried to control it. These included people from Java, Bali, and Makassar, as well as the Dutch and Japanese. The Dutch first arrived in 1605 but didn't fully rule Sumbawa until the early 1900s.
For a short time, a kingdom from Bali called Gelgel ruled part of western Sumbawa. The eastern side of the island was divided into four sultanates (areas ruled by a sultan). These were Sumbawa, Sanggau, Dompo, and Bima. They had strong ties with the Bugis and Makassar people from Sulawesi.
People in the East Indies knew Sumbawa for its honey, horses, and special wood. Sappanwood was used to make red dye, and sandalwood was used for incense and medicines. The island was also known for its good farming. In the 1700s, the Dutch started growing coffee on the slopes of Mount Tambora. This led to a special kind of coffee called Tambora coffee.
Mount Tambora's Big Eruption
Mount Tambora is a volcano on Sumbawa. In 1815, it had a huge eruption. It was the strongest eruption ever recorded! The volcano shot out a massive amount of ash and rocks, about 180 cubic kilometers. This eruption killed up to 71,000 people. It also caused a period of global cooling around the world, leading to what was called the "Year Without a Summer" in 1816. The eruption also destroyed a small local culture known as the "Tambora culture."
How Sumbawa is Governed
Sumbawa is divided into four main areas called regencies and one city. Each has its own capital. These areas are:
- Sumbawa Regency (capital: Sumbawa Besar)
- Dompu Regency (capital: Dompu)
- Bima Regency (capital: Woha)
- West Sumbawa Regency (capital: Taliwang)
- Bima City (capital: Bima)
There have been talks about making Sumbawa Island its own separate province. However, the Indonesian government has put a hold on creating new provinces for now.
People of Sumbawa
Islam is the main religion on Sumbawa. It was brought to the island by the Makassarese from Sulawesi.
Historically, people on Sumbawa spoke three main languages that were very different from each other. The Sumbawa people in the west speak Basa Semawa, which is similar to the language spoken on Lombok. The Bima people in the east speak Nggahi Mbojo, which is more like languages spoken on Flores and Sumba. The "Tambora culture" once spoke a different language, but they disappeared after the 1815 eruption.
Today, the island is still divided into two main cultural parts, centered around the towns of Sumbawa Besar and Bima. A small group called the Don Donggo, or "Mountain People," live in the cloudy highlands west of Bima Bay.
About 1.6 million people live on Sumbawa. Many people from the island go to work overseas, especially in the Middle East. They often work as laborers or domestic helpers because there aren't enough jobs on the island, and it often has droughts.
Island Geography
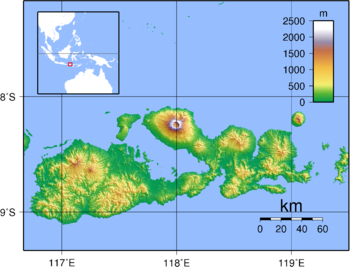
Sumbawa is surrounded by water. To the west is the Alas Strait, and to the south is the Indian Ocean. The Flores Sea is along the northern coast. The Saleh Bay is a big bay that cuts into the middle of the island. To the east, the Sape Strait separates Sumbawa from Flores and the Komodo Islands. There are also other bays like Bima Bay and Cempi Bay.
The most famous features of Sumbawa are Saleh Bay and the Sanggar Peninsula. On this peninsula stands Mount Tambora, a very large volcano. Its huge eruption in 1815 changed its shape, making its top much lower and leaving a six-kilometer-wide caldera (a large crater). Even so, Tambora is still the highest point on the island. There are also other high areas across the island.
Several other islands are close to Sumbawa. These include Moyo Island, the active volcano island of Sangeang, and the popular tourist Komodo Islands (which are managed by Flores). Sumbawa is part of the Lesser Sundas deciduous forests ecoregion, which means it has forests that lose their leaves in the dry season.
Islands Around Sumbawa
Many smaller islands are located near Sumbawa and are part of its regencies:
- West Sumbawa Regency: Susait, Dua, Belang, Songi, Ular, Kenawa, Natano
- Sumbawa Besar Regency: Panjang Island, Saringi, Kemudang, Ayer Tawat, Romo, Medang Island
- Saleh Bay, Sumbawa Besar Regency: Moyo Island, Dangar Besar, Liang, Ngali, Tengar, Kelapang, Dompo, Takebo, Paming, Lipa, Rakit
- Dompu Regency: P. Besar, P. Nisa Pudu, P. Nisa Rate
- Bima Regency, Tambora Peninsula exclave: Satonda Island
- Bima Regency: Sangeang Island, Sanai Island, Matagate Island, Banta Island
Island Economy
Many people on Sumbawa work in agriculture. Sometimes, if there isn't enough rain, crops can fail, which can make it hard for people to find food. Tourism is also starting to grow, with some famous surf spots like Jelenga and Supersuck Beaches, and Hu'u and Lakey Beach in the Gulf of Cempi.
The Batu Hijau Mine
A big gold and copper mine called Batu Hijau mine started working in 2000. It's located in southwest Sumbawa. This mine is one of the largest copper mines in the world, and its resources are expected to last until 2034. Because of this mine, the West Sumbawa Regency has one of the highest income rates per person in Indonesia. Another important gold and copper deposit was found near Onto in 2020, and mining there might start around 2030.
Getting Around Sumbawa
Sumbawa has a road network, but some parts are not in good condition. There are regular ferry services to Sumbawa (Poto Tano) from Lombok (Labuhan Lombok). However, ferries to Flores from Sape are less frequent. Bima is the biggest city on Sumbawa and has ferry and bus services that go directly to Java and Bali.
The easiest way to get to Sumbawa is by flying. The main airport is Bima airport. You can fly there from Denpasar (Bali) and Makassar.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sumbawa para niños
In Spanish: Sumbawa para niños
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |