French Southern and Antarctic Lands facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
French Southern and Antarctic Lands
Terres australes et antarctiques françaises (French)
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Overseas territory
|
|||
|
|||
| Motto(s): | |||
| Anthem: La Marseillaise ("The Marseillaise") |
|||
Location of French Southern and Antarctic Lands (circled in red)
in the Indian Ocean (light blue) |
|||
| Sovereign state | |||
| Territorial status | 6 August 1955 | ||
| Capital | Saint Pierre, Réunion (headquarters, not geographically assigned) 43°00′S 67°00′E / 43.000°S 67.000°E |
||
| Largest settlement | Port-aux-Français | ||
| Official languages | French | ||
| Demonym(s) | French | ||
| Leaders | |||
| Emmanuel Macron | |||
|
• Prefect, Administrator Superior
|
Florence Jeanblanc-Risler | ||
|
• Secretary General
|
Amélie Puccinelli | ||
| Legislature | Advisory Council of the TAAF | ||
| Area | |||
|
• Total
|
439,666.4 km2 (169,756.1 sq mi) | ||
| Population | |||
|
• Estimate
|
Officially 400~800 permanent scientists and military personnel No known permanent population |
||
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) | ||
| Time zone | |||
| Driving side | right | ||
| ISO 3166 code |
|
||
| Internet TLD | .tf | ||
The French Southern and Antarctic Lands (French: Terres australes et antarctiques françaises, often called TAAF) is a special overseas territory of France. It is made up of several distant islands and a part of Antarctica.
The TAAF includes:
- Adélie Land (Terre Adélie), which is France's claim on the continent of Antarctica.
- The Crozet Islands (Îles Crozet), a group of islands in the southern Indian Ocean. They are located south of Madagascar.
- The Kerguelen Islands (Archipel des Kerguelen), which are volcanic islands in the southern Indian Ocean. They are southeast of Africa and southwest of Australia.
- The Saint Paul and Amsterdam Islands (Îles Saint Paul et Amsterdam), a group of islands north of the Kerguelen Islands.
- The Scattered Islands (Îles Éparses), which are small islands found around the coast of Madagascar.
No one lives in the TAAF permanently. Around 150 to 310 people are usually there at any time. These people are mostly military staff, government workers, and scientists doing research.
In 2019, the Crozet Islands, Kerguelen Islands, and Saint Paul and Amsterdam Islands became a UNESCO World Heritage Site. They were recognized for their untouched nature, many different kinds of plants and animals, and huge bird colonies.
| Top - 0-9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
Discovering the French Southern Lands
The islands that make up the French Southern and Antarctic Lands were found over many years.
- Amsterdam Island was first seen by the Spanish in 1522. The Dutch later claimed and named it.
- Saint Paul Island was discovered by the Portuguese in 1559.
- The Crozet islands were found by French explorer Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne in 1772.
- Adelie Land was the last to be discovered in 1840. This happened during a French trip led by Jules Dumont d'Urville. A research station there is now named after him.
These lands are important for science and nature. Because they are so far away, they have unique wildlife.
How the Territory is Managed
The French Southern and Antarctic Lands have been an overseas territory of France since 1955. This means they are part of France but are far away.
Before 2004, the territory was managed from Paris. Now, a special administrator called a préfet is in charge. The current prefect is Florence Jeanblanc-Risler. Her main office is in Saint Pierre on Réunion Island.
The TAAF administration works with the French Polar Institute and the French Navy. They use an icebreaker ship called Astrolabe. This ship brings people and supplies to the Dumont d'Urville Station. It also helps with research and patrols. The French armed forces also have small groups of soldiers on some of the Scattered Islands. This helps protect France's claim to these areas.
The territory is split into five main areas, called districts:
| District | Administrative centre | Population | Area | EEZ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter | Summer | (km2) | |||
| Adélie Land | Dumont d'Urville Station | 30 | 110 | 432,000 | — |
| Crozet Islands | Alfred Faure | 25 | 45 | 352 | 567,475 |
| Kerguelen Islands | Port-aux-Français | 70 | 110 | 7,215 | 563,869 |
| Saint Paul and Amsterdam Islands | Martin-de-Viviès | 25 | 45 | 61 | 502,533 |
| Scattered Islands | Saint Pierre, Réunion | 56 | 56 | 38.4 | 640,400 |
| TAAF | Saint Pierre, Réunion | 206 | 366 | 439,666.4 | 2,274,277 |
Each district has a chief. This chief has duties similar to a mayor in France. Since there are no permanent residents, there are no elections. The territory does not send representatives to the French parliament.
Geography of the Islands
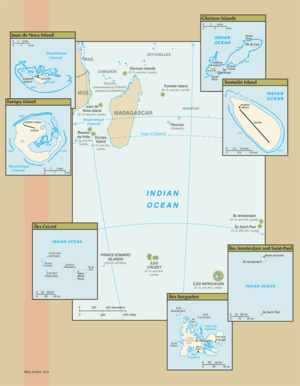
Adélie Land (in Antarctica) and Banc du Geyser and Bassas da India (in the Îles Éparses district) are not shown.
The French Southern and Antarctic Lands are located in the southern Indian Ocean. They are near 43°S, 67°E. This includes the Crozet Islands, Kerguelen Islands, and Saint Paul and Amsterdam Islands. It also includes Adélie Land, which is France's claim in Antarctica.
Adélie Land was named by French explorer Jules Dumont d’Urville after his wife. It covers about 432,000 square kilometers (167,000 sq mi). The islands themselves cover 7,781 square kilometers (3,004 sq mi). No native people live there. In 1997, about 100 researchers were present. This number changes between winter and summer.
Amsterdam Island and Saint Paul Island are both extinct volcanoes. They are part of a special area called the Amsterdam and Saint-Paul Islands temperate grasslands ecoregion. The highest point in the territory is Mont Ross. It is on Kerguelen Island and is 1,850 meters (6,070 ft) tall.
There are very few airstrips on the islands. They are only found on islands that have weather stations. The coastline is 1,232 kilometers (766 mi) long. It does not have any large ports, only places where ships can anchor offshore.
The islands in the Indian Ocean get their supplies from a special ship called the Marion Dufresne. This ship sails from Le Port in Réunion Island. Terre Adélie, the part of Antarctica claimed by France, gets supplies from the ship L’Astrolabe. This ship sails from Hobart in Tasmania, Australia.
Amazing Animals and Plants

|
Designations
|
|
| Official name: French Austral Lands and Seas | |
| Criteria: | Natural: (vii), (ix), (x) |
|---|---|
| Designated: | 2019 (43rd session) |
| Reference #: | 1603 |
| Region: | Western Europe |
| Official name: Réserve Naturelle Nationale des Terres Australes Francaises | |
| Designated: | 15 September 2008 |
| Reference #: | 1837 |
These French islands in the southern Indian Ocean are very isolated. This makes them one of the last big wilderness areas on Earth. The islands are also located where the Antarctic Convergence happens. This is where cold and warm ocean waters meet, bringing up many nutrients. Because of this, many birds and marine mammals gather on the islands.
More than 50 million birds from 47 different species breed on these islands. This includes over half of the world's population of 16 different bird species. The Crozet Islands have the largest number of king penguins. Amsterdam Island is home to the most endangered Indian yellow-nosed albatrosses. Other rare birds found here include Eaton's pintail and the Amsterdam albatross. The Amsterdam albatross is special because it is found only on these islands.
The French Southern Lands also have the second largest group of southern elephant seals in the world, with about 200,000 of them. They also have the third largest group of Antarctic fur seals.
Because they are so isolated and cold, these islands do not have many types of plants. Saint-Paul and Crozet islands do not have any native trees or shrubs. However, eight of the 36 higher plant species found here are unique to these islands. Some special insects, like moths and flies, have also been found. These insects have lost their wings because there are no predators to fly away from.
What the Economy is Like
The French Southern and Antarctic Lands have limited natural resources. They mainly have fish and crustaceans. The economy is mostly about supporting the weather and science research stations. It also supports French and other fishing boats.
The main types of fish caught are Patagonian toothfish and spiny lobster. Sometimes, foreign boats try to catch these illegally. The French Navy patrols the area to stop this. Boats caught poaching can face big fines or even be taken away.
France used to sell permits to foreign fishing companies to catch Patagonian toothfish. But because too many were being caught, fishing is now limited. Only a few fishing companies from Réunion Island are allowed to fish there. The territory earns about €16 million (Euros) each year from these activities.
Research Stations and Locations
Even though no one lives here permanently, there are several research stations where people stay.
- Île Amsterdam has a weather station called Martin-de-Viviès.
- The Îles Crozet have the Alfred Faure research station. About 20 to 30 people work there.
- One of the busiest stations is Port-aux-Francais in the Îles Kerguelen. It has between 50 and 100 researchers.
- The Îles Éparses have a French military base and are used for weather studies.
- The Dumont d’Urville station is very important. Scientists there study wildlife, the atmosphere, and the ice caps.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Tierras Australes y Antárticas Francesas para niños
In Spanish: Tierras Australes y Antárticas Francesas para niños
- Administrative divisions of France
- French colonial empire
- French Fifth Republic
- List of French islands in the Indian and Pacific oceans
- List of French possessions and colonies
- Outline of France
- Overseas France




