Dunkirk facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Dunkirk
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Dunkirk Town Hall and port
|
|||
|
|||
| Country | France | ||
| Region | Hauts-de-France | ||
| Department | Nord | ||
| Arrondissement | Dunkerque | ||
| Canton | Dunkerque-1 Dunkerque-2 Grande-Synthe |
||
| Intercommunality | Dunkerque | ||
| Area
1
|
43.89 km2 (16.95 sq mi) | ||
| Population
(2021)
|
86,788 | ||
| • Density | 1,977.40/km2 (5,121.4/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) | ||
| INSEE/Postal code |
59183 /59140, 59240, 59640
|
||
| Elevation | 0–17 m (0–56 ft) (avg. 4 m or 13 ft) |
||
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |||
Dunkirk (pronounced "dun-KURK" in the UK and "DUN-kurk" in the US) is a big port city in northern France. It's located about 10 kilometers (6 miles) from the border with Belgium. Dunkirk has the third-largest harbor in France. In 2019, about 86,279 people lived there.
Contents
- What does the name Dunkirk mean?
- A Look at Dunkirk's History
- How many people live in Dunkirk?
- What is Dunkirk's Coat of Arms?
- How is Dunkirk managed?
- What is Dunkirk's economy like?
- What kind of food is popular in Dunkirk?
- What is the prototype meter?
- What can you see in Dunkirk?
- How do people travel in Dunkirk?
- What sports are popular in Dunkirk?
- Who are some famous people from Dunkirk?
- Does Dunkirk have sister cities?
- What is the climate like in Dunkirk?
- See also
What does the name Dunkirk mean?
The name Dunkirk comes from an old language called West Flemish. It means 'church in the dunes'. Dunes are hills of sand found near the sea. There was another small town nearby with the same name. To avoid confusion, it was later called Oostduinkerke.
Until the mid-1900s, a local type of Dutch was commonly spoken here.
A Look at Dunkirk's History
How did Dunkirk start?
Dunkirk began as a small fishing village around the year 960. It was part of the County of Flanders, which was linked to the French Crown. To protect the village from Viking attacks, a town wall was built. Monks from a nearby abbey helped drain the wet lands, making them good for farming. The name Dunkirka was first used in a document in 1067.
Later, in the 12th century, the city got rights to hold markets. A plan was also made to build a canal from Dunkirk to Bergues.
Dunkirk and the Hundred Years' War
In the late 1200s, Dunkirk was involved in a war between Flanders and France. The people of Dunkirk supported the French king. Later, during the Hundred Years' War (which started in 1337), trade was stopped, causing problems for the citizens.
After a count of Flanders died in 1346, a truce was made with England. Trade grew again, and the port became much bigger. However, the city was attacked by English forces in 1378, causing a lot of damage.
Dunkirk under different rulers
After 1384, Dunkirk became part of the Duchy of Burgundy. The city's defenses were made stronger, including a tall tower called a belfry, which helped ships find their way. Dunkirk was important, so many rulers wanted to control it. It was taken over by different dukes and archdukes.
Eventually, Dunkirk became part of the Habsburg Netherlands. Later, it was part of the Southern Netherlands, controlled by Habsburg Spain.
Dunkirk as a Pirate Base
Dunkirk was often fought over by Spain, the Netherlands, England, and France. In 1583, Spanish forces took control, and Dunkirk became a base for famous pirates known as the Dunkirkers. These pirates attacked enemy ships.
Dunkirk was captured by the French in 1646 but taken back by the Spanish in 1652. In 1658, French and English forces captured it together. The city was given to England.
In 1662, King Charles II of England sold Dunkirk to France for a large sum of money. The French government then made it a very strong port with many defenses. They built a large harbor that could hold many warships.
During the time of King Louis XIV, many privateers (people allowed by their government to attack enemy ships) and pirates used Dunkirk as their home base. The most famous was Jean Bart.

Because Dunkirk was so close to England, the British worried it could be used to invade them. So, in 1713, parts of the port and its defenses were destroyed as part of a peace treaty. Later treaties also talked about how much France could fortify Dunkirk.
Dunkirk in World War I
During World War I, Dunkirk's port was very important for British forces. The city was heavily bombed starting in 1915. German forces used a huge gun called 'Lange Max' to fire shells from far away. These attacks killed many people and destroyed hundreds of buildings. The city's population dropped a lot during the war.
In 1918, the United States Navy set up a base for seaplanes in Dunkirk. For its bravery during the war, Dunkirk received special awards, including the French Croix de Guerre and Legion of Honour, and the British Distinguished Service Cross. These awards are now shown on the city's coat of arms.
Dunkirk in World War II
The famous evacuation of 1940
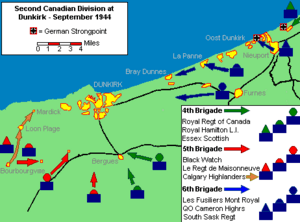
During World War II, in 1940, a major event happened in Dunkirk. British, French, and Belgian soldiers were trapped by the German army near the port. Over 400,000 soldiers were surrounded.
Suddenly, the German tank attack stopped for a few days. This pause gave the Allied soldiers time to strengthen their defenses. It also allowed for a huge rescue mission called Operation Dynamo. British Prime Minister Winston Churchill asked for any boat available, big or small, to help.
More than 338,000 soldiers, including 123,000 French troops, were saved. Churchill called it the miracle of Dunkirk. Over 900 boats helped, with most soldiers leaving from the harbor and over 100,000 from the beaches. However, many vehicles and military supplies had to be left behind. About 40,000 Allied soldiers were captured or had to find their own way home.
When was Dunkirk freed?
Dunkirk was fought over again in 1944. Allied forces tried to free the city, but German forces had turned it into a strong fortress and refused to give it up. The Allies decided it would take too many resources to capture the city, so they went around it.
The German forces in Dunkirk finally surrendered on May 9, 1945, the day after the war in Europe ended. During the German occupation, Dunkirk was heavily damaged by Allied bombing.
Dunkirk after the wars
In 2002, a large car carrier ship called the MV Tricolor sank off Dunkirk Harbour. This created a danger for other ships in the English Channel.
How many people live in Dunkirk?
The population numbers below are for the city of Dunkirk itself. Over the years, Dunkirk has grown by joining with several nearby towns.
| Historical population | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: EHESS and INSEE (1968-2017) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
What is Dunkirk's Coat of Arms?
| The Coat of Arms of Dunkirk shows a black lion walking on a gold background. Below it is a blue dolphin swimming on a silver background.
At the bottom of the arms, you can see symbols of four medals the city received. These include the Legion of Honour, Croix de Guerre, and British Distinguished Service Cross from World War I. There is also a second Croix de Guerre from World War II. The city also has its own flag. It has six horizontal stripes that are white and blue. |
|
How is Dunkirk managed?
Dunkirk has grown a lot by joining with nearby towns over the years. For example, it merged with Malo-les-Bains in 1970. Later, in 2010, Saint-Pol-sur-Mer and Fort-Mardyck also became part of Dunkirk.
What is Dunkirk's economy like?
Dunkirk has the third-largest harbor in France. This means it's a very important city for shipping and industry. Its economy relies heavily on industries like steel making, food processing, oil refining, ship-building, and chemical production.
What kind of food is popular in Dunkirk?
The food in Dunkirk is very similar to Flemish food. One well-known dish is coq à la bière. This is chicken cooked in a creamy beer sauce.
What is the prototype meter?
In 1792, two French astronomers, Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre and Pierre François André Méchain, started a project. They wanted to measure the distance from Dunkirk to Barcelona. These two cities are on roughly the same line of longitude (north-south line). The belfry (bell tower) in Dunkirk was used as the starting point.
By measuring this distance and knowing the cities' latitudes, they could figure out the distance from the North Pole to the Equator. This measurement was then used to create the first prototype of the metre. The meter was defined as one ten-millionth of that distance. The first official meter bar, made of platinum, was presented in France in 1799.
Dunkirk was also an important point for an earlier survey between France and England. This survey used triangles to measure the exact distance between the Paris Observatory and the Royal Greenwich Observatory.
What can you see in Dunkirk?
Dunkirk has some interesting places to visit:
- Two belfries (bell towers) in Dunkirk are special. One is near the Church of Saint-Éloi, and the other is at the town hall. In 2005, these belfries were added to the UNESCO World Heritage List. They are important examples of old city buildings.
- The 63-meter-high Dunkirk Lighthouse, also called the Risban Light, was built between 1838 and 1843. It helps guide ships and can be seen from 48 kilometers (28 miles) away. It became a historical monument in 2010.
Dunkirk also has two museums:
- The Musée Portuaire shows pictures and items about the history of the port.
- The Musée des Beaux-Arts has a large collection of paintings and sculptures from different countries.
How do people travel in Dunkirk?
Dunkirk has a ferry service that goes to Dover in England. This trip takes about two hours. Another ferry route connects Dunkirk to Rosslare in Ireland, mainly for trucks.
The Gare de Dunkerque railway station connects Dunkirk to other French cities like Calais, Lille, Arras, and Paris.
In 2018, Dunkirk's public bus service became completely free. This made it the largest city in Europe to offer free public transport. After this change, the number of bus passengers increased a lot. The city also added more buses, including some that run on natural gas.
What sports are popular in Dunkirk?
- USL Dunkerque is a French soccer club from Dunkirk. They play in Ligue 2.
- The Four Days of Dunkirk is an important professional road bicycle racing event.
- In 2007, Stage 2 of the 2007 Tour de France bicycle race started from Dunkirk.
Who are some famous people from Dunkirk?
- Jean Bart (1650—1702), a famous naval commander and privateer.
- Eugène Chigot, a 19th-century painter.
- Jean-Paul Rouve (born 1967), an actor.
- François Rozenthal (born 1975), an ice hockey player.
- Maurice Rozenthal (born 1975), an ice hockey player.
Does Dunkirk have sister cities?
Dunkirk is "twinned" with several cities around the world. This means they have special friendly relationships.
 Krefeld, Germany (since 1974)
Krefeld, Germany (since 1974) Middlesbrough, England, United Kingdom (since 1976)
Middlesbrough, England, United Kingdom (since 1976) Gaza, Palestine (since 1996)
Gaza, Palestine (since 1996) Rostock, Germany (since 2000)
Rostock, Germany (since 2000) Ramat HaSharon, Israel (since 1997)
Ramat HaSharon, Israel (since 1997) Qinhuangdao, China (since 2000)
Qinhuangdao, China (since 2000)
Dunkirk also has co-operation agreements with:
- Dartford, England, United Kingdom (since 1988)
- Thanet, England, United Kingdom (since 1993)
What is the climate like in Dunkirk?
Dunkirk has an oceanic climate. This means it has cool winters and warm summers. The weather is greatly affected by the ocean currents. Summer temperatures usually average around 20 to 21 degrees Celsius (68 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit).
| Climate data for Dunkirk (1991–2020 averages, records 1892–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.4 (61.5) |
19.1 (66.4) |
24.0 (75.2) |
28.4 (83.1) |
34.0 (93.2) |
34.4 (93.9) |
41.3 (106.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
35.2 (95.4) |
30.0 (86.0) |
20.1 (68.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
41.3 (106.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 7.6 (45.7) |
8.0 (46.4) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.1 (55.6) |
16.0 (60.8) |
18.9 (66.0) |
21.2 (70.2) |
21.7 (71.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
8.3 (46.9) |
14.3 (57.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.5 (41.9) |
5.7 (42.3) |
7.7 (45.9) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.3 (55.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
18.4 (65.1) |
18.8 (65.8) |
16.5 (61.7) |
13.0 (55.4) |
9.0 (48.2) |
6.2 (43.2) |
11.7 (53.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 3.4 (38.1) |
3.5 (38.3) |
5.3 (41.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
10.5 (50.9) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
15.8 (60.4) |
13.6 (56.5) |
10.4 (50.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
9.2 (48.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −13.4 (7.9) |
−18.0 (−0.4) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
6.6 (43.9) |
4.0 (39.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−2.4 (27.7) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−18.0 (−0.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 53.9 (2.12) |
45.4 (1.79) |
41.9 (1.65) |
36.7 (1.44) |
45.5 (1.79) |
54.5 (2.15) |
58.5 (2.30) |
64.2 (2.53) |
64.9 (2.56) |
73.0 (2.87) |
79.5 (3.13) |
72.8 (2.87) |
690.8 (27.20) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 11.4 | 9.9 | 9.2 | 7.9 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 9.9 | 11.9 | 13.1 | 12.8 | 121.3 |
| Average snowy days | 2.9 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 11.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86 | 84 | 81 | 80 | 79 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 81 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 81.8 |
| Source: Météo France, Infoclimat.fr (humidity and snowy days, 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: Dunkerque para niños
In Spanish: Dunkerque para niños
 | Isaac Myers |
 | D. Hamilton Jackson |
 | A. Philip Randolph |