El Monte, California facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
El Monte, California
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||
|
|||
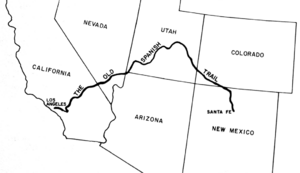
| Nickname(s):
"The End of the Santa Fe Trail"
|
|||
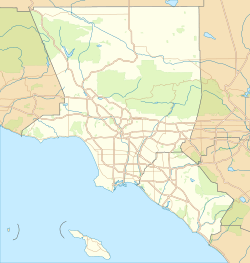
Location of El Monte in Los Angeles County, California
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| State | California | ||
| County | Los Angeles | ||
| Incorporated | November 18, 1912 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Council-Manager | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 9.65 sq mi (24.99 km2) | ||
| • Land | 9.56 sq mi (24.77 km2) | ||
| • Water | 0.09 sq mi (0.22 km2) 0.89% | ||
| Elevation | 299 ft (91 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 109,450 | ||
| • Rank | 12th in Los Angeles County 66th in California |
||
| • Density | 11,341.97/sq mi (4,379.75/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−8 (Pacific) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (PDT) | ||
| ZIP Codes |
91731–91735
|
||
| Area code(s) | 626 | ||
| FIPS code | 06-22230 | ||
| GNIS feature IDs | 1652702, 2410413 | ||
El Monte is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States. It is located in the San Gabriel Valley, just east of the city of Los Angeles.
El Monte's slogan is "Welcome to Friendly El Monte." It is also known as "The End of the Santa Fe Trail." In 2020, about 109,450 people lived there. This makes El Monte the 66th largest city in California.
Contents
- What's in a Name? The Origin of El Monte
- A Look Back: The History of El Monte
- Where is El Monte? Geography and Climate
- Who Lives in El Monte? Demographics
- El Monte's Economy: Top Employers
- Learning in El Monte: Education
- Getting Around: Transportation
- News and Information: Media
- Famous People from El Monte
- Friendship Across Borders: Sister Cities
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name? The Origin of El Monte
El Monte is found between the San Gabriel and Rio Hondo Rivers. People who lived there long ago said anything could grow in this area. Between 1770 and 1830, Spanish soldiers and missionaries often rested here. They called the area 'El Monte,' which means 'the mountain' in Spanish.
However, there are no mountains in this valley. The word 'Monte' in old Spanish meant "the wood" or "the forest." The first explorers found this rich, low land covered with thick willow trees, alders, and cattails. They also found wild grapevines and watercress. El Monte is about 7 miles long and 4 miles wide. When California organized its townships in the 1850s, it was called the El Monte Township. Soon after, it went back to its original name, El Monte.
A Look Back: The History of El Monte
For thousands of years, the Tongva people lived in this area near the San Gabriel River. Spanish explorers and missionaries came through in 1769-1770. This land was part of a large Spanish land grant called Rancho La Puente. Mission San Gabriel Arcángel was the main center for Spanish activities nearby.
The 1800s: Early Settlers and Trails
In late 1841, a group of travelers called the Workman-Rowland Party arrived in Alta California. They used the Old Spanish Trail to reach the Pueblo de Los Ángeles.
The Santa Fe Trail was a trade route from Kansas City to Santa Fe. From 1847, the Southern Emigrant Trail connected the Santa Fe Trail westward. This new path passed by the El Monte area, leading to the Pueblo of Los Angeles.
People started settling here in 1849. El Monte became a popular stop for American immigrants heading to the gold fields during the California Gold Rush. The first permanent families arrived around 1849-1850. Many came from Texas, Arkansas, and Missouri. They were looking for gold in California. Some of the first settlers were Nicholas Schmidt, Ira W. Thompson, and the Cuddeback, Corbin, and Sheldon families.
These migrants found rich, fertile land along the San Gabriel River. They began to build farms and homes. The farmers were happy with their success, and El Monte's farming community grew steadily.
In the 1850s, American settlers briefly called the town Lexington. But soon, it went back to being called El Monte or Monte. It was a key crossing point for routes between Los Angeles, San Bernardino, and the harbor at San Pedro. In the early days, it was known as a place where people sometimes had conflicts. To protect against raids and bandit gangs, a local group called the Monte Rangers was formed in 1854.
In 1858, the Monte Station was built. It was a stop for stagecoaches on the Butterfield Overland Mail route.
By 1861, El Monte was a growing settlement. During the American Civil War, some people in El Monte supported the Southern states. A local group called the Monte Mounted Rifles was formed in 1861. However, this effort did not succeed. Union troops set up New Camp Carleton near the town in 1862 to keep peace. It closed three years later when the war ended.
The Southern Pacific built a train station in El Monte in 1873. This helped local farming grow even more.
The 1900s: Growth and Change
El Monte officially became a city in 1912. In the 1930s, it was part of a government program called the New Deal. This program helped people get single-family homes. Many white immigrants from the Dust Bowl moved here. Famous photographer Dorothea Lange took many pictures of these homes. During this time, there were also conflicts over workers' rights. The El Monte Berry Strike of 1933 showed problems faced by Japanese and Latino farm workers.
Over time, El Monte has become a city with a large Hispanic community. To remember the history of the Santa Fe Trail, El Monte built the Santa Fe Trail Historical Park in 1989. The El Monte Historical Museum at 3150 Tyler Avenue is considered one of the best community museums in California.
The 2000s: New Residents
By 2008, more people of Asian descent began moving to El Monte. This was partly because nearby cities like Alhambra and Monterey Park had become very crowded.
Where is El Monte? Geography and Climate
El Monte is located at 34°4′24″N 118°1′39″W / 34.07333°N 118.02750°W. The city covers about 9.6 square miles (24.9 square kilometers). Most of this area is land, with a small amount of water.
El Monte's Weather: Climate
El Monte has a Mediterranean climate. This means it has warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
| Climate data for El Monte, California | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 67 (19) |
68 (20) |
70 (21) |
73 (23) |
76 (24) |
80 (27) |
85 (29) |
87 (31) |
85 (29) |
79 (26) |
73 (23) |
67 (19) |
76 (24) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 45 (7) |
47 (8) |
50 (10) |
53 (12) |
57 (14) |
61 (16) |
65 (18) |
65 (18) |
63 (17) |
57 (14) |
49 (9) |
44 (7) |
55 (13) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.68 (93) |
4.66 (118) |
3.00 (76) |
1.10 (28) |
.38 (9.7) |
.15 (3.8) |
.04 (1.0) |
.07 (1.8) |
.33 (8.4) |
.78 (20) |
1.45 (37) |
2.42 (61) |
18.06 (459) |
Who Lives in El Monte? Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1920 | 1,283 | — | |
| 1930 | 3,479 | 171.2% | |
| 1940 | 4,746 | 36.4% | |
| 1950 | 8,101 | 70.7% | |
| 1960 | 13,163 | 62.5% | |
| 1970 | 69,892 | 431.0% | |
| 1980 | 79,494 | 13.7% | |
| 1990 | 106,209 | 33.6% | |
| 2000 | 115,965 | 9.2% | |
| 2010 | 113,475 | −2.1% | |
| 2020 | 109,450 | −3.5% | |
| 2021 (est.) | 106,907 | −5.8% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Since the 1970s, El Monte's population has grown by over 40%. Homes have replaced the walnut groves that the city was once known for. The city has a long history of having a large Mexican and Latino community.
Population in 2020
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 2000 | Pop 2010 | Pop 2020 | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 8,542 | 5,556 | 3,667 | 7.37% | 4.90% | 3.35% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 640 | 502 | 745 | 0.55% | 0.44% | 0.68% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 331 | 133 | 146 | 0.29% | 0.12% | 0.13% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 21,315 | 28,264 | 32,940 | 18.38% | 24.91% | 30.10% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 90 | 84 | 34 | 0.08% | 0.07% | 0.03% |
| Other Race alone (NH) | 107 | 116 | 356 | 0.09% | 0.10% | 0.33% |
| Mixed race or Multiracial (NH) | 995 | 503 | 743 | 0.86% | 0.44% | 0.68% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 83,945 | 78,317 | 70,819 | 72.39% | 69.02% | 64.70% |
| Total | 115,965 | 113,475 | 109,450 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
Population in 2010
In 2010, El Monte had 113,475 people. This meant there were about 11,761 people per square mile. The population was made up of different groups. About 38.8% were White, 0.8% African American, 1.0% Native American, and 25.1% Asian. About 31.0% were from other races, and 3.2% were from two or more races. A large part of the population, 69.0%, was Hispanic or Latino.
Most people (99.0%) lived in homes. About 27,814 households were counted. Many households (52.3%) had children under 18. The average household had about 4 people. The average family had about 4.2 people.
The population included 28.4% under 18 years old. About 11.3% were aged 18 to 24. People aged 25 to 44 made up 29.3% of the population. Those aged 45 to 64 were 21.6%, and 9.3% were 65 or older. The average age was 31.6 years.
In 2010, the average household income in El Monte was $39,535. About 24.3% of the people lived below the poverty line.
Population in 2000
In 2000, El Monte had 115,965 people. There were 27,034 households and 23,005 families. The population density was about 12,139 people per square mile. The city's racial makeup included 72.39% Hispanic or Latino. About 35.67% were White, 0.77% Black, and 18.51% Asian.
About 53.3% of households had children under 18. The average household size was 4.24 people. The average family size was 4.43 people.
About 34.1% of the population was under 18. The average age was 27 years. The average income for a household was $32,439. About 26.1% of the population lived below the poverty line. This included 33.9% of those under 18.
El Monte's Economy: Top Employers
El Monte has many different businesses and organizations that provide jobs. Here are some of the top employers in the city, based on a 2018 report:
| # | Employer | # of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | El Monte City Elementary School District | 1,500 |
| 2 | El Monte Union High School District | 1,400 |
| 3 | Mountain View Elementary School District | 1,000 |
| 4 | Longo Toyota-Lexus | 831 |
| 5 | City of El Monte | 505 |
| 6 | McGill Corporation | 475 |
| 7 | Staffing Solutions | 266 |
| 8 | Asian Pacific Health Care Venture | 260 |
| 9 | The Home Depot | 251 |
| 10 | Sam's Club | 203 |
Cathay Bank also has a corporate center in El Monte.
Learning in El Monte: Education
El Monte has several school districts that serve its students.
High Schools
The El Monte Union High School District includes these high schools:
- Arroyo High School
- El Monte High School
- Mountain View High School
- South El Monte High School
- Fernando R. Ledesma High School, formerly Valle Lindo Continuation School
- Rosemead High School
- El Monte-Rosemead Adult School
Elementary Schools
The El Monte City School District has 17 elementary schools. These schools serve students from kindergarten up to 8th grade. The district also runs four preschool programs called Head Start.
- Cherrylee Elementary School
- Columbia Elementary School
- Cortada Elementary School
- Durfee Elementary School
- Gidley Elementary School
- Legore Elementary School
- Mulhall Elementary School
- New Lexington Elementary School
- Norwood Elementary School
- Potrero Elementary School
- Rio Vista Elementary School
- Shirpser Elementary School
- Thompson, (Byron E.) Elementary School
- Wilkerson Elementary School
- Wright Elementary School
- Cleminson Elementary School
- Rio Hondo Elementary School
The Mountain View School District serves students from kindergarten to 8th grade. It has ten elementary schools, one intermediate school, and one middle school. It also has a program for older students and a Children's Center. About 8,600 students attend schools in this district.
- Baker Elementary School
- Children's Center/Head Start/State Preschool
- Cogswell Elementary School
- Kranz Intermediate School
- La Primaria Elementary School
- Madrid Middle School
- Magnolia Learning Center
- Maxson Elementary School
- Miramonte Elementary School
- Monte Vista Elementary School
- Parkview Elementary School
- Payne Elementary School
- Twin Lakes Elementary School
- Voorhis Elementary School
Getting Around: Transportation
El Monte has several ways to get around. It is served by Metro buses and trains. Foothill Transit also provides bus service. The city has its own bus system called El Monte Transit.
Metro's J Line ends at El Monte Station. You can also take a train with Metrolink's San Bernardino Line. This line stops at the El Monte station.
Interstate 10, a major highway, goes through El Monte. For air travel, the San Gabriel Valley Airport is located in El Monte. It is used for general aviation.
News and Information: Media
You can find local news about El Monte in the San Gabriel Valley Tribune, which is published daily. Other local newspapers include Mid-Valley News and El Monte Examiner, both published weekly.
Famous People from El Monte
Many interesting people have connections to El Monte:
- Cris Abrego, a television producer
- Art Acevedo, a police officer
- Rob Bottin, who creates special make-up effects for movies
- A.L.T., a Chicano rapper
- Timothy Carey, a film and television actor
- Glenn Corbett, an actor
- James Ellroy, an author
- Mary Ford, a singer and guitar player
- Virginia Gilmore, an actress
- Alexandra Hay, an actress
- Roger Hernández, a politician
- Cathy LeFrançois, a professional bodybuilder
- Country Joe McDonald, lead singer for the band Country Joe & the Fish
- Tom Morgan, a Major League Baseball pitcher
- Lorenzo Oatman and his sister Olive Oatman, who survived a historical event in Arizona
- Bill Piercy, a Major League Baseball pitcher
- Salvador Plascencia, an author
- Kim Rhode, an Olympic shooter
- Emily Rios, an actress known for Breaking Bad
- Scatman John, a musician
- Willie Shoemaker, a famous jockey
- Robert P. Shuler, a reformer and minister
- Hilda Solis, a politician
Friendship Across Borders: Sister Cities
El Monte has a sister city, which means it has a special friendship with a city in another country:
 Zamora, Mexico
Zamora, Mexico
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: El Monte (California) para niños
In Spanish: El Monte (California) para niños