Methane facts for kids
Methane is a hydrocarbon that is a gas at normal room temperature (about 20°C). It's the simplest hydrocarbon! Its molecular formula is CH4, which means each methane molecule has one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Methane is the main part of natural gas and is a colorless, odorless gas.
Methane is also a greenhouse gas, which means it helps trap heat in Earth's atmosphere, contributing to climate change. It's about 22 times stronger at trapping heat than carbon dioxide, but it doesn't stay in the atmosphere as long. Over time, it slowly changes into carbon dioxide and water when it reacts with oxygen.
Contents
What Methane Looks Like
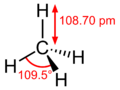
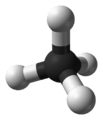
The methane molecule is very simple. Imagine a central carbon atom with four hydrogen atoms attached to it, spreading out evenly in a 3D shape called a tetrahedron. It looks a bit like a pyramid with a triangular base.
How Methane is Found
Methane can be made in labs, but we usually find it deep underground as part of natural gas. To get it, natural gas is cooled down until it becomes a liquid. Then, different parts of the gas are separated using a process called fractional distillation.
How We Use Methane
Methane is super important in many industries. It can be transported as a very cold liquid called liquefied natural gas (LNG). While cold LNG vapor is heavier than air, methane gas at normal temperatures is lighter than air. Huge amounts of natural gas, mostly methane, are moved through pipelines across countries.
As a Fuel
Methane is a common fuel for many things. We use it in ovens, to heat homes and water, in factories, and even in some cars and power plants. Special materials like Activated carbon can store methane.
Natural Gas for Power
Methane is key for making electricity. It's burned as a fuel in large gas turbines or steam generators. When methane burns, it produces less carbon dioxide for the amount of heat it gives off compared to other hydrocarbon fuels.
Methane gives off a lot of heat when it burns. For example, in many cities, methane is sent through pipes directly into homes for heating and cooking. Here, it's usually called natural gas. It has a lot of energy, about 39 megajoules per cubic meter.
Methane, when compressed (called compressed natural gas), is also used as a vehicle fuel. Many people think it's better for the environment than gasoline or diesel fuel. Scientists are also looking into new ways to store methane for cars.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is basically natural gas (mostly methane) that has been turned into a liquid. This makes it much easier to store and transport.
LNG takes up about 600 times less space than natural gas in its gas form. It doesn't have a smell, is clear, and isn't poisonous or corrosive. But be careful, if it turns back into a gas, it's very flammable! Also, it's extremely cold, so it can cause freezing, and it can reduce oxygen in the air, leading to asphyxia.
To make LNG, natural gas is cleaned first. Things like dust, water, and other gases are removed. Then, the natural gas is cooled down to about -162°C, which turns it into a liquid.
Because LNG takes up so little space, it's a very good way to transport natural gas over long distances, especially where there are no pipelines. Special cryogenic ships called LNG carriers or road tankers are used to move it. Even if it's under pressure, methane needs to be cooled below -82.3°C to become a liquid.
LNG is mostly used to get natural gas to places where it's needed. Once it arrives, it's turned back into a gas and sent through pipelines. Some vehicles can also run on LNG, but it's more common for vehicles to use compressed natural gas. Making LNG and storing it in special cold tanks can be expensive, which has slowed down its widespread use in vehicles.
Sometimes, natural gas found far from cities is just released into the air or burned off in a flare. But there are also technologies that can turn this gas into liquid fuels that are easier to transport.
Liquid Methane for Rockets
Very pure liquid methane is used as a rocket fuel. One big advantage of methane over fuels like kerosene is that it leaves less carbon buildup inside rocket engines. This makes it easier to reuse rocket parts.
Methane is also found in many places in our Solar system, like on Mars or Titan. Scientists think we might be able to make methane fuel from materials found on these planets. This could help future space missions by providing fuel for the return journey!
For Making Chemicals
Methane can be changed into a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, called synthesis gas, using a process called steam reforming. This process needs a lot of energy and high temperatures (around 700–1100°C) and uses special chemicals called catalysts.
Images for kids
-
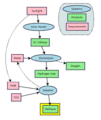
This diagram shows a method for producing methane sustainably. See: electrolysis, Sabatier reaction
-
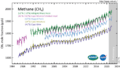
Methane (CH4) measured in the lower atmosphere (troposphere) at stations around the world.
-
Methane (CH4) on Mars—potential sources and sinks.
See also
 In Spanish: Metano para niños
In Spanish: Metano para niños