Timeline of rocket and missile technology facts for kids
This article is like a journey through time, showing you the most important moments in the history of rocket and missile technology. From ancient fire arrows to modern spacecraft, you'll see how these amazing machines have changed over the centuries.
Contents
Early Days: 11th to 13th Century
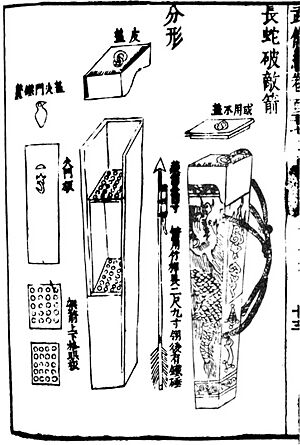
- 11th century AD: The very first records of what seems to be gunpowder and the "fire arrow" appear in China. These fire arrows were an early type of rocket. They are described in an old Chinese book called Wujing Zongyao.
- Around 1250: In Europe, two important thinkers, Roger Bacon and the author of a book called Liber Ignium, wrote down ways to build devices that looked like early rockets.
Rocket Progress: 17th to 19th Century
- 1633: A person named Lagâri Hasan Çelebi in Istanbul, Turkey, launched a large rocket. It had seven wings and used a lot of gunpowder!
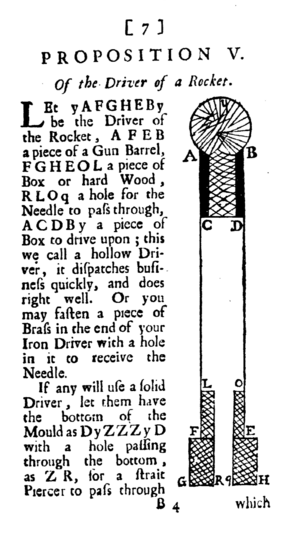
- 1650: A book called Artis Magnae Artilleriae pars prima (which means "Great Art of Artillery, the First Part") was printed. It was written by Kazimierz Siemienowicz and was very important for rocket design.
- 1696: Robert Anderson suggested a big idea: making rockets out of metal. He thought a metal casing, like a gun barrel, would be much stronger than wood or cardboard.
- 1798: In India, Tipu Sultan, the King of Mysore, developed and used iron-cased rockets against the British Army. These were called Mysorean rockets.
- 1801: The British Army then created their own Congreve rockets. They based them on the powerful rockets they had seen Tipu Sultan use.
- 1806: Claude Ruggieri, an Italian living in France, did some wild experiments! He launched animals on rockets and brought them back safely using parachutes. He even wanted to launch a child, but the police stopped him.
- 1813: The first time the "rocket equation" appeared in a book was in "A Treatise on the Motion of Rockets" by William Moore. This equation helps scientists understand how rockets move.
- 1844: William Hale invented the spin-stabilized rocket. This meant the rocket would spin as it flew, making it much more stable and accurate.
- 1861: William Leitch wrote an essay called "A Journey Through Space." He suggested that rockets would be great for space travel because they work even better in the emptiness of space.
The 20th Century: Space Dreams Come True
- 1902: French filmmaker Georges Méliès directed A Trip to the Moon. This was one of the first movies about traveling to space.
- 1903: Konstantin Tsiolkovsky from Russia started writing about how rockets could reach outer space. He talked about using liquid fuels and staging (where parts of the rocket fall away as fuel is used up).
- 1922: Hermann Oberth published his important book, Die Rakete zu den Planetenräumen ("By Rocket into Planetary Space"). It was about rockets and exploring space.
- 1926: Robert Goddard in the USA launched the first rocket powered by liquid fuel. Many people see this as the true beginning of the Space Age.
- 1927: The "Spaceflight Society" (Verein für Raumschiffahrt or VfR) was started in Germany. This group helped push rocket science forward.
- 1928: In Germany, public rocket experiments became popular. Max Valier and Fritz von Opel used rockets to set speed records for cars and trains.
- 1929: Woman in the Moon was released. It's seen as one of the first serious science fiction films about space.
- 1933: Sergei Korolev and Mikhail Tikhonravov launched the first liquid-fueled rocket in the Soviet Union.
- 1935: Emilio Herrera Linares from Spain designed the first full-pressure astronaut suit. It was called the escafandra estratonáutica. Later, the Russians used a model of his suit for their space flights.
- 1936: Rocket research began at the Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory (GALCIT) in California. This group later became the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which builds many of NASA's robotic spacecraft.
- 1939: The Katyusha multiple rocket launchers were first built and used by the Soviet Union. These launchers could fire many rockets at once.
- 1942: Wernher von Braun and Walter Dornberger launched the first V-2 rocket in Germany.
- 1944: A V-2 rocket (called MW 18014) reached an amazing height of 176 kilometers. This made it the first human-made object to reach space!
- 1945: After World War II, many German rocket scientists were moved to the United States (in Operation Paperclip) and the Soviet Union (in Operation Osoaviakhim) to help with their rocket programs.
- 1947: The first animals sent into space were fruit flies. They flew aboard a V-2 rocket launched from New Mexico, USA.
- 1947: Chuck Yeager became the first person to fly faster than the speed of sound in a Bell X-1 rocket-powered plane.
- 1957: The USSR launched the first ICBM (Intercontinental Ballistic Missile), called the R-7.
- 1957: The USSR launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth! This was a huge moment in history.
- 1958: The U.S. launched Explorer 1, their first artificial satellite, on a Jupiter-C rocket.
- 1961: The USSR launched Vostok 1, carrying Yuri Gagarin. He became the first person to orbit Earth!
- 1961: The U.S. launched Mercury-Redstone 2 with the chimpanzee Ham, who became the first ape in space.
- 1961: The U.S. launched Freedom 7 with Alan B. Shepard. He became the first American in space, though his flight was a shorter "suborbital" one.
- 1962: John Glenn became the first American to orbit Earth aboard Friendship 7.
- 1962: Pakistan launched Rehbar-I, becoming the first country in the Islamic world to send a vessel into outer space.
- 1963: The USSR launched Vostok 6, carrying Valentina Tereshkova. She was the first woman (and first civilian) to fly into space and orbit Earth.
- 1965: France launched Diamant, their first rocket to reach orbit. This made France the third country to send a satellite into space.
- 1966: The USSR's Luna 9 made the first soft landing on the Moon. This meant it landed gently without crashing.
- 1968: The U.S. Apollo 8 mission was the first time humans traveled to and orbited the Moon.
- 1969: The U.S. Apollo 11 mission achieved the first crewed landing on the Moon! Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walked on the lunar surface.
- 1975: The European Space Agency (ESA) was created. This agency brings together many European countries to work on space projects.
- 1981: The U.S. Space Shuttle began flying. It was a reusable spacecraft that could launch like a rocket and land like a plane.
- 1998: Russia launched the Zarya module, which was the very first part of the International Space Station (ISS).
The 21st Century: New Frontiers
- 2001: The Russian Soyuz spacecraft took the first space tourist, Dennis Tito, to the International Space Station.
- 2004: SpaceShipOne, a privately built spacecraft, made the first crewed (suborbital) spaceflight by a private company. It showed that private companies could send people to space.
- 2008: SpaceX, a private company, successfully launched its Falcon 1 rocket into orbit. This was a big step for private space travel.
- 2012: The SpaceX Dragon 1 capsule became the first private spacecraft to dock with the International Space Station.
- 2015: SpaceX achieved a major breakthrough! For the first time, the first stage of an orbital rocket (a Falcon 9) landed successfully back on Earth after launch. This made rockets much more reusable.
- 2017: SpaceX made history again by successfully reusing a Falcon 9 rocket that had already flown to space before.
- 2018: The Electron rocket, from New Zealand, reached orbit. It uses special electric-powered engines. It also carried a shiny satellite called "Humanity Star" that reflects sunlight.
- 2020: The SpaceX Dragon 2 capsule launched astronauts to space on a Falcon 9 rocket. This was the first time a private company sent humans to orbit.
- 2023: India launched Chandrayaan-3, which successfully landed a spacecraft on the Moon's south pole, a challenging and unexplored area.
See also
- History of rockets
- List of missiles
- Lists of rockets

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Timeline of rocket and missile technology Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.