Trans-Pecos facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
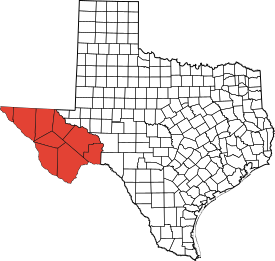
Trans-Pecos
|
|
|---|---|

Ocotillo in the Chihuahuan Desert of the Trans-Pecos
|
|
 |
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| Largest city | El Paso |
| Area | |
| • Land | 81,530 km2 (31,479 sq mi) |
| Population
(2020)
|
919,421 |
The Trans-Pecos is a special part of Texas. It lies west of the Pecos River. People also call it Far West Texas. This area is part of the Chihuahuan Desert. This desert is the largest in North America!
The Trans-Pecos is very mountainous and dry. Most of its huge area does not have many people living there. The biggest city is El Paso. This region has some of the largest counties in Texas. It is famous for the natural beauty of the Big Bend area. The Rio Grande river also flows through a deep gorge here. Part of the river is even a special "National Wild and Scenic River."
Most of the land in Trans-Pecos is private ranchland. But there are also big parks like Big Bend Ranch State Park, Big Bend National Park, and Guadalupe Mountains National Park. Besides El Paso, other important cities are Pecos, Fort Stockton, and Alpine.
Contents
Understanding the Trans-Pecos Population
The Trans-Pecos region includes nine counties. These are Brewster, Culberson, El Paso, Hudspeth, Jeff Davis, Pecos, Presidio, Reeves, and Terrell.
Exploring Brewster County
Brewster County is the biggest county in the region. It covers about 6,193 square miles. This is like a state 10% larger than Connecticut! But Brewster County has very few people. There are only about 1.4 people per square mile. In contrast, Connecticut has about 723 people per square mile.
Discovering Terrell County
Terrell County is the least populated county. It borders both the Pecos River and the Rio Grande. In 2000, Terrell County had only 984 residents. It covers 2,358 square miles. This means less than 0.5 people live per square mile.
El Paso County: A Busy Area
El Paso County is the opposite of Terrell County. It is the smallest county but has the most people. El Paso County is only 1,015 square miles. Yet, it has over 800,000 people! This means about 789 people live per square mile. This is even more crowded than Connecticut. El Paso County holds most of the region's total population.
Overall Population Density
The Trans-Pecos region has about 856,187 people in total. It covers 31,479 square miles. This results in about 27 people per square mile. This is much less than the rest of Texas. If Trans-Pecos were its own state, it would be one of the least populated.
Traveling Through Trans-Pecos Roads
Major roads help people travel across the Trans-Pecos. Interstate 10 and Interstate 20 are the largest freeways.
Key US Highways in the Region
Important federal highways include US Highway 90 and US Highway 67. These two highways sometimes run together. Highway 90 goes east from Alpine to Del Rio. Highway 67 goes south from Marfa to the Mexico–United States border. It connects to Mexican Federal Highway 16 in Mexico.
State Highways for Exploration
State Highway 17 starts in Pecos. It passes through Balmorhea State Park. Then it joins Route 67 in Marfa. State Highway 118 begins near where Interstates 10 and 20 meet, near Kent. It goes south to Study Butte. This town is at the entrance of Big Bend National Park.
Wine Production in Trans-Pecos
The Trans-Pecos region is home to special areas for growing grapes. These are called American Viticultural Areas.
Designated Wine Regions
There are three main wine regions here. They are the Escondido Valley AVA and the Texas Davis Mountains AVA. A part of the Mesilla Valley AVA is also in Trans-Pecos. Most of the Mesilla Valley AVA is actually in New Mexico.
Images for kids
-
Rio Grande valley in the Big Bend area



