Video game console facts for kids
A video game console is an electronic device that shows video games on a screen. You play these games using a game controller. Consoles can be for your home, like a PlayStation or Xbox, connecting to your TV. Or they can be handheld, like a Nintendo Switch, which has its own screen and controls so you can play anywhere. Some consoles, called hybrid consoles, can do both!
Video game consoles are like special computers made just for playing games. They are designed to be easy to use and affordable for everyone. They might not be as powerful as a super-fancy computer, but they are perfect for gaming. Games often come on game cartridges or discs, or you can download them. Modern consoles can also play movies and music, acting like a media player.
New video game consoles usually come out every 5 to 7 years. This period is called a "generation." Companies often sell consoles at a low price, sometimes even losing money on them. They make their profit from selling games and accessories. This encourages people to buy the next console when it comes out. Right now, the main companies making consoles are Sony (with PlayStation), Microsoft (with Xbox), and Nintendo (with the Nintendo Switch).
Contents
History of Video Game Consoles
The very first video game consoles appeared in the early 1970s. A person named Ralph H. Baer came up with the idea of playing simple games on a TV screen in 1966. This idea led to the Magnavox Odyssey console in 1972.
Inspired by a table tennis game on the Odyssey, the creators of the famous arcade game Pong decided to make a home version. This home Pong console came out in 1975. These early consoles could only play a few games that were built right into them.
Then, in 1976, the Fairchild Channel F introduced something new: consoles that used game cartridges you could swap out. This meant you could buy new games! The Atari 2600, released in 1977, made this idea very popular.
Handheld consoles started to appear as technology got better. Early examples include the Microvision in 1979 and Game & Watch in 1980. The Game Boy in 1989 truly brought handheld gaming to life.
Over time, both home and handheld consoles became much more advanced. This was thanks to better computer chips, amazing 3D graphics, the internet, wireless connections, and larger game storage. Each new generation of consoles brought more power and new features, usually lasting about five years.
Different Types of Consoles
Most consoles today are "programmable." This means you can switch between different games. You can do this by using physical game cartridges or discs. Now, it's also very common to download games online and save them on the console.
Some consoles are called "dedicated consoles." These consoles have games built right into them, and you can't add new games. You usually switch between the built-in games using buttons or menus. Dedicated consoles were common in the very first generation of gaming. More recently, they've been used for "retro-consoles" like the NES Classic Edition and Sega Genesis Mini, which come with many classic games already installed.
Home Video Game Consoles
Home video game consoles connect to a TV or monitor and need to be plugged into an outlet. This means you usually play them in one fixed spot, like your living room. You use separate controllers, which can be wired or wireless, to play the games.
Examples of home consoles include the Atari 2600, Nintendo Entertainment System, and Sega Genesis. More modern examples are the Wii U, PlayStation 5, and Xbox Series X.
Handheld Game Consoles
Handheld game consoles are devices that have their own screen and game controls built right into them. They also have a rechargeable battery or use regular batteries. This design lets you carry them around and play games almost anywhere!
Famous handheld consoles include the Game Boy, PlayStation Portable, and Nintendo 3DS.
Hybrid Video Game Consoles
Hybrid video game consoles can be used in two ways: as a handheld device or as a home console. They can connect to a TV using a wired connection or a docking station. This allows you to play on a big screen with separate controllers. But you can also pick them up and play them on the go like a handheld.
While some older consoles had similar features, many people consider the Nintendo Switch to be the first true hybrid console.
Microconsoles
A microconsole is a home video game console that uses less expensive computer parts. This makes the console cheaper than other home consoles. Most microconsoles are based on the Android system and come with gamepads. You connect them to your TV to play games downloaded from app stores like Google Play.
Plug and Play / Retro Consoles
In recent years, special consoles have come out that offer many games built-in. Most of these "plug directly into your television," which is why they are often called "plug-and-play" consoles. They are also dedicated consoles, meaning you can't usually add new games.
These consoles often come with the unit itself, controllers, and everything needed to connect to your TV. Many recent plug-and-play consoles are designed to let you play many retro games from a specific older console. Examples include the Atari Flashback series, the NES Classic Edition, and the Sega Genesis Mini. There are also handheld retro consoles like the Nintendo Game & Watch color screen series.
Parts of a Console
Video game consoles have many parts working together to let you play games. Here are some common ones:
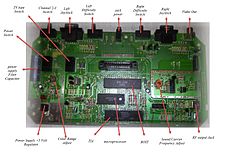
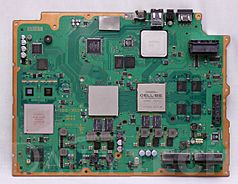
- Motherboard
- This is the main circuit board inside the console. All the important chips, like the CPU, are attached to it.
- Central processing unit (CPU)
- The CPU is like the "brain" of the console. It does most of the calculations and work for the game. CPUs are measured by their "word size" (like 8-bit or 64-bit) and "clock speed" (how fast they run). A bigger word size and faster clock speed usually mean better performance. Newer CPUs can have "multiple processing cores," which means they can do many tasks at once, like handling game graphics, physics, and your controls all at the same time.
- Graphical processing unit (GPU)
- The GPU is a special chip that creates the images you see on your screen. In older consoles, GPUs handled simple graphics. But with the rise of 3D games, modern GPUs became very powerful. They can do complex math to create realistic 3D worlds in real-time. Modern console GPUs are very good at doing many calculations at once, which helps games look amazing.
- Random-access memory (RAM)
- RAM is a type of fast memory that stores game data while you are playing. It helps the console quickly access information without having to read from the slower game disc or download. RAM usually clears when the console is turned off. The amount of RAM and how fast it can transfer data (bandwidth) are important for console performance.
- Internal storage
- Newer consoles have built-in storage like flash memory, hard drives, or solid-state drives (SSD). This storage saves game progress, downloaded games, updates, and other media. Modern consoles like the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X use very fast SSDs. These SSDs not only store games but also help games load incredibly quickly, almost as fast as RAM.
- Power supply
- This part converts the electricity from your wall outlet into the right kind of power for the console. Some consoles have the power supply built inside, while others use a separate "power brick" that plugs into the wall. Handheld consoles use batteries or a rechargeable battery pack.
- Cooling systems
- Powerful consoles generate heat. Cooling systems, like fans and cooling fins, help keep the console from getting too hot. They move air through the console to keep the parts at a safe temperature.
- Media reader
- Most consoles have a slot for game cartridges or a drive for optical discs (like CDs, DVDs, or Blu-rays). Some newer consoles offer versions without a disc drive, relying only on downloaded games.
- Case
- The case is the outer shell of the console. It protects the electronic parts inside and helps with air circulation for cooling.
- Input/output ports
- These are the places where you plug things in, like the power cord, controllers, TV cables, or external storage devices. Controller ports are usually on the front, while most other connections are on the back.
Game Controllers
All game consoles need a game controller so you can play. Controllers let you move characters, jump, interact with the game world, and more. While controllers have become more advanced, they still offer a different way to play compared to a computer mouse and keyboard. This has led game designers to create games that work well with console controllers.
Controllers have come in many different styles throughout gaming history:
- Paddle
- An early type of controller with a single knob or dial and usually one or two buttons. Turning the knob would move something on screen, like a paddle in a table tennis game.
- Joystick
- A controller with a long handle that you can push in different directions. It also has one or more buttons. Joysticks let you move in two directions at once.
- Gamepad
- This is the most common type of controller today. It has many buttons, triggers, and directional controls like D-pads or analog sticks. Gamepads are designed to be comfortable to hold while giving you many ways to control the game.
Many other types of controllers exist, including those that use motion controls (like the Wii Remote), touchscreens on handhelds, and special controllers for specific games (like racing wheels or light guns). Some modern consoles also let you use a mouse and keyboard.
Controllers can connect to the console with a wire or wirelessly. Wired controllers get power from the console. Wireless controllers need batteries or a rechargeable pack. Handheld consoles usually have controls built-in, but some also let you use separate wireless controllers.
Game Media
The first game consoles had games built right into them. But then, the Fairchild Channel F introduced the idea of storing games separately on cartridges. This meant people could buy new games to play on their console. Since then, almost all consoles have allowed you to buy and swap games, though the ways games are stored have changed with technology.
- ROM cartridge or game cartridge
- These were first used with the Fairchild Channel F. A cartridge is a plastic case with a circuit board inside that holds the game software. Later cartridges could even have extra chips to make the console perform better. Cartridges became less common when optical discs appeared, but they are still used today for consoles like the Nintendo 3DS and Switch, using modern flash memory.
- Optical media
- Discs like CD-ROMs, DVDs, and Blu-rays became the main way to buy games in stores starting with the fifth generation of consoles. Discs were cheaper to make, faster to produce, and could hold much more game data, even full-motion videos.
- Digital distribution
- Since the seventh generation of consoles, most consoles can connect to the Internet. This allows players to buy and download new games directly to their console without needing a physical disc or cartridge. Companies like Nintendo, Sony, and Microsoft have online stores where you can buy games.
- Cloud gaming
- With faster internet, cloud gaming has become another way to play. Instead of downloading games, you play them directly from a cloud gaming service. Your controller commands go to a server, and the game's video and audio are sent back to your console. The main challenge with cloud gaming is making sure there's no delay (latency) in the connection.
External Storage
Besides built-in storage, many newer consoles let you use external storage. This is for saving game data, downloaded games, or other media. Early external storage used memory cards, which became popular with the PlayStation. Nintendo still uses SD cards for its 3DS and Switch consoles. As consoles started having USB ports, they also added support for USB external hard drives, like with the Xbox 360.
Online Services
Consoles that connect to the internet often offer online services. Some are free, like creating a user profile and accessing the online game store. Others require a paid subscription. Paid services let you play games online with friends, chat with other players, save your game progress to the cloud, and sometimes get free games. Examples include the Xbox network, PlayStation Network, and Nintendo Switch Online.
Console Add-ons and Accessories
Over the years, many add-ons and accessories have been made to extend what consoles can do.
- Console Add-ons
- These are devices that attach to the console to add new features. A good example is the CD-ROM add-ons for fourth-generation consoles like the TurboGrafx CD or Sega CD. Another example is the Game Boy Player for the GameCube, which let you play Game Boy games on your TV.
- Accessories
- These are extra items you can buy for your console.
- Video cameras: These can be used for chatting with friends or for games that use augmented reality or motion sensing. Devices like the EyeToy for PlayStation and the Kinect for Xbox were popular for these types of games.
- Standard Headsets: These combine headphones and a microphone. They let you chat with other players online without disturbing people around you.
- Virtual reality headsets: Some VR headsets can work with consoles. The PlayStation VR is an example of a VR headset made for a console.
- Docking stations: For handheld or hybrid consoles like the Nintendo Switch, a docking station makes it easy to charge the console and connect it to a TV screen.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Videoconsola para niños
In Spanish: Videoconsola para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |