Cartagena, Spain facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Cartagena
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
City Hall
The wall of Carlos III
Panorama view
Pedreño Palace
Gran Hotel
|
|||
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Muy noble, muy leal y siempre heroica ciudad de Cartagena
|
|||
| Country | Spain | ||
| Autonomous community | Region of Murcia | ||
| Province | Province of Murcia | ||
| Comarca | Campo de Cartagena | ||
| Judicial district | Cartagena | ||
| Founded | 227 BC | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 558.08 km2 (215.48 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 10 m (30 ft) | ||
| Highest elevation | 50 m (160 ft) | ||
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | ||
| Population
(2018)
|
|||
| • Total | 213,943 | ||
| • Density | 383.355/km2 (992.886/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Cartageneros | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||
| Postal code |
302xx and 303xx
|
||
| Dialing code | (+34) 968 | ||
Cartagena is a historic city in Spain, located on the Mediterranean coast in the southeast. It's a very important naval base and port. As of 2018, about 218,943 people live there, making it the second-largest city in the Region of Murcia. The larger area around Cartagena, called Campo de Cartagena, has over 400,000 residents.
This city has been around for more than 2,000 years! It was founded around 227 BC by a Carthaginian leader named Hasdrubal the Fair. He called it Qart Hadasht, which means "New Town," just like the original city of Carthage. Later, under the Roman Empire, it was known as Carthago Nova (New Carthage) and became a very important capital.
Cartagena's special port has always been key to its history. It's been a major naval port for Spain since the 16th century and is still a main military harbor today, with a large shipyard. Because so many different cultures have lived here, Cartagena has a unique mix of history, buildings, and art. You can see ancient Roman theatres, Phoenician, Roman, Byzantine, and Moorish ruins, plus beautiful Art Nouveau buildings from the early 1900s. Today, Cartagena is a popular spot for cruise ships and a growing cultural center. It was also the first of several cities around the world to be named Cartagena, like Cartagena, Colombia.
Contents
Geography and Climate of Cartagena
Where is Cartagena Located?
The city of Cartagena is in the southeastern part of Spain, within an area called the Campo de Cartagena. This region is mostly a large, gently sloping plain. It's surrounded by mountains: coastal mountains to the south and southwest, and pre-coastal mountains to the north and northwest.
The ground here is mostly made of metamorphic rocks like slate and marble, and sedimentary rocks like limestone. The most common type of soil is calcic xerosol, which is typical for dry areas.
Cartagena is easy to reach by the new AP-7 motorway. Some nearby villages that are part of the Cartagena municipality include La Azohía, Isla Plana, Los Urrutias, and Los Nietos.
The old part of the city is built among five small hills, similar to Rome. In the past, there was an inner sea between these hills that eventually dried up. This area is where the "Ensanche" (New Town) was built in the early 20th century.
Cartagena's Weather
Cartagena has a climate that is a mix between a hot semi-arid climate and a hot desert climate, leaning more towards the desert side. Being close to the sea helps keep temperatures moderate. It usually gets less than 300 millimeters (about 12 inches) of rain each year. Cartagena has never recorded a temperature below freezing (0°C or 32°F).
The average yearly temperature is about 19.2°C (66.6°F). January is the coldest month, averaging 12.7°C (54.9°F). August is the warmest, with an average of 27.0°C (80.6°F). Wind is also an important part of the weather here.
| Climate data for Cartagena 1991-2020 normals, extremes (1988-present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 25.6 (78.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
29.4 (84.9) |
27.7 (81.9) |
31.9 (89.4) |
36.9 (98.4) |
38.3 (100.9) |
41.5 (106.7) |
34.0 (93.2) |
33.9 (93.0) |
28.8 (83.8) |
24.7 (76.5) |
41.5 (106.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 16.6 (61.9) |
17.0 (62.6) |
18.7 (65.7) |
20.4 (68.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
27.0 (80.6) |
29.8 (85.6) |
30.4 (86.7) |
27.5 (81.5) |
23.9 (75.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
17.5 (63.5) |
22.7 (72.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 12.7 (54.9) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.1 (59.2) |
17.0 (62.6) |
20.1 (68.2) |
23.6 (74.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
27.0 (80.6) |
24.3 (75.7) |
20.6 (69.1) |
16.4 (61.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
19.2 (66.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) |
9.7 (49.5) |
11.4 (52.5) |
13.6 (56.5) |
16.7 (62.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.7 (74.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
17.2 (63.0) |
12.8 (55.0) |
9.9 (49.8) |
15.7 (60.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 1.3 (34.3) |
1.9 (35.4) |
2.9 (37.2) |
5.6 (42.1) |
7.4 (45.3) |
13.7 (56.7) |
18.4 (65.1) |
17.9 (64.2) |
14.5 (58.1) |
9.3 (48.7) |
4.4 (39.9) |
1.4 (34.5) |
1.3 (34.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 30.6 (1.20) |
21.0 (0.83) |
25.2 (0.99) |
23.9 (0.94) |
14.5 (0.57) |
5.3 (0.21) |
1.1 (0.04) |
3.4 (0.13) |
39.3 (1.55) |
29.5 (1.16) |
35.5 (1.40) |
30.9 (1.22) |
260.2 (10.24) |
| Source: Agencia Estatal de Meteorologia (AEMET OpenData) | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Cartagena | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average sea temperature °C (°F) | 14.8 (58.6) |
14.4 (57.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
18.9 (66.0) |
22.0 (71.6) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
22.0 (71.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
16.6 (61.9) |
19.5 (67.1) |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 10.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 12.6 |
| Average Ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 5.8 |
| Source: Weather Atlas | |||||||||||||
How Cartagena is Divided
The municipality of Cartagena is divided into 24 areas called diputaciones (councils). This system started in the 18th century as the population grew. The main city of Cartagena is in the district called Cartagena Casco. Other important districts include San Antonio Abad, El Plan, and Rincón de San Ginés. Each district has its own unique features and communities.
Nature and Environment in Cartagena
Even with a lot of mining, tourism, and industry over the centuries, the area around Cartagena is full of amazing natural beauty and different kinds of plants and animals. Many parts of it are protected by law.
Plants of Cartagena
The coastal mountains of Cartagena have some of the most diverse plant life on the Iberian Peninsula. You can find unique plants that grow only in southern Spain (mostly in Murcia and Almería) and North Africa. One special tree is the Tetraclinis articulata, also called Sandarac or Cartagena cypress. It grows in hot, dry Mediterranean woodlands.
Some plants are very rare and in danger of disappearing, like the siempreviva de Cartagena (Limonium carthaginense) and the garbancillo de Tallante (Astragalus nitidiflorus).
Animals of Cartagena

Cartagena is home to many interesting animals, including some that are threatened or endangered. You might see birds like the peregrine falcon, the Eurasian eagle-owl, and the golden eagle. There are also animals like the spur-thighed tortoise and the greater horseshoe bat. A very special fish, the Spanish toothcarp, lives only in southeastern Spain.
You might also spot the common chameleon, which is the only chameleon in Europe! Other animals include the greater flamingo, red fox, European rabbit, European badger, common genet, wildcat, and wild boar.
Protected Natural Areas
Several areas around Cartagena are protected to keep their natural beauty safe:
- Mar Menor: This is a large, salty lagoon separated from the Mediterranean Sea by a sand bar. It's about 22 kilometers (14 miles) long and has warm, clear water. It's recognized internationally for its importance as a wetland. Its five volcanic islands and other nearby hills and beaches are also protected.
- Calblanque, Monte de las Cenizas and Peña del Águila: This area is a Natural Park and an important site for nature. It's located in the southeast of the municipality.
- Sierra de la Muela, Cabo Tiñoso and Roldán mountain: This is another Natural Park and a special protection area in the southwest.
- Sierra de la Fausilla: This area is also a special protection area, located between Cartagena and Calblanque.
- Islands and Islets of the Mediterranean coast: Several islands, like Grossa Island and Hormigas Islands, are protected areas.
History of Cartagena
Early History and Ancient Times
People have lived in the Cartagena area for a very long time! Evidence of early humans from 1.3 million years ago has been found in Cueva Victoria. Neanderthal remains have also been discovered in caves like Cave of los Aviones. Later, during the Stone Age, more human activity was present, especially in the southeast.
The city was first known as Mastia. Because it has one of the best harbors in the western Mediterranean, the Carthaginian general Hasdrubal the Fair re-founded it in 228 BC. He named it Qart Hadasht, meaning "New City," to be a base for conquering Spain.
In 209 BC, the Roman general Scipio Africanus conquered it and renamed it Carthago Nova (New New City) to tell it apart from the original Carthage. It became a very important Roman city, known for its silver mines and for making a special fish sauce called garum. It was even the capital of a Roman province called Carthaginensis.
Middle Ages and Later
After the Roman Empire declined, Cartagena was ruled by different groups, including the Vandals, Visigoths, and Eastern Romans. The Eastern Romans even made it the capital of their westernmost province, Spania.
Later, it was ruled by various Muslim dynasties until a Castilian army took it back in 1245. For a while, it was part of the Crown of Aragon but then returned to Castile. Cartagena didn't fully recover until the 18th century, when it became a leading naval port again.
Modern History and Today
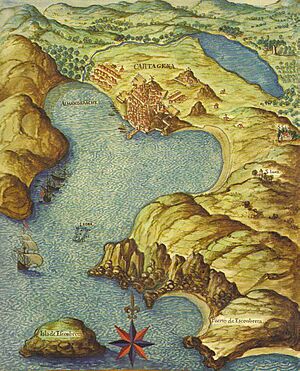
In 1728, Cartagena became the main base for the Spanish Navy in the Mediterranean. The city was heavily fortified with new castles, barracks, and a huge naval arsenal. This caused the city's population to grow rapidly from about 10,000 to 50,000 people.
In 1873, the city declared itself a self-governing area during the Cantonal Revolution. Government forces surrounded the city for several months until it surrendered.

During the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939), Cartagena was a key base for the Spanish Republican Navy. It was one of the last cities to surrender to General Francisco Franco's forces. The city's industries grew in the 1950s, bringing more wealth, but this slowed down in the late 1980s.
Today, Cartagena is part of the Region of Murcia and is home to the Regional Assembly of Murcia, which is like the region's parliament. It continues to be an important maritime city.
Population and Economy
Cartagena's Population
As of January 2011, Cartagena had 218,210 people living there. This makes it the 24th largest city in Spain by population. Most people live in the main urban area, with others in smaller surrounding communities. About 14.73% of the people living in Cartagena are from other countries. The larger metropolitan area, which includes nearby towns, has over 390,000 residents.
| Demographic evolution of Cartagena since 1842 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: INE Note: The municipal extension varies from the 1857 census and the previous one because of the annexation of La Palma and La Unión segregated. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
What Drives Cartagena's Economy?
Energy-related businesses are very important in Cartagena, especially in the Valle de Escombreras. Farming is also a big part of the economy, with many fields growing melons, lettuce, potatoes, lemons, and almonds. Shipbuilding, though not as big as it once was, is still moderately important at the port. Plastic production also happens in the area.
In recent years, the service industry, especially tourism and hotels, has grown a lot. Many jobs are related to serving visitors, showing how important tourism has become to the city.
Main Sights and Attractions
Cartagena's long history and important location mean it has many amazing places to see. The "Cartagena, Port of Cultures" project helps visitors explore the city's rich history and culture.
Ancient Ruins and Archaeological Sites
While there are some ruins from the Carthaginian period, like parts of the Punic rampart (built in 227 BC), most of the oldest monuments are from the time when Cartagena was a thriving Roman city.
The recently restored Roman Theatre of Carthago Nova is a major highlight and one of the city's most famous landmarks. You can also visit the Roman Theatre Museum. During Roman times, the mines near Cartagena provided silver and lead for the entire Roman Empire.
Other Roman ruins you can explore include the Roman Colonnade, the House of Fortune, and the Augusteum. The Torre Ciega was a Roman burial tower. The Roman Amphitheatre, though mostly hidden, is slowly being uncovered.
Beyond Roman history, you can see the remains of the Santa María la Vieja Cathedral, which was damaged during the Spanish Civil War. It dates back to the late 13th century. A Byzantine rampart is also located near the Roman Theatre. Besides the Roman Theatre Museum, there are two other important archaeological museums: the Municipal Archaeological Museum and the Arqua (National Museum of Maritime Archaeology).
Historic Buildings
Many buildings show Cartagena's military importance. The Campus Muralla del Mar, an old military hospital, is now part of the Polytechnic University. Other military buildings include the Charles III Rampart, the Castillo de San Julián, the Arsenal, and the Naval Headquarter Palace.
You can also find beautiful Baroque and Neo-classical churches like El Carmen and Santa Maria de Gracia. The Molina House, with its simple outside, holds the Centre of Arts and Craft.
Modernist and Eclectic Architecture
Cartagena has many stunning Art Nouveau buildings from the early 1900s. These were built when the city became wealthy from mining. Famous examples include the City Hall, the Grand Hotel, and the Casino.
The Railway Station has cool iron doors and columns. You can still see the original ticket office inside. Other beautiful buildings include the Aguirre Palace (which houses the Regional Museum of Modern Art), the Cervantes House, and the Llagostera House.
These buildings are found along charming, lively streets like Calle Mayor, which is a popular pedestrian and shopping street with boutiques and "tapas" bars. The Caridad church is very important as it's dedicated to Cartagena's patron saint. It has a dome similar to the Pantheon in Rome and sculptures by the famous artist Francisco Salzillo.
Modern Sights and Beaches
The Civil War Shelter-Museum is built into tunnels dug into Concepción hill, used as air-raid shelters during the Spanish Civil War. You can also visit the Cartagena Naval Museum and see the famous Peral Submarine. This submarine was invented by Isaac Peral, who was born in Cartagena, and was launched in 1888 as one of the first submarines ever!
Other modern attractions include the Monument to the Heroes of Santiago de Cuba and Cavite, which honors Spanish sailors. You can also see the Regional Assembly, which is the parliament of the Region of Murcia.
Beaches of Cartagena
Even though Cartagena is a port city, it has many beautiful beaches! Part of La Manga del Mar Menor is within the city limits. Cartagena also has a section of the Murcian Mediterranean Coast. It's proud to have 10 beaches certified with a "Q for Quality" award. These include Cala Cortina, Islas Menores, Playa Honda beach, Mar de Cristal, and El Galúa beach.
Life in Cartagena
Healthcare Services
Cartagena is part of Health Area II in the Region of Murcia. This area has 17 smaller health zones, with 13 of them located within the municipality of Cartagena. There are two hospitals in the region, both found in Cartagena. The city also has many local health centers and smaller clinics for primary care.
Getting Around Cartagena
Cartagena is well-connected by roads, including the Autopista AP-7 along the coast and the Autovía A-30 to Murcia. The city also has a railway station that opened in 1903, and it will soon be a stop on Spain's high-speed rail network. There's also a smaller train line that connects Cartagena to nearby towns like La Unión and Los Nietos.
Buses are available for getting around the city and to neighboring municipalities like La Unión and Torre-Pacheco.
Education in Cartagena
Cartagena has many schools for children of all ages. There are public and semi-private centers for early childhood, primary, and secondary education. There are also special education centers.
For older students, Cartagena has a public university called Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena (UPCT), which focuses on engineering and architecture. There are also campuses for other universities, offering a variety of degrees. The city also has vocational education centers and places where adults can learn new skills or languages like English, French, and Arabic.
Sports in Cartagena
Cartagena is home to several sports teams. The most well-known is Fútbol Club Cartagena, a football (soccer) team that plays in Spain's second division. There's also a futsal (indoor soccer) team, Futsal Cartagena, and a successful table tennis team, UCAM Cartagena Tenis de Mesa.
Other sports played in the city include basketball with Club Basket Cartagena, handball with C.A.B. Cartagena, and badminton with UPCT Bádminton Cartagena. Cartagena also hosts international competitions, like one for aesthetic group gymnastics. The city has several sports facilities, including two main pavilions and a stadium.
Famous People from Cartagena
Many notable people have come from Cartagena throughout history:
- Hasdrubal the Fair (c. 270 BC – 221 BC), a Carthaginian military leader who founded the city.
- Isaac Peral (1851–1895), an engineer and naval officer who designed one of the first submarines.
- Carmen Conde (1907–1996), a famous writer.
- Arturo Pérez-Reverte (b. 1951), a well-known novelist and journalist.
- Robert Sanchez (b. 1997), a professional football player.
Festivals and Celebrations
Cartagena has some exciting festivals:
- Cartagena's Holy Week: This is a very important religious festival with solemn parades called processions. The processions in Cartagena are known for their special arrangements and movements of participants.
- Carthaginians and Romans: This is one of the city's main festivals, declared a National Tourist Interest. It's a colorful event with parades and activities that remember the ancient Punic Wars and the Roman conquest of the city. It takes place in the last ten days of September.
- Cruces de Mayo: This festival involves setting up beautiful Christian crosses decorated with flowers.
Local Festivities in the Districts
Throughout the municipality, different districts hold their own Patron saint festivities. These celebrations honor various patron saints and often include small religious parades and romerías. A romería is a festive religious event where a statue of the Virgin Mary or Christ is carried in a procession, ending with a large gathering at a church.
Sister Cities
Cartagena is connected with other cities around the world:
 Terni, Italy
Terni, Italy
Cartagena also works closely with Carthage, Tunisia, due to their shared historical name.
See also
 In Spanish: Cartagena (España) para niños
In Spanish: Cartagena (España) para niños